Java Programming [8/12] : Arrays and Collection
- 1. บทที่ 8 อะเรย์แ ละคอลเล็ก ชั่น (Arrays and Collections) อ.ธนิศ า เครือ ไวศยวรรณ คณะเทคโนโลยีส ารสนเทศ สถาบัน เทคโนโลยีพ ระจอมเกล้า เจ้า คุณ ทหารลาดกระบัง
- 2. วัต ถุป ระสงค์ อธิบ ายการประกาศและสร้า งอะเรย์ข องข้อ มูล ชนิด พื้น ฐานและชนิด คลาส อธิบ ายการกำา หนดค่า เริ่ม ต้น ให้ก ับ สมาชิก ขอ งอะเรย์ อธิบ ายการประกาศและสร้า งอะเรย์ห ลายมิต ิ แนะนำา การสร้า งอะเรย์ส องมิต ท ี่แ ต่ล ะแถวมี ิ จำา นวนคอลัม น์ไ ม่เ ท่า กัน แนะนำา เมธอดทีเ กีย วข้อ งกับ อะเรย์ ่ ่
- 3. วัต ถุป ระสงค์ แนะนำา อิน เตอร์เ ฟสสำา คัญ ทีอ ยูใ น ่ ่ Collection API เช่น Collection, Set,List และ Map อธิบ ายการนำา คลาสสำา คัญ ทีอ ยูใ น ่ ่ Collection API เช่น HashSet, ArrayList,Vector,LinkedList และ HashMap ไปใช้ง าน แนะนำา อิน เตอร์เ ฟส Iterator,ListIterator และ Enumeration
- 4. ความหมายของอะเรย์ อะเรย์ใ นภาษาจาวาคือ ตัว แปรทีเ ป็น ชนิด ข้อ มูล ่ แบบอ้า งอิง ที่ส ามารถใช้เ ก็บ ข้อ มูล ชนิด เดีย วกัน ได้ห ลายค่า ตัว อย่า ง • ตัว แปรอะเรย์ท ี่ช ื่อ ch • เก็บ ข้อ มูล ชนิด char • มีจ ำา นวนสมาชิก 5 ตัว • หมายเลขสมาชิก ตั้ง แต่ 0 ถึง 4
- 5. ประเภทของอะเรย์ ภาษาจาวาแบ่ง ตัว แปรอะเรย์เ ป็น สองประเภทคือ • อะเรย์ข องข้อ มูล ชนิด พื้น ฐาน • อะเรย์ข องข้อ มูล ชนิด คลาส อะเรย์ข องข้อ มูล ชนิด พืน ฐานคือ อะเรย์ท ส ามารถ ้ ี่ ใช้เ ก็บ ข้อ มูล ทีม ช นิด ข้อ มูล แบบพืน ฐานชนิด ใด ่ ี ้ ชนิด หนึง ได้ห ลายค่า เช่น ่ • อะเรย์ข องข้อ มูล ชนิด int • อะเรย์ข องข้อ มูล ชนิด boolean อะเรย์ข องข้อ มูล ชนิด คลาสคือ อะเรย์ท ส ามารถใช้ ี่ เก็บ ข้อ มูล ทีเ ป็น ออปเจ็ค ของคลาสใดๆได้ห ลา ่ ยออปเจ็ค เช่น • อะเรย์ข องข้อ มูล ชนิด String
- 6. การประกาศตัว แปรอะเรย์ รูป แบบการประกาศตัว แปรอะเรย์ คล้า ยกับ การ ประกาศตัว แปรชนิด ข้อ มูล แบบอื่น ๆ แต่ต ัว แป รอะเรย์จ ะมีเ ครื่อ งหมาย [ ] อยูด ้า นหน้า หรือ ด้า น ่ หลัง รูป แบบ [<modifier>] dataType []variableName; หรือ [<modifier>] dataType variableName[]; ตัว อย่า ง char []ch; หรือ char ch[]; Student []s; หรือ Student s[];
- 7. การสร้า งอะเรย์ข องข้อ มูล ชนิด พื้น ฐาน อะเรย์ใ นภาษาจาวาจะเป็น ตัว แปรแบบอ้า งอิง ชนิด หนึง (เช่น เดีย วกับ ่ ออปเจ็ค ) การสร้า งอะเรย์จ ะสามารถทำา ได้โ ดยการเรีย กใช้ คำา สั่ง new รูป แบบ variableName = new dataType[size]; ตัว อย่า ง ch = new char[5]; สำา หรับ การสร้า งอะเรย์ข องข้อ มูล ชนิด พืน ฐาน ้ คำา สั่ง new จะจองเนือ ทีใ นหน่ว ยความจำา สำา หรับ เก็บ ้ ่ ค่า ของสมาชิก ของอะเรย์ ส่ว นตัว แปรอะเรย์จ ะเก็บ
- 8. การรวมคำา สัง ประกาศและสร้า ง ่ ตัว แปร เราสามารถทีจ ะรวมคำา สั่ง ประกาศชื่อ ตัว แปรและ ่ คำา สั่ง การสร้า งตัว แปร อะเรย์ไ ว้ใ นคำา สัง เดีย วกัน ่ ได้ รูป แบบ dataType []variableName = new dataType[size]; หรือ dataType variableName[] = new dataType[size]; ตัว อย่า งเช่น int []x = new int[5];
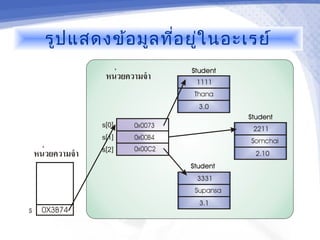
- 9. รูป แสดงข้อ มูล ที่อ ยู่ใ นอะเรย์
- 10. การสร้า งอะเรย์ข องข้อ มูล ชนิด คลาส สำา หรับ การสร้า งอะเรย์ข องข้อ มูล ชนิด คลาส คำา สัง ่ new จะจองเนือ ทีใ นหน่ว ยความจำา สำา หรับ เก็บ ค่า ้ ่ ของสมาชิก ของอะเรย์ ซึ่ง จะเป็น เพีย งแค่ต ำา แหน่ง อ้า งอิง เท่า นัน ้ ตัว อย่า ง Student []s; s = new Student[3];
- 11. รูป แสดงข้อ มูล ที่อ ยู่ใ นอะเรย์
- 12. การสร้า งออปเจ็ค ของคลาสให้ก ับ สมาชิก ดัง นั้น จะต้อ งมีก ารเรีย กใช้ค ำา สั่ง new อีก เพือ สร้า ง ่ ออปเจ็ค ของคลาสให้ก บ สมาชิก แต่ล ะตัว ขอ ั งอะเรย์ ตัว อย่า ง s[0] = new Student(“1111”,“Thana”,3.0); s[1] = new Student(“2211”,“Somchai”,2.10); s[2] = new Student(“3331”,“Supansa”,3.1);
- 13. รูป แสดงข้อ มูล ที่อ ยู่ใ นอะเรย์
- 14. การกำา หนดค่า เริ่ม ต้น ให้ก ับ สมาชิก ของอะเรย์ ค่า เริ่ม ต้น ของสมาชิก ของอะเรย์ จะถูก กำา หนดให้ โดยอัต โนมัต ิ ซึ่ง จะมีค ่า ตามค่า เริ่ม ต้น ของชนิด ข้อ มูล นัน ๆ ้ เราสามารถสร้า งอะเรย์พ ร้อ มกับ กำา หนดค่า เริ่ม ต้น ให้ก บ สมาชิก ของอะเรย์เ องได้ ั รูป แบบ dataType []variableName = {value1,value2,..,valueN}; ตัว อย่า ง int []x = {4,3,5,1,8}; Student []s = {new Student("1111","Thana",3.0), new Student("2211","Somchai",2.10), new Student("3331","Supansa",3.1)};
