Introduction To Project Management
- 1. Introduction to Project Management Avneet Mathur [email_address]
- 2. What is a Project? A project is a temporary endeavor undertaken to produce a unique product or service Temporary – Definitive beginning and end Unique – New undertaking, unfamiliar ground Temporary Unique Characteristics of Projects
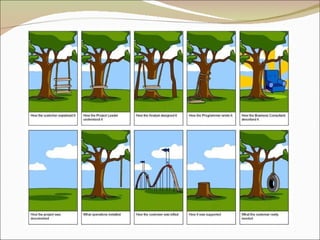
- 4. Project Success Customer Requirements satisfied/exceeded Completed within allocated time frame Completed within allocated budget Accepted by the customer
- 5. Project Failure Scope Creep Poor Requirements Gathering Unrealistic planning and scheduling Lack of resources
- 6. What is Project Management Project Management is the application of skills, knowledge, tools and techniques to meet the needs and expectations of stakeholders for a project. The purpose of project management is prediction and prevention , NOT recognition and reaction
- 7. Triple Contraint Scope Time Cost Quality
- 8. Triple Contraint Increased Scope = increased time + increased cost Tight Time = increased costs + reduced scope Tight Budget = increased time + reduced scope.
- 9. Key Areas of Project Management Scope Management Issue Management Cost Management Quality Management Communications Management Risk Management Change Control Management
- 10. Scope Management Primarily it is the definition and control of what IS and IS NOT included in the project.
- 11. Issue Management Issues are restraints to accomplishing the deliverables of the project. Typically identified throughout the project and logged and tracked through resolution. Rope not thick Issue… already impacting the cost, time or quality
- 12. Cost Management This process is required to ensure the project is completed within the approved budget and includes: Resources people equipment materials Quantities Budget
- 13. Quality Management Quality Management is the process that insure the project will meet the needs “ conformance to requirements” - Crosby “ fitness for use” - Juran “ the totality of characteristics of an entity that bear on its ability to satisfy stated and implied need’ - ISO 8402:1994
- 14. Communications Management This process is necessary to ensure timely and appropriate generation, collection, dissemination, and storage of project information
- 15. Risk Management Risk identification and mitigation strategy Risk update and tracking Tree – location, accessibility, ownership Weather Risk… POTENTIAL negative impact to project
- 16. Change Control Management Define how changes to the project scope will be executed Scope Change Schedule changes Technical Specification Changes All changes require collaboration and buy in via the project sponsor’s signature prior to implementation of the changes
- 18. Initiation Phase Define the need Return on Investment Analysis Make or Buy Decision Budget Development
- 19. Definition Phase Determine goals, scope and project constraints Identify members and their roles Define communication channels, methods, frequency and content Risk management planning
- 20. Planning Phase Resource Planning Work Breakdown Structure Project Schedule Development Quality Assurance Plan
- 21. Work Breakdown Structure For defining and organizing the total scope of a project First two levels - define a set of planned outcomes that collectively and exclusively represent 100% of the project scope. Subsequent levels - represent 100% of the scope of their parent node
- 22. Implementation Phase Execute project plan and accomplish project goals Training Plan System Build Quality Assurance
- 23. Deployment Phase User Training Production Review Start Using
- 24. Closing Phase Contractual Closeout Post Production Transition Lessons Learned
- 25. Project Management Tools PERT Chart - designed to analyze and represent the tasks involved in completing a given project Gantt Chart - popular type of bar chart that illustrates a project schedule
- 26. Role of a Project Manager Process Responsibilities People Responsibilities Project issues Disseminating project information Mitigating project risk Quality Managing scope Metrics Managing the overall work plan Implementing standard processes Establishing leadership skills Setting expectations Team building Communicator skills
- 27. Gantt Chart
- 28. PERT Chart
- 29. Scope Management Project Scope Management is the process to ensure that the project is inclusive of all the work required, and only the work required, for successful completion. Primarily it is the definition and control of what IS and IS NOT included in the project.
