Introduction to Python - Training for Kids
- 1. Welcome to Introduction to Python What do you need? 1. Python: https://www.python.org/downloads/ 2. PyCharm: http://www.jetbrains.com/pycharm/download/ This software has been downloaded for you on the computers in the lab. Wi-Fi: OSCON Password: need update
- 2. Who is helping you today? Aimee Maree : Instructor Cayci Gorlitsky: Assistant
- 3. What are we going to do today ? 1. Python and PyCharm 2. Basics of Python Programming 3. Input and output statements 4. Different data ‘types’ 5. If and basic logic statements 6. Practice Examples! 7. Q&A / Showcase
- 4. Python: Python is a scripting language that can be run on Linux, OSX and Windows. You can download the latest Python from the website. Python3 is the latest version and it is always best to start new projects in the latest version. For today the Computers have Python installed on them for you If you want to install Python at home it is as easy as visiting https://www.python.org/downloads/
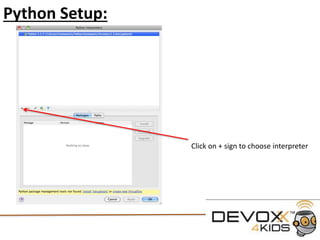
- 5. PyCharm: PyCharm is an IDE (Integrated Development Environment) We use an IDE because it helps us highlight our code and debug any problems Because Python needs to be interpreted when we run PyCharm (or an IDE) it will integrate with the Interpreter when we “Debug” or “Run” the code In an IDE we can create a “Project” this will be a collection of Scripts that we will create For the purpose of the Tutorial lets create a new Project The interpreter should be chosen by default If you need to change it you can modify it here
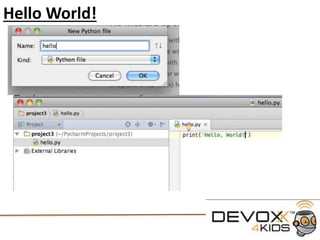
- 6. Creating your first Python Script: To create a new Python Script Select “File” from the top menu and select “New”
- 7. Creating your first Python Script: A New box will drop down Select the “Python File” option A “New Python File” box Will pop-up type in the name It is always good to name files Something that will remind you What they contain.
- 8. Hello World! #This is our first script #print tells the interpreter to print the text to the screen print('Hello, World!')
- 9. Run Hello World! Now that we have created our First Python script we can go To the menu and select “Run” And then click on “Run” from The drop down menu This will execute the code In our IDE interpreter console
- 10. What we just learned We ran our first Script. We printed out some text.. But the main use of programs is to take “inputs” and then turn them into “outputs” We are going to look at the ways that Python takes in Words and Numbers And how we can interact with programs Lets create a script with a variable that holds your name Then we will get the program to ask you for your name
- 11. Hello World! #This is our second script #First we declare a Variable name name = ('Aimee') #here we print the word 'hello' plus the variable name print('Hello, ' + name)
- 12. Hello World! #This is our third script #Lets are the user to input their name #input tells to computer to take something in #We also need to tell the user what we need them to enter name = input('What is your name?') #here we print the word 'hello' plus the variable name print('Hello, ' + name)
- 13. We can create some art with Print Print is a basic function but we can have some fun with it Lets see if we can create some ASCII art ASCII art can be created by printing out the whole Picture Or we can be tricky and reduce the lines of Print we use
- 14. Print a Smiley face #The n symbol means print a new line print ('n') #Here we print each line including the spaces of a smiley face print('** **') print('** **') print('** **') print ('n') print('* *') print(' * * ') print(' *** ')
- 15. Print a Smiley face on one line #If we combine the symbols above and print the n character #where we need to have a new line we can print the picture #using one print command print('** **n** **n** **nn* *n * * n *** n')
- 16. What we learned The easiest way to replicate a picture is to print the ASCII art line-by-line However, this is not the most efficient way Because the interpreter needs to interpret each line separately, by placing all the code on one line, we reduce the size of our file, and also the time it takes to execute the code You will not see much difference with a small program like printing a smiley face. However, for a professional programmer, saving time on a large application is very important In industry, there are people whose specific role is to analyze the performance of code and help developers make their code run/load faster
- 17. Strings and Numbers In programming languages we declare strings and numbers differently The reason we do this is because we want to do different things with them An example of this is comparing strings (letters/words) with upper case and lower case For numbers we need to calculations on them Because we want to do calculations we declare whole numbers such as 10 or 100 Different to how we call numbers with decimals places 20.5 and 4.88 input() (Python 3) and raw_input() (Python 2) always return strings. Convert the result to integer explicitly with int().