- 15. อะเรย์ห ลายมิต ิ เราสามารถทีจ ะประกาศอะเรย์ม ากกว่า หนึง มิต ิไ ด้ ่ ่ กรณีข องอะเรย์ส องมิต ิ มีร ูป แบบการประกาศ ตัว แปรดัง นี้ [modifier] dataType [][]variableName; หรือ [modifier] dataType variableName[][]; ตัว อย่า ง int [][]x; รูป แบบการสร้า งตัว แปรอะเรย์ส องมิต ิเ ป็น ดัง นี้ variableName = new dataType[row][col]; ตัว อย่า ง x = new int[3][4];
- 16. อะเรย์ส องมิต ิท ี่แ ต่ล ะแถวมีจ ำา นวน คอลัม น์ต ่า งกัน การสร้า งอะเรย์ส องมิต ิใ นภาษาจาวา ไม่จ ำา เป็น ที่ จำา นวนคอลัม น์ข องแต่ล ะแถวจะต้อ งเท่า กัน ตัว อย่า ง int [][]x = new int[3][]; x[0] = new int[4]; x[1] = new int[2]; x[2] = new int[3];
- 17. ตัว อย่า งโปรแกรม public class TwoDimensionArrays { public class TwoDimensionArrays { public static void main(String args[]) { public static void main(String args[]) { int x[][] = new int[3][]; int x[][] = new int[3][]; x[0] = new int[4]; x[0] = new int[4]; x[1] = new int[2]; x[1] = new int[2]; x[2] = new int[3]; x[2] = new int[3]; for(int i=0; i<x.length; i++) { for(int i=0; i<x.length; i++) { for(int j=0; j<x[i].length; j++) { for(int j=0; j<x[i].length; j++) { x[i][j] = (i+j)*2; x[i][j] = (i+j)*2; }} }}
- 18. ตัว อย่า งโปรแกรม for(int i=0; i<x.length; i++) { for(int i=0; i<x.length; i++) { for(int j=0; j<x[i].length; j++) { for(int j=0; j<x[i].length; j++) { System.out.print(x[i][j]+" "); System.out.print(x[i][j]+" "); }} System.out.println(); System.out.println(); }} }} }} สดงผลลัพ ธ์ท ไ ด้จ ากการรัน โปรแกรม ี่
- 19. การหาขนาดของอะเรย์ ทุก อะเรย์ใ นภาษาจาวาจะ มีค ุณ ลัก ษณะทีช ื่อ ่ ซึง จะมีค ่า เท่า กับ จำา นวนสมาชิก ทัง หมดขอ length ่ ้ งอะเรย์น น ั้ ตัว อย่า ง int x[] = new int[3]; • x.length มีค ่า เท่า กับ 3 int x[][] = new int[3][4]; • x.length มีค ่า เท่า กับ 3 • x[1].length มีค ่า เท่า กับ 4
- 20. เมธอดที่เ กี่ย วข้อ งกับ อะเรย์ ในภาษาจาวา มีเ มธอดหลายเมธอด มีร ับ พารามิเ ตอร์เ ข้า มาเป็น อะเรย์ข องข้อ มูล ชนิด ต่า งๆ เมธอดใน คลาส Arrays ทีเ กี่ย วข้อ งกับ อะเรย์ม ีด ง ่ ั ต่อ ไปนี้ • sort() • binarySearch() • fill()
- 21. ตัว อย่า งโปรแกรม import java.util.Arrays; import java.util.Arrays; public class MethodsArrays { public class MethodsArrays { public static void main(String args[]) { public static void main(String args[]) { double d[] = {5.3, 3.56, 0.5, 1.65, 7.8}; double d[] = {5.3, 3.56, 0.5, 1.65, 7.8}; Arrays.sort(d); Arrays.sort(d); for(int i=0; i<d.length; i++) { for(int i=0; i<d.length; i++) { System.out.print(d[i]+" "); System.out.print(d[i]+" "); }} System.out.println(); System.out.println();
- 22. ตัว อย่า งโปรแกรม int pos = Arrays.binarySearch(d,1.65); int pos = Arrays.binarySearch(d,1.65); System.out.println("arrays["+pos+"] = 1.65"); System.out.println("arrays["+pos+"] = 1.65"); Arrays.fill(d,1.0); Arrays.fill(d,1.0); for(int i=0; i<d.length; i++) { for(int i=0; i<d.length; i++) { System.out.print(d[i]+" "); System.out.print(d[i]+" "); }} System.out.println(); System.out.println(); }} }} 0.5 1.65 3.56 5.3 7.8 ผลลัพ ธ์ท ไ ด้จ ากการรัน โปรแกรม 1.0 1.0 1.651.0 ี่ arrays[1] = 1.0 1.0
- 23. การคัด ลอกค่า ข้อ มูล ของสมาชิก ขอ งอะเรย์ ภาษาจาวาไม่ย อมให้ม ก ารเปลี่ย นแปลงขนาดขอ ี ง อะเรย์ แต่ค ่า ข้อ มูล ของสมาชิก ของอะเรย์ สามารถทีจ ะถูก คัด ลอกได้ โดยใช้ค ำา สั่ง ่ System.arraycopy();
- 24. ตัว อย่า งโปรแกรม public class CopyArrays { public class CopyArrays { public static void main(String args[]) { public static void main(String args[]) { String []scr = {"Copy","an","array","from", String []scr = {"Copy","an","array","from", " source"," to"," destination."}; " source"," to"," destination."}; String []dst = new String[4]; String []dst = new String[4]; System.arraycopy(scr,3,dst,0,4); System.arraycopy(scr,3,dst,0,4); for(int i=0; i<dst.length; i++) { for(int i=0; i<dst.length; i++) { System.out.print(dst[i]); System.out.print(dst[i]); }} System.out.println(); System.out.println(); }} }} ผลลัพ ธ์ท ไ ด้จ ากการรัน โปรแกรม source ี่ from to destination.
