IRRIGATION MANAGEMENT IN DIFFERENT FIELD CROPS
- 1. IRRIGATION MANAGEMENT IN DIFFERENT CROPS SUBMITTED BY:- MEHARWAN BHEEL M.SC(AGRICULTURE) DEPARTMENT OF AGRONOMY
- 2. INTRODUCTION :- Irrigation management plays a pivotal role in agriculture by ensuring crops receive adequate water to optimize growth, yield, and quality. Proper irrigation is critical for maintaining soil health, minimizing water wastage, and adapting to changing climatic conditions. Different crops require specific irrigation practices based on their water needs, growth stages, and the agro-climatic conditions in which they are cultivated. This assignment explores irrigation management strategies for various crops, focusing on water requirements, methods, and practices to enhance efficiency and sustainability.
- 3. IMPORTANCE OF IRRIGATION MANAGEMENT :- irrigation management is essential for: 1. Maximizing Crop Yield: Adequate water supply ensures optimal photosynthesis, nutrient uptake, and physiological functions in plants. 2. Water Conservation: Efficient methods prevent over-irrigation and reduce water loss due to evaporation or runoff. 3. Sustainability: Proper practices protect water resources and maintain soil fertility, reducing environmental impacts. 4. Economic Benefits: Farmers can save costs on water and energy by adopting efficient irrigation systems.
- 4. CEREALS CROPS ( WHEAT, RICE ,MAIZE ) :- Water Requirements: Wheat: Requires 450–650 mm of water during the growing season. Rice: Needs 1,000–2,000 mm, with significant water use during paddy cultivation. Maize: Requires 500–800 mm based on variety and climate. Key Practices: Wheat: Adopt sprinkler irrigation to save water during critical growth stages such as tillering and grain filling. And other method are a) Flood irrigation , b) Check basin method , c) FIRB method
- 5. Irrigation schedule :- wheat require mostly 5-6 irrigation – i) CRI ( Crown Root Initiation ) - 20 - 25 DAS ii) Tillering stage - 40 – 45 DAS iii) Late Jointing stage - 60 – 65 DAS iv) Flowering stage - 80 – 85 DAS v) Milking stage - 90 – 95 DAS vi) Dough stage - 110 – 115 DAS WHEAT
- 6. Rice ( Paddy ): • Practice alternate wetting and drying (AWD) to reduce water use without compromising yield. • water requirement of rice is higher then that of any other crops of a similar duration , assured and timely supply of irrigation water has a great influence on the yield of the crops . Critical stage :- i) Initial tillering / seedling ii) Tillering to flowering ( most critical ) iii) Flowering / heading stage . NOTE : Flooding is not necessary if weeds can be control. RICE ( PADDY )
- 7. Maize: • Use drip irrigation for precise watering during tasseling and silking stages. • Water stress during this stage can severally impact yield . MAIZE
- 8. Pulses (Chickpeas and Green Gram) Water Requirements: • Pulses generally require 300–500 mm of water, with low water demand during vegetative stages. Key Practices: • Minimize irrigation during vegetative growth to avoid excessive vegetative growth at the expense of yield. • Use rain-fed irrigation systems or supplemental irrigation during flowering and pod development. • Implement contour farming and water harvesting techniques in arid regions. NOTE :- Pre-flowering and Pod formation is critical stage in checkpea . CHICKPEA
- 9. Sugarcane :- Water Requirements: • Sugarcane: Needs 1,500–2,500 mm due to its long growing cycle. • Critical stage :- i) Germination phase ( From planting to 60 Days ) ii) Formative phase ( From 60 – 130 days ) most iii) Grand phase ( From 130 – 250 Days) iv) Maturity phase ( From 250 – 365 Days ) SUGARCANE
- 10. Irrigation method : - 1 . Furrow Flooding Method 2. Border Strip Method 3. Pit Method 4. Typhoon Method • Typhoon Benefits :- 1. Uniform water distribute 2. Reducing evaporation loss 3. Improving water penetration Furrow Flooding Method
- 11. Cotton :- • Cotton: Requires 700–1,200 mm, with peak demand during flowering and boll formation. • Drip Irrigation enhance water use efficiency . • Cotton, adopt furrow irrigation to minimize water contact with foliage and reduce disease risks. COTTON
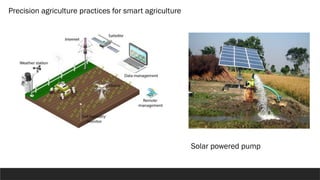
- 12. Recent Irrigation techniques :- 1. Smart irrigation system : AI powered system that use data from soil sensors weather forcast and crop model to automate irrigation decisions. 2. Cloud based monitoring :- platform allows farmers to remotely monitoring and control irrigation systems using smartphones or computers . 3. Precision Sprinkler systems : Automated control ensure uniform water distribution , reducing water waste . 4. Solar Powered Pump.
- 13. Precision agriculture practices for smart agriculture Solar powered pump
- 14. Conclusion :- • Irrigation management is integral to sustainable agriculture and food security. • Adopting crop-specific strategies, modern irrigation technologies, and water- saving practices can enhance agricultural productivity while conserving water resources. • Governments, researchers, and farmers must collaborate to address challenges, improve irrigation infrastructure, and promote efficient water use in agriculture. • This approach ensures resilience against climate change and secures livelihoods for millions dependent on farming.
- 15. REFFERANCES :- Books and Manuals: Allen, R.G., Pereira, L.S., Raes, D., & Smith, M. (1998). Crop Evapotranspiration: Guidelines for Computing Crop Water Requirements. FAO Irrigation and Drainage. Reddy SR 2018 Rainfed agriculture and watershed management . Kalyani publishers , Ludhiana , new delhi . Online Resources: FAO’s website on irrigation and water management: www.fao.org. Research papers available on platforms like ResearchGate, PubMed, or ScienceDirect. Educational articles from agricultural universities (e.g., ICAR, University of California Agriculture and Natural Resources).