- 18. Numbers and Operands When we want to do calculations in Python we need to use operands that the Language understands some basic operands are + Addition - Adds values on either side of the operator 2 + 2 will give us 4 - Subtraction - Subtracts right hand operand from left hand operand 5 - 2 will give 3 * Multiplication - Multiplies values on either side of the operator 2 * 2 will give 4 / Division - Divides left hand operand by right hand operand 4 / 2 will give 2
- 19. Numbers and Operands #Lets do some calculations on numbers a = 4 / 2 b = 10 + 5 c = 2 * 2 d = 50 - 10 E = (2 + 2) – 1 # We can print out the variables on one line print(a, b, c, d, e) #Or we can do further math with them print(a + b) print(c - e) print(d * b)
- 20. Conditional Statements A conditional statement is a set of rules performed when certain condition/s are meet. Here we are looking at an if else statement If a certain condition is true Perform an action If the condition is false Perform a different action Then Stop
- 21. Comparison Operations == Checks if the values are equal or not, if yes then condition becomes true. (a == b) is not true. != Checks if the value of two operands are equal or not, if values are not equal then condition becomes true. (a != b) is true. > Checks if the value of left operand is greater than the value of right operand, if yes then condition becomes true. (a > b) is not true. < Checks if the value of left operand is less than the value of right operand, if yes then condition becomes true. (a < b) is true. >= Checks if the value of left operand is greater than or equal to the value of right operand, if yes then condition becomes true. (a >= b) is not true. <= Checks if the value of left operand is less than or equal to the value of right operand, if yes then condition becomes true. (a <= b) is true.
- 22. Conditional Statements #declare the variable name name = 'Aimee' #if the variable name == to 'Aimee' #note we must include : at the end of the if statement if (name == 'Aimee'): #then print this text to the screen print ('You Found me!') #if the variable name equals anything else print this text #This is also an example of error catching else: print('Try again')
- 23. Conditional Statements #declare the variable name name = 'Aimee' #if the variable name == to 'Aimee' #note we must include : at the end of the if statement if (name == 'Ben'): #then print this text to the screen print ('You Found me!') #if the variable name equals anything else print this text #This is also an example of error catching else: print('Try again')
- 24. Conditional Statements #Here we define a grade from 1 to 100 grade = 10 #Now we start our Conditional Statement #if the Grade is greater then 90 print the below statement if (grade > 90): print ('Congratulations, You achieved A Grade') #for all other grades less then 90 print the below statement else: print ('Better try again')
- 25. Conditional Statements #Here we define a grade from 1 to 100 grade = 70 #Lets add in some more choices if (grade >= 90): print ('Congratulations, You achieved A Grade') #elif means if the grade is not >=90 but is >=70 do this elif (grade >= 70): print ('You achieved a B Grade') elif (grade >= 50): print ('You achieved a Pass') #Last we put in a final else to catch all other grades <50 else: print ('Better Luck next time')
- 26. Conditional Statements with input #Here we ask the user for our name which is a string name = input('What is your name?') #Here we ask the user for an integer and use int(input())) grade = int(input('Enter your grade: ')) print('Hello, ' + name) #The grade entered runs through our conditional statement if (grade >= 90): print ('Congratulations, You achieved A Grade') elif (grade >= 70): print ('You achieved a B Grade') elif (grade >= 50): print ('You achieved a Pass') else: print ('Better Luck next time')
- 27. What we just learned So we ran some conditional statements That took some numbers and gave us an output Based on the grade number we had assigned to the grade variable Now lets combine our input with some conditional Statements First we took input as Words in programming we calls these Strings Now lets look at taking input as Numbers and specifically Integers Integers are whole digit numbers example 1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10....