- 25. Collection API คลาสใน Collection API สามารถทีจ ะนำา มาใช้ ่ เก็บ ข้อ มูล ทีเ ป็น ออปเจ็ค ได้ห ลายตัว ่ โครงสร้า งข้อ มูล ของคลาสใน Collection API จะ คล้า ยกับ ของ อะเรย์ ต่า งกัน ตรงทีข นาดโครงสร้า ง ่ ข้อ มูล ของ คลาสใน Collection API สามารถทีจ ะ ่ ถูก เปลี่ย นแปลงได้
- 26. Collection API Collection API ประกอบไปด้ว ยอิน เตอร์เ ฟสที่ สำา คัญ ดัง นี้ • Collection • Set • List • Map Collection API ประกอบไปด้ว ยคลาสทีส ำา คัญ ่ ดัง นี้ • HashSet • ArrayList • Vector • LinkedList • HashMap
- 27. รูป แสดงส่ว นประกอบที่ส ำา คัญ ของ Collection API
- 28. อิน เตอร์เ ฟส Collection มีค ุณ สมบัต ิค ือสามารถทีจ ะระบุห รือ ไม่ร ะบุล ำา ดับ ่ ความสำา คัญ ของสมาชิก และสามารถที่จ ะกำา หนด ให้ค ่า ข้อ มูล ของสมาชิก ซำ้า กัน หรือ ไม่ก ไ ด้ ็ อิน เตอร์เ ฟส Collection มีเ มธอดทีส ำา คัญ ดัง นี้ ่ • boolean add(Object element) • boolean remove(Object element) • int size() • boolean isEmpty() • boolean contains(Object element) • Iterator iterator()
- 29. อิน เตอร์เ ฟส Set สืบ ทอดมาจากอิน เตอร์เ ฟส Collection ค่า ข้อ มูล ของสมาชิก จะไม่ส ามารถซำ้า กัน ได้ และ ลำา ดับ ของสมาชิก ไม่ม ค วามสำา คัญ ี คลาสสำา คัญ ที่ implement อิน เตอร์เ ฟส Set คือ คลาส HashSet
- 30. ตัว อย่า งโปรแกรม import java.util.*; import java.util.*; public class SampleSet { public class SampleSet { public static void main(String args[]) { public static void main(String args[]) { Set s = new HashSet(); Set s = new HashSet(); s.add("C#"); s.add("C#"); s.add("Java"); s.add("Java"); s.add("Pascal"); s.add("Pascal"); System.out.println("The size of this set is "+s.size()); System.out.println("The size of this set is "+s.size()); System.out.println("The contents are "+s); System.out.println("The contents are "+s); System.out.println("Removing C#"); System.out.println("Removing C#");
- 31. ตัว อย่า งโปรแกรม s.remove("C#"); s.remove("C#"); System.out.println("Now this set contains C#: "+ System.out.println("Now this set contains C#: "+ s.contains("C#")); s.contains("C#")); s.add("Java"); s.add("Java"); System.out.println("Now the size is "+s.size()); System.out.println("Now the size is "+s.size()); System.out.println("The contents are "+s); System.out.println("The contents are "+s); }} }} ผลลัพ ธ์ท ไ ด้จ ากการรัน โปรแกรม ี่ The size of this set is 3 The contents are [Java, Pascal, C#] Removing C# Now this set contains C#: false Now the size is 2 The contents are [Java, Pascal]
- 32. อิน เตอร์เ ฟส List สืบ ทอดมาจากอิน เตอร์เ ฟส Collection ค่า ข้อ มูล ของสมาชิก อาจจะสามารถซำ้า กัน ได้ และ ลำา ดับ ของสมาชิก มีค วามสำา คัญ อิน เตอร์เ ฟส List มีเ มธอดทีส ำา คัญ ทีเ พิม มาจาก ่ ่ ่ อิน เตอร์เ ฟส Collection ดัง นี้ • void add(int index,Object element) • Object remove(int index) • Object get(int index) • void set(int index,Object element) • int indexOf(Object element) • ListIterator listIterator() คลาสสำา คัญ ที่ implement อิน เตอร์เ ฟส List คือ คลาส ArrayList, Vector และ LinkedList
- 33. ตัว อย่า งโปรแกรม import java.util.*; import java.util.*; public class SampleList { public class SampleList { public static void main(String args[]) { public static void main(String args[]) { List l = new LinkedList(); List l = new LinkedList(); l.add("C#"); l.add("C#"); l.add("Java"); l.add("Java"); l.add("Pascal"); l.add("Pascal"); System.out.println("The size is "+l.size()); System.out.println("The size is "+l.size()); System.out.println("The contents are "+l); System.out.println("The contents are "+l); System.out.println("The first one is "+l.get(0)); System.out.println("The first one is "+l.get(0));
