Introduction to Reactive programming
- 1. Reactive Programming Dwi Randy H - iOS Engineer
- 2. Overview ● What is Reactive Programming? ○ Reactive programming is a general programming term that is focused on reacting to changes, such as data values or events. It can and often is done imperatively. A callback,delegate is an approach to reactive programmingdone imperatively. ● Why we need Reactive Programming ○ More loosely coupled code ○ Make it easy to manage thread ○ A lot of operators that simplify work ○ Help to solve Real-Time Complex UI ○ Multi-platform standard
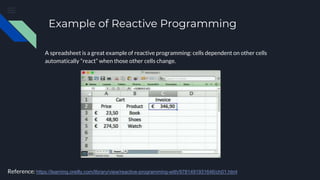
- 3. Example of Reactive Programming A spreadsheet is a great example of reactive programming: cells dependent on other cells automatically “react” when those other cells change. Reference: https://learning.oreilly.com/library/view/reactive-programming-with/9781491931646/ch01.html
- 4. Rx Basic Building Blocks ● Observables = Dog ● Subscribers = Child ● Operators = Process Down
- 5. Observables Observable are the data source/stream, then that observer reacts to whatever item or sequence of items the observables emits. They can emit data, completion and also failure
- 6. Hot and Cold Observables Cold observables don’t do anything until someone starts observing them (subscribe in Rx). They only start running when they are consumed Hot Observables that can active before subscription, when an observer subscribes to hot observable it will get all values in the stream that are emitted
- 9. When We Need Cold or Hot When we need to observable to generating new values when someone subscribing it and the values are also not shared among subscribers For example when we call the API, Getting data from local database When you have Observable and we want multiple subscribers to it, and you don’t want them to cause regenerating the values but rather reusing existing values For example as LiveData in MVVM iOS Reference: https://github.com/Reactive-Extensions/RxJS/blob/master/doc/gettingstarted/creating.md#cold-vs-hot-observables
- 10. Operator An operator is simply a function that performs a specific action. It takes a value, does something with it and then returns it ● Creating ● Transforming ● Filtering ● Combining
- 11. Operator (Creating) ● Create Create an observable from scratch by calling observer method programmatically ● Just Convert an object into Observable that emits that object
- 12. Operator (Transforming) ● Map Transform the items emitted by an Observable by applying a function to each item ● FlatMap Transform the items emitted by an Observable into Observables, then flatten the emissions from those into a single Observable
- 13. Observers Observers consumes the data stream emitted by observables Observers subscribe to observable using subscribeOn() method to receive data and then the data will be received in onNext() callback()
- 14. Observer Callback OnNext() The callback to receive a valueless notification of type complete from the Observable. OnComplete() The callback to receive a valueless notification of type complete from the Observable. onError() The callback to receive notifications of type error from the Observable, with an attached Error.
- 15. Scheduler Scheduler are component that tells observables and observers on which thread they should run - subscribeOn() Specifies on which Scheduler to Observables should operate - observeOn() Specifies on which Scheduler/Thread the Subscribers should be notified
- 16. Scheduler Types Used - Schedulers.io() It is used for non CPU-intensive I/O type work including interaction with the file system, performing network calls, database interactions. This is usually used in subscribeOn method - Schedulers.computation It is used for computational or CPU-intensive work such as resizing images, processing large data sets, Reference: https://proandroiddev.com/understanding-rxjava-subscribeon-and-observeon- 744b0c6a41ea - AndroidSchedulers.trampoline This is used to executes tasks in a FIFO (First In, First Out). This scheduler runs the code on current thread for example for Unit Testing - AndroidSchedulers.mainThread() This is used to bring back the execution to the main thread so that UI modification can be made. This is usually used in observeOn method.
- 17. RxBinding & RxCocoa - Library that makes it easier to use UI Component with reactive techniques. Reference: https://github.com/ReactiveX/RxSwift
- 18. Thank you!
Editor's Notes
- #3: imperative programming is a programming paradigm that uses statements that change a program's state. In much the same way that the imperative mood in natural languages expresses commands, an imperative program consists of commands for the computer to perform. Imperative programming focuses on describing how a program operates.
- #4: Reactive programming adalah paradigma pemrograman yang berkaitan dengan aliran data dan juga penyebaran perubahan Ketika menggunakan reactive programming data stream akan menjadi pondasi dari aplikasi kita Events, Messages, Calls bahkan failures akan di sampaikan oleh data stream dengan reactive programming kita meng observe data stream dan melakukan reaksi ketika nilai di berikan
- #7: https://github.com/dwirandyh/bdlproperti-android/blob/6bb087dca0f466ad82e48c56d5d21b390dca95d3/app/src/main/java/com/dwirandyh/bdlproperti/core/rxbinding/RxSearchObservable.kt