Introduction to Data Structure & algorithm
- 1. What is Data Structure?
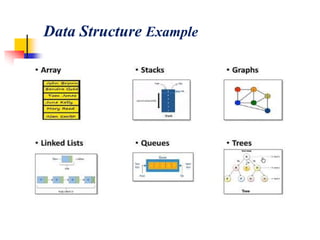
- 2. Definition of Data Structure Data Structure can be defined as the group of data elements which provides an efficient way of storing and organizing data in the computer.
- 4. Dictionary
- 5. Google Maps
- 9. Data Structures are the main part of many computer science algorithms as they enable the programmers to handle the data in an efficient way. Data Structure uses in Computer Science
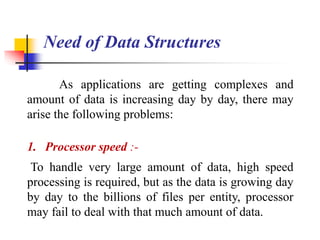
- 13. As applications are getting complexes and amount of data is increasing day by day, there may arise the following problems: 1. Processor speed :- To handle very large amount of data, high speed processing is required, but as the data is growing day by day to the billions of files per entity, processor may fail to deal with that much amount of data. Need of Data Structures
- 14. 2. Data Search:- Consider an inventory size of 106 items in a store, If our application needs to search for a particular item, it needs to traverse 106 items every time, results in slowing down the search process. Need of Data Structures
- 15. 3. Multiple requests:- If thousands of users are searching the data simultaneously on a web server, then there are the chances that a very large server can be failed during that process in order to solve the above problems, data structures are used. Data is organized to form a data structure in such a way that all items are not required to be searched and required data can be searched instantly. Need of Data Structures
- 16. 1. Efficiency: Efficiency of a program depends upon the choice of data structures. For example: suppose, we have some data and we need to perform the search for a particular record. Advantages of Data Structures
- 17. 2. Reusability: Data structures are reusable, i.e. once we have implemented a particular data structure, we can use it at any other place. 3. Abstraction: Data structure is specified by the ADT which provides a level of abstraction. The client program uses the data structure through interface only, without getting into the implementation details. Advantages of Data Structures
- 19. Definition of Algorithm Dictionary Definition: A process or Set of Rules to be followed in calculations or problem-solving operation, especially by a computer. Formal Definition: An algorithm is a finite set of instructions that are in a specific order to perform specific task.
- 20. Characteristics of an Algorithm 1. Input: An algorithm has some input values. We can pass 0 or some input value to an algorithm. 2. Output: We will get 1 or more output at the end of an algorithm.
- 21. Characteristics of an Algorithm 3. Unambiguity: An algorithm should be unambiguous which means that the instructions in an algorithm should be clear and simple. 4. Finiteness: An algorithm should have finiteness. Here, finiteness means that the algorithm should contain a limited number of instructions, i.e., the instructions should be countable.
- 22. Characteristics of an Algorithm 5. Effectiveness: An algorithm should be effective as each instruction in an algorithm affects the overall process. 6. Language independent: An algorithm must be language-independent so that the instructions in an algorithm can be implemented in any of the languages with the same output.
- 23. Dataflow of an Algorithm 1. Problem: A problem can be a real-world problem or any instance from the real-world problem for which we need to create a program or the set of instructions. 2. Algorithm: An algorithm will be designed for a problem which is a step by step procedure.
- 24. Dataflow of an Algorithm 3. Input: After designing an algorithm, the required and the desired inputs are provided to the algorithm. 4. Processing unit: The input will be given to the processing unit, and the processing unit will produce the desired output. 5. Output: The output is the outcome or the result of the program.