- 34. ตัว อย่า งโปรแกรม l.add("Java"); l.add("Java"); System.out.println("The contents are "+l); System.out.println("The contents are "+l); System.out.println("The index of Java is "+ System.out.println("The index of Java is "+ l.indexOf("Java")); l.indexOf("Java")); }} }} ผลลัพ ธ์ท ไ ด้จ ากการรัน โปรแกรม ี่ The size is 3 The contents are [C#, Java, Pascal] The first one is C# The contents are [C#, Java, Pascal, Java] The index of Java is 1
- 35. อิน เตอร์เ ฟส Map จะมีก ารเก็บ ค่า คีย ค ู่ก บ ค่า ข้อ มูล ของสมาชิก เสมอ ์ ั โดยทีค ่า คีย จ ะต้อ งไม่ซ ำ้า กัน แต่ค ่า ข้อ มูล ของ ่ ์ สมาชิก สามารถทีจ ะซำ้า กัน ได้ ่ อิน เตอร์เ ฟส Map มีเ มธอดทีส ำา คัญ ดัง นี้ ่ • Object put(Object key,Object value) • Object remove(Object key) • Object get(Object key) • Set entrySet() • Set keySet() • int size() คลาสสำา คัญ ที่ implement อิน เตอร์เ ฟส Map คือ คลาส HashMap
- 36. ตัว อย่า งโปรแกรม import java.util.*; import java.util.*; public class SampleMap { public class SampleMap { public static void main(String args[]) { public static void main(String args[]) { Map m = new HashMap(); Map m = new HashMap(); m.put("1","C#"); m.put("1","C#"); m.put("2","Java"); m.put("2","Java"); m.put("3","Pascal"); m.put("3","Pascal"); System.out.println("Removing Pascal"); System.out.println("Removing Pascal"); m.remove("3"); m.remove("3"); System.out.println("The size is "+m.size()); System.out.println("The size is "+m.size()); System.out.println("The first one is "+m.get("1")); System.out.println("The first one is "+m.get("1"));
- 37. ตัว อย่า งโปรแกรม m.put("3","Java"); m.put("3","Java"); System.out.println("The key of this map are "+ System.out.println("The key of this map are "+ m.keySet()); m.keySet()); System.out.println("The contents are "+m.entrySet()); System.out.println("The contents are "+m.entrySet()); }} }} ผลลัพ ธ์ท ไ ด้จ ากการรัน โปรแกรม ี่ Removing Pascal The size is 2 The first one is C# The key of this map are [3, 2, 1] The contents are [3=Java, 2=Java, 1=C#]
- 38. อิน เตอร์เ ฟส Iterator เป็น อิน เตอร์เ ฟสทีม ไ ว้เ พือ ใช้ใ นการอ้า งถึง ข้อ มูล ่ ี ่ สมาชิก ประเภท Set โดยมีเ มธอดทีส ำา คัญ ดัง นี้ ่ • boolean hasNext() • Object next() • void remove() ภายในอิน เตอร์เ ฟส Collection จะมีเ มธอดทีช ื่อ ่ iterator() ซึง เป็น เมธอดทีจ ะส่ง ค่า กลับ เป็น ่ ่ Iterator
- 39. ตัว อย่า งโปรแกรม import java.util.*; import java.util.*; public class SampleIterator {{ public class SampleIterator public static void main(String args[]) {{ public static void main(String args[]) Set scrSet == new HashSet(); Set scrSet new HashSet(); scrSet.add("C#"); scrSet.add("C#"); scrSet.add("Java"); scrSet.add("Java"); scrSet.add("Pascal"); scrSet.add("Pascal"); Iterator it == scrSet.iterator(); Iterator it scrSet.iterator(); Set dstSet == new HashSet(); Set dstSet new HashSet(); for(int i=0; i<scrSet.size(); i++) {{ for(int i=0; i<scrSet.size(); i++) if(it.hasNext()) {{ if(it.hasNext()) dstSet.add(it.next()); dstSet.add(it.next()); }} }} System.out.println(dstSet);ผลลัพ ธ์ท ไ ด้จ ากการรัน โปรแก System.out.println(dstSet); ี่ }} [Java, Pascal, C#] }}
- 40. อิน เตอร์เ ฟส ListIterator สืบ ทอดมาจากอิน เตอร์เ ฟส Iterator ใช้ใ นการอ้า งถึง ข้อ มูล สมาชิก ประเภท List อิน เตอร์เ ฟส ListIterator มีเ มธอดทีส ำา คัญ ทีเ พิ่ม ่ ่ มาจาก Iterator ดัง นี้ • boolean hasPrevious() • Object previous() • void add(Object element) • void set(Object element) ภายในอิน เตอร์เ ฟส List จะมีเ มธอดทีช ื่อ ่ listIterator() ซึ่ง เป็น เมธอดทีจ ะส่ง ค่า กลับ เป็น ่ ListIterator
- 41. อิน เตอร์เ ฟส Enumeration คล้า ยกับ อิน เตอร์เ ฟส Iterator มีเ มธอดทีส ำา คัญ ่ ดัง นี้ • boolean hasMoreElement() • Object nextElement()