- 28. Conditional Statements A conditional statement is a set of rules performed when certain condition/s are meet. Here we are looking at a while loop While a certain condition is true Perform an action When this condition is false Perform another action or Stop
- 29. Conditional Statements and Input #Here we declare a while loop and assign a condition #While the count is less then 5 while(count < 5): #Print what the count is and add one to the count print('The count is: ', count) count = count + 1 print ('This program is done!')
- 30. Conditional Statements and Input #While the below condition is (True) while(True): #Capture the input from the user count = int(input('Please enter a number:')) #If the number entered is greater then or equal to 5 if (count >= 5): print(count, 'is more than or equal to 5') #capture other numbers by checking the variable is less then 5 else: #Print the below statement print(count, 'is less than 5') #Then exit the program exit()
- 31. What we just learned A way to make programs make decisions is to use Conditional statements The conditional statement tells the program that It has some options it can take Conditional statements that we leart where If, else And While
- 32. List “A list contains items separated by commas and enclosed within square brackets ([])” We using a list we can have a Groups of items that We can call We call each item by referring to Its position in the list
- 33. Lists # First we create a list of options for fighting the Dragon choicelist = ['1:wait', '2:fight', '3:run away'] #We can print the whole list by calling it print(choicelist)
- 34. Lists # First we create a list of options for fighting the Dragon choicelist = ['1:wait', '2:fight', '3:run away'] #We can print each option by calling it by its key remember we #always start with 0 print (choicelist[0]) #Print the second option in the list by calling 1 print (choicelist[1]) #Print the third option in the list by calling 2 print (choicelist[2])
- 35. Lets put it all together in a Game Now that we have learnt some of the basics of Python We can put all this together in a command line adventure game Before computer graphics had advanced games used to be Text based This would mean that there would be some text on the screen That would inform the user of the task at hand and then It would ask the user to pick a choice or type in what to do next Lets create a text adventure game by using some of The techniques we have learnt We can also include some ASCII art in our game
- 36. Dragon Game # First we create a list of options for fighting the Dragon choicelist = ['1:wait', '2:fight', '3:run away'] print('Dragon Slayer n Let the Games Begin ') name = input('Name your character: ') print ('You are ' + name + ', the young warrior. You have been sent to save the Towns people from an angry dragon.') print (choicelist[0]) print (choicelist[1]) print (choicelist[2]) myanswer = input("press the corresponding number and ENTER:") print("You choose the answer number {0}".format(myanswer))
- 37. Dragon Game ...continued... while myanswer == 1: print ("nothing happens, the dragon also waits") myanswer = input("chose your next turn ENTER:") if myanswer == "2": print ("you fight with the dragon.") print ("the dragon has been slayed and the towns people rejoice. Game Over.") elif myanswer == "3": print ("You run away, but the dragon is faster than you. The dragon chased you and ate you for lunch. Game Over") else: print ("wrong key pressed")
- 38. Further Work Now that we have a basic game we can make it longer and Include more options or even some ASCII art. We can also import a Python module to include a dice This way instead of having the user enter there choice They can roll a dice to make a random selection.
- 39. Extra Work in ASCII Art #Below we are creating a Dragon, can you include some art in your game? print(' <>=======()') print(' (/___ /| ()==========<>_ ') print(' _/ | //| ______/ )') print(' _| // | _/') print(' |/|_ // //') print(' (oo) _// / ') print(' //_/_/ / | ') print(' @@/ |= |') print(' _=_ | ') print(' == | ') print(' __(===( ) ') print(' (((~) __(_/ | ') print(' (((~) / ') print(' ______/ / ') print(' ______/ ')
- 40. Rolling a dice #here we import a Python module called random this creates a random #number like when a person rolls a dice import random #here we declare the variable called dice #random.randrange is a way we set the possible number set for the dice dice = random.randrange(6) print ('Press enter to Roll the Dice: ', dice) #to learn more about options we can use for random check the #documentation https://docs.python.org/3.0/library/random.html
- 41. Rolling a dice with options #here we import a Python module called random this creates a random #number import random #here we declare out list options choicelist = ['1:wait', '2:fight', '3:run away'] #random.randrange set the dice range between 1 and 3 dice = random.randrange(1,4) print ('Press enter to Roll the Dice: ', dice) print('You are faced with three options...') print(choicelist[0]) print(choicelist[1]) print(choicelist[2])
- 42. Rolling a dice with options continued #here we assign the myanswer variable the dice outcome myanswer = dice #Then we print the option out the the user print("You choose to do number {0}".format(myanswer))
- 43. Further Work Can you add the Dragon art into the dragon Game? Can you create 6 options in the list for the Rolling dice code? Can you include the Rolling dice code into the dragon Game?