- 30. Issue Management Issues are restraints to accomplishing the deliverables of the project. Issues are typically identified throughout the project and logged and tracked through resolution. In this section of the plan the following processes are depicted: Where issues will be maintained and tracked The process for updating issues regularly The escalation process The vehicle by which team members can access documented issues
- 31. Cost Management This process is required to ensure the project is completed within the approved budget and includes: Resource Planning - The physical resources required (people, equipment, materials) and what quantities are necessary for the project Budget Budget estimates Baseline estimates Project Actuals
- 32. Quality Management Quality Management is the process that insure the project will meet the needs via: Quality Planning, Quality Assurance, and Quality Control Clearly Defined Quality Performance Standards How those Quality and Performance Standards are measured and satisfied How Testing and Quality Assurance Processes will ensure standards are satisfied Continuous ongoing quality control
- 33. Communications Management This process is necessary to ensure timely and appropriate generation, collection, dissemination, and storage of project information using: Communications planning Information Distribution Performance Reporting Define the schedule for the Project Meetings (Team, OSC, ESC), Status Meetings and Issues Meetings to be implemented
- 34. Risk Management Risk identification and mitigation strategy When\if new risks arise Risk update and tracking
- 35. Change Control Management Define how changes to the project scope will be executed Formal change control is required for all of the following Scope Change Schedule changes Technical Specification Changes Training Changes All changes require collaboration and buy in via the project sponsor’s signature prior to implementation of the changes
- 36. Bio Avneet Mathur is currently CTO of Zeratec, Inc., and has been involved in IT for the last decade. He is a Certified Project Management Professional, as awarded by the Project Management Institute, USA. Avneet holds an MBA in General Business Administration, with an additional Master's Degree in Computer Science and Networking from University of Missouri, Kansas City. He also has a Bachelor's Degree in Computer Science from the Aurangabad University, India. He can be reached at [email_address] Project Perfect is a project management software consulting and training organisation based in Sydney Australia. Their focus is to provide creative yet pragmatic solutions to Project Management issues. Project Perfect sell “Project Administrator” software, which is a tool to assist organisations better manage project risks, issues, budgets, scope, documentation planning and scheduling. They also created a technique for gathering requirements called “Method H” , and sell software to support the technique. For more information on Project tools or Project Management visit www.projectperfect.com.au
Editor's Notes
- #10: SCOPE MANAGEMENT – Ensuring all the appropriate work within the project scope is completed and only the work within scope is being conducted TIME MANAGEMENT – Schedule Management COST MANAGEMENT – How costs are controlled and incurred costs are paid QUALITY MANAGEMENT – Quality Assurance Plan – How quality control is measured and satisfied HUMAN RESOURCE MANAGEMENT – Development of the project team, reporting structure, resource capacity COMMUNICATIONS MANAGEMENT – How project communications will be handled to ensure all project stakeholders are informed RISK MANAGEMENT – Risk Management plan to have all project stakeholders in agreement on how project risks will be handled (aversion, mitigation or assumption) PROCUREMENT MANAGEMENT – Procurement process, contract processes INTEGRATION MANAGEMENT – Integration of all areas of project management to develop a cohesive project plan
- #11: This component is used to communicate How the scope was defined How the project scope will be managed Who will manage the scope (e.g., PM, QA) Change Control
- #12: Issues not easily resolved are escalated for resolution. Issues are typically identified throughout the project and logged and tracked through resolution. In this section of the plan the following processes are depicted: Where issues will be maintained and tracked The process for updating issues regularly The escalation process The vehicle by which team members can access documented issues Issue… already impacting the cost, time or quality Risk… POTENTIAL negative impact to project
- #13: Resource Planning - Full Time Employees, Professional Services, Cost, and Contingency Resource Planning - The physical resources required (people, equipment, materials) and what quantities are necessary for the project Budget Budget estimates Baseline estimates Project Actuals
- #14: What is Quality - conformance to requirements’ - Crosby ‘ fitness for use’ - Juran ‘ the totality of characteristics of an entity that bear on its ability to satisfy stated and implied need’ - ISO 8402:1994 Customer-Based -> Fitness for use, meeting customer expectations. Manufacturing-Based -> Conforming to design, specifications, or requirements. Having no defects. Product-Based -> The product has something that other similar products do not that adds value. Value-Based -> The product is the best combination of price and features. 5. Transcendent It is not clear what it is, but it is something good... via: Quality Planning, Quality Assurance, and Quality Control Clearly Defined Quality Performance Standards How those Quality and Performance Standards are measured and satisfied How Testing and Quality Assurance Processes will ensure standards are satisfied Continuous ongoing quality control