- 42. คลาส Vector เป็น คลาสที่ implements อิน เตอร์เ ฟส List มี constructor แบบต่า งๆดัง นี้ • new Vector() • new Vector(int initialCapacity) • new Vector(int initialCapacity,int capacityIncrement)
- 43. ตัว อย่า งโปรแกรม import java.util.*; import java.util.*; public class SampleEnumeration { public class SampleEnumeration { public static void main(String args[]) { public static void main(String args[]) { Vector v = new Vector(); Vector v = new Vector(); v.add("C#"); v.add("C#"); v.add("Java"); v.add("Java"); v.add("Pascal"); v.add("Pascal"); Enumeration e = v.elements(); Enumeration e = v.elements(); while (e.hasMoreElements()) { while (e.hasMoreElements()) { System.out.print(e.nextElement()+" "); System.out.print(e.nextElement()+" "); }} }} }} ผลลัพ ธ์ท ไ ด้จ ากการรัน โปรแกรม Java ี่ C# Pascal
- 44. สรุป เนื้อ หาของบท อะเรย์ข องข้อ มูล ชนิด พืน ฐานจะมีค ่า ข้อ มูล เป็น ้ สมาชิก ของอะเรย์ แต่ส ำา หรับ อะเรย์ข องข้อ มูล ชนิด คลาส สมาชิก ของอะเรย์จ ะเป็น ตำา แหน่ง อ้า งอิง ไปยัง ค่า ข้อ มูล สำา หรับ อะเรย์ส องมิต ิ จำา นวนคอลัม น์ใ นแต่ล ะแถว ไม่จ ำา เป็น ต้อ งเท่า กัน ในคลาส Arraysมีเ มธอดสำา คัญ ทีเ กี่ย วข้อ ่ งกับ อะเรย์ค ือ sort(), binarySearch() และ fill() เมธอด arraycopy() จากคลาส System ใช้ใ นการคัด ลอกค่า ของสมาชิก ของอะเรย์
- 45. สรุป เนื้อ หาของบท Collection,Set,List และ Map เป็น อิน เตอร์เ ฟสสำา คัญ ทีอ ยูใ น Collection API โดยทีอ ิน เตอร์เ ฟส Set ่ ่ ่ และ List สืบ ทอดมาจากอิน เตอร์เ ฟส Collection อิน เตอร์เ ฟส Set จะไม่ส ามารถมีค ่า ข้อ มูล ของ สมาชิก ทีซ ำ้า กัน ได้ และลำา ดับ ของสมาชิก ไม่ม ี ่ ความสำา คัญ ส่ว นอิน เตอร์เ ฟส List จะสามารถมีค ่า ข้อ มูล ของ สมาชิก ทีซ ำ้า กัน ได้ และลำา ดับ ของสมาชิก มีค วาม ่ สำา คัญ สำา หรับ อิน เตอร์เ ฟส Map จะมีก ารเก็บ ค่า คีย ค ู่ก บ ค่า ์ ั ข้อ มูล ของสมาชิก
- 46. สรุป เนื้อ หาของบท เราสามารถนำา คลาสที่ implements อิน เตอร์เ ฟส เหล่า นี้ไ ปใช้ใ นการเก็บ ข้อ มูล ทีเ ป็น ออปเจ็ค ได้ ่ หลายตัว คล้า ยกับ อะเรย์ แต่ส ามารถเปลี่ย นแปลง ขนาดได้ อิน เตอร์เ ฟส Iterator,ListIteratorและ Enumeration ใช้ใ นการอ้า งถึง ข้อ มูล สมาชิก ของคลาสทีอ ยู่ใ น ่ Collection API คลาส Vector เป็น คลาสทีใ ช้ใ นการเก็บ กลุ่ม ขอ ่ งออปเจ็ค ของคลาสใดๆโดยไม่จ ำา กัด จำา นวน ประเภทเดีย วกับ List
- 47. แบบฝึก หัด ข้อ ที่ 1 • จากโปรแกรมจำา ลองระบบธนาคาร ให้ท ดลองปรับ ปรุง คลาส Customer โดยการใช้อ ะเรย์เ พื่อ กำา หนดให้ม ี คุณ ลัก ษณะที่ส ามารถเก็บ บัญ ชีธ นาคารได้ห ลายบัญ ชี ข้อ ที่ 2 • จากโปรแกรมจำา ลองระบบธนาคาร ให้ท ดลองเขีย น คลาสที่ช ื่อ Bank ที่ม ีค ุณ ลัก ษณะเพื่อ เก็บ ข้อ มูล ลูก ค้า (ออปเจ็ค ชนิด Customer) หลายๆคน โดยกำา หนดให้ เป็น ข้อ มูล แบบ Vector และมีเ มธอดในการเพิ่ม ลูก ค้า และเรีย กดูข ้อ มูล ลูก ค้า






![การประกาศตัว แปรอะเรย์
รูป แบบการประกาศตัว แปรอะเรย์ คล้า ยกับ การ
ประกาศตัว แปรชนิด ข้อ มูล แบบอื่น ๆ แต่ต ัว แป
รอะเรย์จ ะมีเ ครื่อ งหมาย [ ] อยูด ้า นหน้า หรือ ด้า น
่
หลัง
รูป แบบ
[<modifier>] dataType []variableName;
หรือ [<modifier>] dataType variableName[];
ตัว อย่า ง
char []ch; หรือ char ch[];
Student []s; หรือ Student s[];](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter8-130103205430-phpapp01/85/Java-Programming-8-12-Arrays-and-Collection-6-320.jpg)
![การสร้า งอะเรย์ข องข้อ มูล ชนิด พื้น
ฐาน
อะเรย์ใ นภาษาจาวาจะเป็น ตัว แปรแบบอ้า งอิง ชนิด
หนึง (เช่น เดีย วกับ
่ ออปเจ็ค )
การสร้า งอะเรย์จ ะสามารถทำา ได้โ ดยการเรีย กใช้
คำา สั่ง new
รูป แบบ
variableName = new dataType[size];
ตัว อย่า ง
ch = new char[5];
สำา หรับ การสร้า งอะเรย์ข องข้อ มูล ชนิด พืน ฐาน
้ คำา
สั่ง new จะจองเนือ ทีใ นหน่ว ยความจำา สำา หรับ เก็บ
้ ่
ค่า ของสมาชิก ของอะเรย์ ส่ว นตัว แปรอะเรย์จ ะเก็บ](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter8-130103205430-phpapp01/85/Java-Programming-8-12-Arrays-and-Collection-7-320.jpg)
![การรวมคำา สัง ประกาศและสร้า ง
่
ตัว แปร
เราสามารถทีจ ะรวมคำา สั่ง ประกาศชื่อ ตัว แปรและ