- 44. Further Learning Games are a great way to learn the fundamentals of Programming https://github.com/amaree/Python-KidsDay Today we learnt some of the very basics of Python But there is a lot more to learn Learning programming works best when we are doing something We enjoy this makes us want to learn more Most people from my generation learnt how to program By writing simple games A great place to start learning games and python is http://thepythongamebook.com/ Code examples for the book https://github.com/horstjens/ThePythonGameBook/
Editor's Notes
- #9: HelloWorld.py
- #12: HelloName.py
- #13: HelloName-Input.py
- #15: HelloName.py
- #16: HelloName.py
- #20: HelloName.py
- #23: Grades.py
- #24: Grades.py
- #25: Grades.py
- #26: Grades-levels.py
- #27: Grades-input.py
- #30: HelloName-Input.py
- #31: HelloName-Input.py
- #34: HelloName-Input.py
- #35: HelloName-Input.py
- #37: HelloName-Input.py
- #38: HelloName-Input.py
- #40: HelloName-Input.py
- #41: HelloName-Input.py
- #42: HelloName-Input.py
- #43: HelloName-Input.py






























![List
“A list contains items separated by
commas and enclosed within
square brackets ([])”
We using a list we can have a
Groups of items that
We can call
We call each item by referring to
Its position in the list](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introtopython-140813145158-phpapp02/85/Introduction-to-Python-Training-for-Kids-32-320.jpg)
![Lists
# First we create a list of options for fighting the Dragon
choicelist = ['1:wait', '2:fight', '3:run away']
#We can print the whole list by calling it
print(choicelist)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introtopython-140813145158-phpapp02/85/Introduction-to-Python-Training-for-Kids-33-320.jpg)
![Lists
# First we create a list of options for fighting the Dragon
choicelist = ['1:wait', '2:fight', '3:run away']
#We can print each option by calling it by its key remember we
#always start with 0
print (choicelist[0])
#Print the second option in the list by calling 1
print (choicelist[1])
#Print the third option in the list by calling 2
print (choicelist[2])](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introtopython-140813145158-phpapp02/85/Introduction-to-Python-Training-for-Kids-34-320.jpg)

![Dragon Game
# First we create a list of options for fighting the Dragon
choicelist = ['1:wait', '2:fight', '3:run away']
print('Dragon Slayer n Let the Games Begin ')
name = input('Name your character: ')
print ('You are ' + name + ', the young warrior. You have been sent to
save the Towns people from an angry dragon.')
print (choicelist[0])
print (choicelist[1])
print (choicelist[2])
myanswer = input("press the corresponding number and ENTER:")
print("You choose the answer number {0}".format(myanswer))](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introtopython-140813145158-phpapp02/85/Introduction-to-Python-Training-for-Kids-36-320.jpg)




![Rolling a dice with options
#here we import a Python module called random this creates a random
#number
import random
#here we declare out list options
choicelist = ['1:wait', '2:fight', '3:run away']
#random.randrange set the dice range between 1 and 3
dice = random.randrange(1,4)
print ('Press enter to Roll the Dice: ', dice)
print('You are faced with three options...')
print(choicelist[0])
print(choicelist[1])
print(choicelist[2])](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introtopython-140813145158-phpapp02/85/Introduction-to-Python-Training-for-Kids-41-320.jpg)