- #15: Communications planning: Determining the needs (who needs what information, when they need it, and how it will be delivered) Information Distribution: Defining who and how information will flow to the project stakeholders and the frequency Performance Reporting: Providing project performance updates via status reporting. Communications planning Information Distribution Performance Reporting Define the schedule for the Project Meetings (Team, OSC, ESC), Status Meetings and Issues Meetings to be implemented
- #17: Formal change control is required for all of the following Scope Change Schedule changes Technical Specification Changes Training Changes All changes require collaboration and buy in via the project sponsor’s signature prior to implementation of the changes
- #27: Process Responsibilities The project manager normally is responsible for defining and planning the project. This results in the completion of a Project Definition and a project workplan. Once the project starts, the project manager must successfully manage and control the work, including: Identifying, tracking managing and resolving project issues Proactively disseminating project information to all stakeholders Identifying, managing and mitigating project risk Ensuring that the solution is of acceptable quality Proactively managing scope to ensure that only what was agreed to is delivered, unless changes are approved through scope management Defining and collecting metrics to give a sense for how the project is progressing and whether the deliverables produced are acceptable Managing the overall workplan to ensure work is assigned and completed on time and within budget To manage the project management processes, a person should be well organized, have great follow-up skills, be process oriented, be able to multi-task, have a logical thought process, be able to determine root causes, have good analytical ability, be a good estimator and budget manager, and have good self-discipline. People Responsibilities In addition to process skills, a project manager must have good people management skills. This includes: Having the discipline and general management skills to make sure that people follow the standard processes and procedures Establishing leadership skills to get the team to willingly follow your direction. Leadership is about communicating a vision and getting the team to accept it and strive to get there with you. Setting reasonable, challenging and clear expectations for people, and holding them accountable for meeting the expectations. This includes providing good performance feedback to team members Team building skills so that the people work together well, and feel motivated to work hard for the sake of the project and their other team members. The larger your team and the longer the project, the more important it is to have good team-building skills. Proactive verbal and written communicator skills, including good, active listening skills. Multiple Roles Depending on the size and complexity of the project, the project manager may take on other responsibilities in addition to managing the work. For instance, the project manager may assist with gathering business requirements. Or they may help design a database management system or they may write some of the project documentation. Project management is a particular role that a person fills, even if the person who is the project manager is working in other roles as well.
- #30: This component is used to communicate How the scope was defined How the project scope will be managed Who will manage the scope (e.g., PM, QA) Change Control
- #31: Issues not easily resolved are escalated for resolution.
- #32: Resource Planning - Full Time Employees, Professional Services, Cost, and Contingency
- #33: What is Quality - conformance to requirements’ - Crosby ‘ fitness for use’ - Juran ‘ the totality of characteristics of an entity that bear on its ability to satisfy stated and implied need’ - ISO 8402:1994 Customer-Based -> Fitness for use, meeting customer expectations. Manufacturing-Based -> Conforming to design, specifications, or requirements. Having no defects. Product-Based -> The product has something that other similar products do not that adds value. Value-Based -> The product is the best combination of price and features. 5. Transcendent It is not clear what it is, but it is something good...
- #34: Communications planning: Determining the needs (who needs what information, when they need it, and how it will be delivered) Information Distribution: Defining who and how information will flow to the project stakeholders and the frequency Performance Reporting: Providing project performance updates via status reporting.
![Introduction to Project Management Avneet Mathur [email_address]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introduction-to-project-management-091218121131-phpapp01/85/Introduction-To-Project-Management-1-320.jpg)

































![Bio Avneet Mathur is currently CTO of Zeratec, Inc., and has been involved in IT for the last decade. He is a Certified Project Management Professional, as awarded by the Project Management Institute, USA. Avneet holds an MBA in General Business Administration, with an additional Master's Degree in Computer Science and Networking from University of Missouri, Kansas City. He also has a Bachelor's Degree in Computer Science from the Aurangabad University, India. He can be reached at [email_address] Project Perfect is a project management software consulting and training organisation based in Sydney Australia. Their focus is to provide creative yet pragmatic solutions to Project Management issues. Project Perfect sell “Project Administrator” software, which is a tool to assist organisations better manage project risks, issues, budgets, scope, documentation planning and scheduling. They also created a technique for gathering requirements called “Method H” , and sell software to support the technique. For more information on Project tools or Project Management visit www.projectperfect.com.au](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introduction-to-project-management-091218121131-phpapp01/85/Introduction-To-Project-Management-36-320.jpg)