่
คำา สั่ง การสร้า งตัว แปร อะเรย์ไ ว้ใ นคำา สัง เดีย วกัน
่
ได้
รูป แบบ
dataType []variableName = new
dataType[size];
หรือ dataType variableName[] = new
dataType[size];
ตัว อย่า งเช่น
int []x = new int[5];](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter8-130103205430-phpapp01/85/Java-Programming-8-12-Arrays-and-Collection-8-320.jpg)

![การสร้า งอะเรย์ข องข้อ มูล ชนิด
คลาส
สำา หรับ การสร้า งอะเรย์ข องข้อ มูล ชนิด คลาส คำา สัง
่
new จะจองเนือ ทีใ นหน่ว ยความจำา สำา หรับ เก็บ ค่า
้ ่
ของสมาชิก ของอะเรย์ ซึ่ง จะเป็น เพีย งแค่ต ำา แหน่ง
อ้า งอิง เท่า นัน
้
ตัว อย่า ง
Student []s;
s = new Student[3];](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter8-130103205430-phpapp01/85/Java-Programming-8-12-Arrays-and-Collection-10-320.jpg)

![การสร้า งออปเจ็ค ของคลาสให้ก ับ
สมาชิก
ดัง นั้น จะต้อ งมีก ารเรีย กใช้ค ำา สั่ง new
อีก เพือ สร้า ง
่
ออปเจ็ค ของคลาสให้ก บ สมาชิก แต่ล ะตัว ขอ
ั
งอะเรย์
ตัว อย่า ง
s[0] = new Student(“1111”,“Thana”,3.0);
s[1] = new Student(“2211”,“Somchai”,2.10);
s[2] = new Student(“3331”,“Supansa”,3.1);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter8-130103205430-phpapp01/85/Java-Programming-8-12-Arrays-and-Collection-12-320.jpg)
![การกำา หนดค่า เริ่ม ต้น ให้ก ับ สมาชิก
ของอะเรย์
ค่า เริ่ม ต้น ของสมาชิก ของอะเรย์ จะถูก กำา หนดให้
โดยอัต โนมัต ิ ซึ่ง จะมีค ่า ตามค่า เริ่ม ต้น ของชนิด ข้อ
มูล นัน ๆ
้
เราสามารถสร้า งอะเรย์พ ร้อ มกับ กำา หนดค่า เริ่ม ต้น
ให้ก บ สมาชิก ของอะเรย์เ องได้
ั
รูป แบบ
dataType []variableName = {value1,value2,..,valueN};
ตัว อย่า ง
int []x = {4,3,5,1,8};
Student []s = {new Student("1111","Thana",3.0),
new Student("2211","Somchai",2.10),
new Student("3331","Supansa",3.1)};](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter8-130103205430-phpapp01/85/Java-Programming-8-12-Arrays-and-Collection-14-320.jpg)
![อะเรย์ห ลายมิต ิ
เราสามารถทีจ ะประกาศอะเรย์ม ากกว่า หนึง มิต ิไ ด้
่ ่
กรณีข องอะเรย์ส องมิต ิ มีร ูป แบบการประกาศ
ตัว แปรดัง นี้
[modifier] dataType [][]variableName;
หรือ [modifier] dataType variableName[][];
ตัว อย่า ง
int [][]x;
รูป แบบการสร้า งตัว แปรอะเรย์ส องมิต ิเ ป็น ดัง นี้
variableName = new dataType[row][col];
ตัว อย่า ง
x = new int[3][4];](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter8-130103205430-phpapp01/85/Java-Programming-8-12-Arrays-and-Collection-15-320.jpg)
![อะเรย์ส องมิต ิท ี่แ ต่ล ะแถวมีจ ำา นวน
คอลัม น์ต ่า งกัน
การสร้า งอะเรย์ส องมิต ิใ นภาษาจาวา ไม่จ ำา เป็น ที่
จำา นวนคอลัม น์ข องแต่ล ะแถวจะต้อ งเท่า กัน
ตัว อย่า ง
int [][]x = new int[3][];
x[0] = new int[4];
x[1] = new int[2];
x[2] = new int[3];](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter8-130103205430-phpapp01/85/Java-Programming-8-12-Arrays-and-Collection-16-320.jpg)
![ตัว อย่า งโปรแกรม
public class TwoDimensionArrays {
public class TwoDimensionArrays {
public static void main(String args[]) {
public static void main(String args[]) {
int x[][] = new int[3][];
int x[][] = new int[3][];
x[0] = new int[4];
x[0] = new int[4];
x[1] = new int[2];
x[1] = new int[2];
x[2] = new int[3];
x[2] = new int[3];
for(int i=0; i<x.length; i++) {
for(int i=0; i<x.length; i++) {
for(int j=0; j<x[i].length; j++) {
for(int j=0; j<x[i].length; j++) {
x[i][j] = (i+j)*2;
x[i][j] = (i+j)*2;
}}
}}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter8-130103205430-phpapp01/85/Java-Programming-8-12-Arrays-and-Collection-17-320.jpg)
![ตัว อย่า งโปรแกรม
for(int i=0; i<x.length; i++) {
for(int i=0; i<x.length; i++) {
for(int j=0; j<x[i].length; j++) {
for(int j=0; j<x[i].length; j++) {
System.out.print(x[i][j]+" ");
System.out.print(x[i][j]+" ");
}}
System.out.println();
System.out.println();
}}
}}
}}
สดงผลลัพ ธ์ท ไ ด้จ ากการรัน โปรแกรม
