IPTV Basics
- 2. IPTV Transmission IPTV supports two kinds of services: • 1. Multicast IPTV, which consists of an emitter which sends the same content to multiple receivers the same time. • Unicast IPTV, which also consists of an emitter which sends TV content to multiple receivers. In contrast to multicast IPTV every receiver receives different content. This kind of service can be used to send personalized TV content, e.g. video on demand.
- 3. Mpeg Transport Stream Several Codecs combine to create a transport stream for the media being transmitted. Codecs are used to encode video and audio information into a compressed data stream.
- 4. Real-time transport Streaming Protocol • The Real-time Transport Streaming Protocol (RTSP) enables a client to control a media server by • issuing commands. Necessary for Unicast . • RTSP reuses many design principle from HTTP: – URL identifies resources; – requests contain a method name and various parameters; – replies contain a status code and parameters; – messages are text based. • RTSP is a stateful protocol. The server maintains state of the client. • With RTSP, every message contains a session identifier, enabling the server to link received commands to a given multimedia session. .
- 5. Typical Video setup message
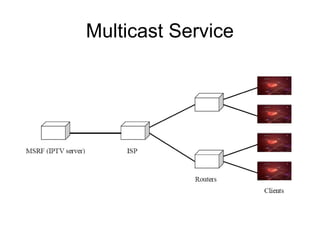
- 6. Multicast • Multicast IPTV enables a TV content provider to send TV content to many subscribers at the same • time. • IP multicast saves considerable bandwidth, since only one stream is transmitted over the network • When a server multicasts data to several clients, it sends this data to the corresponding router only once. • Similarly to regular TV, multicast IPTV supports multiple channels and sends them at the same time. • IPTV does not broadcast to a user all channels at the same time. – IPTV divides channels into groups and sends to each user the group that contains the requested channel. – The user can switch between channels at any time.
- 8. Unicast • Unicast IPTV sends a given TV content to a given user. Video on Demand is a typical service of IPTV, which enables a user to request a specific movie and to receive it on his TV set. • Contrary to multicast IPTV, unicast IPTV does not save bandwidth, since the server must send the content once for each user. • Unicasting can be extremely demanding on the server if multiple streams must be generated by the media server and transmitted over the network.
- 10. QoE – Quality of Experience • QoE is reliant upon error free delivery of packet data without retransmission. • Very similar to packet voice where packets are not acknowledged • Customers are much less accepting of poor video quality
- 11. Error Free Transmission • Pixelation due to poor transmission
- 12. Components of a typical IPTV System • A National head-end - Origination point of network Broadcasts for transmission over the IP network. • Core networks - Usually an IP/MPLS network transporting traffic to the access network • Access networks - Distributes the IPTV streams to the DSLAMs • Regional head-end – Origination point for local content • Customer premises - Where the IPTV stream is terminated and viewed using a Set Top Box or Computer.
- 13. Typical IPTV Network Design
- 14. Datastream Delivery • Broadcast information coming from the national head-end is typically distributed using MPEG-2 encoding to the video service nodes. • Competing compression algorithms are growing in popularity such as H.264 (MPEG-4 Part 10) or the Society of Motion Picture and Television Engineers (SMPTE) 421M (also known as VC-1) • The channel content can be of standard or high definition. • Distribution over the access network is done though digital subscriber line access multiplexers (DSLAM) and fiber-to-the-home (FTTH) services. • The subscriber’s set top box (STB) acts as the terminating interface for the network providing output to the television. • For IPTV, each channel is distributed using a multicast IP address.
- 15. Factors Affecting Service • Encoding and Compression – The quality of a transmission can be affected from the source depending on the encoding technique and level of compression. Generally speaking increased compression leads to a poorer video quality but a smaller data stream. There is a tradeoff between bandwidth and compression level. • Jitter in IPTV transmission is defined as a short-term variation in the packet arrival time. Jitter is typically caused by network or server congestion. To help combat jitter, STB’s use buffers to smooth out the arrival times of the data packets. I the buffer overflows or underflows, at the STB, there is often a degradation of the video output. • Limited Bandwidth – Bandwidth availability is often an issue that affects the access network or the customers home network. When traffic utilizes the entire bandwidth, packets are dropped, leading to video quality degradation. • Packet Loss Loss of IP packets may occur for multiple reasons: – bandwidth limitations – network congestion – failed links – transmission errors – Packet loss usually presents a bursty behavior, commonly related to periods of network congestion.
- 16. Mpeg-2 Compression •Frame Types •I frames- least compressed reconstructed independently •P frames use data from previous frames leading to greater compression •B frames use data from previous as well as following video frames leading to even greater compression. •Affect of err’d packets is greatest on I frames.
- 17. Key QoE Metrics • IPTV is evolving and is not well defined for testing. • The most popular parameters for testing delivery of IPTV packets are the media delivery index (MDI) and PCR jitter for MPEG-2 TS. • Other parameters are also used in the IPTV network, but require intense packet inspection to determine transmission problems.
- 18. Media Deliver Index (MDI) • MDI is a standards based video quality metric (RFC-4445) • MDI measures two factors: – Delay Factor – Media Loss Rate • Factors lead to a QoS measure that directly relates to the customers QoE
- 19. Benefits of Using MDI • MDI does not perform any type of stream decoding to achieve its metrics and therefore does not require significant real-time processing power. • MDI can be used with encrypted media payloads. • MDI is not dependent on any one type of video-encoding technique, so it can easily be scaled to monitor video quality on hundreds of simultaneous channels. • MDI is typically sampled at multiple points throughout the stream path with the measurements serving as indicators of problems in the network that can be proactively addressed before they become service-affecting issues. • Since MDI relies on transport-layer metrics (DF and MLR), it can be used to set network margins and it directly correlates to impending network problems with respect to video quality. • Since MDI uses packet-level metrics, it helps validate the performance of network equipment such as switches and routers that play a key role in determining whether a packet is delayed or dropped.
- 20. MDI Values increase through network.
- 21. References • IPTV related standardization activities – from international Telecommunication Union Website http://www.docstoc.com/docs/10154710/IPTV-Presentations- Presentation%5B641%5D • EXFO Test Equipment Manufacturer Website - http://www.exfo.com/en/applications/IPTV-Overview.aspx • Video Compression picture types form Wikipedia http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Video_compression_picture_types • Definition and Specifications of IPTV and VoIP Services from Adamantium Web Site http://www.ict- adamantium.eu/documents/deliverables/ADAMANTIUM_D2.3.pdf