ี่](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter8-130103205430-phpapp01/85/Java-Programming-8-12-Arrays-and-Collection-18-320.jpg)
![การหาขนาดของอะเรย์
ทุก อะเรย์ใ นภาษาจาวาจะ มีค ุณ ลัก ษณะทีช ื่อ
่
ซึง จะมีค ่า เท่า กับ จำา นวนสมาชิก ทัง หมดขอ
length ่ ้
งอะเรย์น น
ั้
ตัว อย่า ง
int x[] = new int[3];
• x.length มีค ่า เท่า กับ 3
int x[][] = new int[3][4];
• x.length มีค ่า เท่า กับ 3
• x[1].length มีค ่า เท่า กับ 4](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter8-130103205430-phpapp01/85/Java-Programming-8-12-Arrays-and-Collection-19-320.jpg)

![ตัว อย่า งโปรแกรม
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class MethodsArrays {
public class MethodsArrays {
public static void main(String args[]) {
public static void main(String args[]) {
double d[] = {5.3, 3.56, 0.5, 1.65, 7.8};
double d[] = {5.3, 3.56, 0.5, 1.65, 7.8};
Arrays.sort(d);
Arrays.sort(d);
for(int i=0; i<d.length; i++) {
for(int i=0; i<d.length; i++) {
System.out.print(d[i]+" ");
System.out.print(d[i]+" ");
}}
System.out.println();
System.out.println();](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter8-130103205430-phpapp01/85/Java-Programming-8-12-Arrays-and-Collection-21-320.jpg)
![ตัว อย่า งโปรแกรม
int pos = Arrays.binarySearch(d,1.65);
int pos = Arrays.binarySearch(d,1.65);
System.out.println("arrays["+pos+"] = 1.65");
System.out.println("arrays["+pos+"] = 1.65");
Arrays.fill(d,1.0);
Arrays.fill(d,1.0);
for(int i=0; i<d.length; i++) {
for(int i=0; i<d.length; i++) {
System.out.print(d[i]+" ");
System.out.print(d[i]+" ");
}}
System.out.println();
System.out.println();
}}
}}
0.5 1.65 3.56 5.3 7.8
ผลลัพ ธ์ท ไ ด้จ ากการรัน โปรแกรม 1.0 1.0 1.651.0
ี่ arrays[1] =
1.0 1.0](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter8-130103205430-phpapp01/85/Java-Programming-8-12-Arrays-and-Collection-22-320.jpg)

![ตัว อย่า งโปรแกรม
public class CopyArrays {
public class CopyArrays {
public static void main(String args[]) {
public static void main(String args[]) {
String []scr = {"Copy","an","array","from",
String []scr = {"Copy","an","array","from",
" source"," to"," destination."};
" source"," to"," destination."};
String []dst = new String[4];
String []dst = new String[4];
System.arraycopy(scr,3,dst,0,4);
System.arraycopy(scr,3,dst,0,4);
for(int i=0; i<dst.length; i++) {
for(int i=0; i<dst.length; i++) {
System.out.print(dst[i]);
System.out.print(dst[i]);
}}
System.out.println();
System.out.println();
}}
}}
ผลลัพ ธ์ท ไ ด้จ ากการรัน โปรแกรม source
ี่ from to destination.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter8-130103205430-phpapp01/85/Java-Programming-8-12-Arrays-and-Collection-24-320.jpg)





![ตัว อย่า งโปรแกรม
import java.util.*;
import java.util.*;
public class SampleSet {
public class SampleSet {
public static void main(String args[]) {
public static void main(String args[]) {
Set s = new HashSet();
Set s = new HashSet();
s.add("C#");
s.add("C#");
s.add("Java");
s.add("Java");
s.add("Pascal");
s.add("Pascal");
System.out.println("The size of this set is "+s.size());
System.out.println("The size of this set is "+s.size());
System.out.println("The contents are "+s);
System.out.println("The contents are "+s);
System.out.println("Removing C#");
System.out.println("Removing C#");](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter8-130103205430-phpapp01/85/Java-Programming-8-12-Arrays-and-Collection-30-320.jpg)
![ตัว อย่า งโปรแกรม
s.remove("C#");
s.remove("C#");
System.out.println("Now this set contains C#: "+
System.out.println("Now this set contains C#: "+
s.contains("C#"));
s.contains("C#"));
s.add("Java");
s.add("Java");
System.out.println("Now the size is "+s.size());
System.out.println("Now the size is "+s.size());
System.out.println("The contents are "+s);
System.out.println("The contents are "+s);
}}
}}
ผลลัพ ธ์ท ไ ด้จ ากการรัน โปรแกรม
ี่
The size of this set is 3
The contents are [Java, Pascal, C#]
Removing C#
Now this set contains C#: false
Now the size is 2
The contents are [Java, Pascal]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter8-130103205430-phpapp01/85/Java-Programming-8-12-Arrays-and-Collection-31-320.jpg)

![ตัว อย่า งโปรแกรม
import java.util.*;
import java.util.*;
public class SampleList {
public class SampleList {
public static void main(String args[]) {
public static void main(String args[]) {
List l = new LinkedList();
List l = new LinkedList();
l.add("C#");
l.add("C#");
l.add("Java");
l.add("Java");
l.add("Pascal");
l.add("Pascal");
System.out.println("The size is "+l.size());
System.out.println("The size is "+l.size());
System.out.println("The contents are "+l);
System.out.println("The contents are "+l);
System.out.println("The first one is "+l.get(0));
System.out.println("The first one is "+l.get(0));](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter8-130103205430-phpapp01/85/Java-Programming-8-12-Arrays-and-Collection-33-320.jpg)
![ตัว อย่า งโปรแกรม
l.add("Java");
l.add("Java");
System.out.println("The contents are "+l);
System.out.println("The contents are "+l);
System.out.println("The index of Java is "+
System.out.println("The index of Java is "+
l.indexOf("Java"));
l.indexOf("Java"));
}}
}}
ผลลัพ ธ์ท ไ ด้จ ากการรัน โปรแกรม
ี่
The size is 3
The contents are [C#, Java, Pascal]
The first one is C#
The contents are [C#, Java, Pascal, Java]
The index of Java is 1](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter8-130103205430-phpapp01/85/Java-Programming-8-12-Arrays-and-Collection-34-320.jpg)

![ตัว อย่า งโปรแกรม
import java.util.*;
import java.util.*;
public class SampleMap {
public class SampleMap {
public static void main(String args[]) {
public static void main(String args[]) {
Map m = new HashMap();
Map m = new HashMap();
m.put("1","C#");
m.put("1","C#");
m.put("2","Java");
m.put("2","Java");
m.put("3","Pascal");
m.put("3","Pascal");
System.out.println("Removing Pascal");
System.out.println("Removing Pascal");
m.remove("3");
m.remove("3");
System.out.println("The size is "+m.size());
System.out.println("The size is "+m.size());
System.out.println("The first one is "+m.get("1"));
System.out.println("The first one is "+m.get("1"));](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter8-130103205430-phpapp01/85/Java-Programming-8-12-Arrays-and-Collection-36-320.jpg)
![ตัว อย่า งโปรแกรม
m.put("3","Java");
m.put("3","Java");
System.out.println("The key of this map are "+
System.out.println("The key of this map are "+
m.keySet());
m.keySet());
System.out.println("The contents are "+m.entrySet());
System.out.println("The contents are "+m.entrySet());
}}
}}
ผลลัพ ธ์ท ไ ด้จ ากการรัน โปรแกรม
ี่
Removing Pascal
The size is 2
The first one is C#
The key of this map are [3, 2, 1]
The contents are [3=Java, 2=Java, 1=C#]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter8-130103205430-phpapp01/85/Java-Programming-8-12-Arrays-and-Collection-37-320.jpg)

![ตัว อย่า งโปรแกรม
import java.util.*;
import java.util.*;
public class SampleIterator {{
public class SampleIterator
public static void main(String args[]) {{
public static void main(String args[])
Set scrSet == new HashSet();
Set scrSet new HashSet();
scrSet.add("C#");
scrSet.add("C#");
scrSet.add("Java");
scrSet.add("Java");
scrSet.add("Pascal");
scrSet.add("Pascal");
Iterator it == scrSet.iterator();
Iterator it scrSet.iterator();
Set dstSet == new HashSet();
Set dstSet new HashSet();
for(int i=0; i<scrSet.size(); i++) {{
for(int i=0; i<scrSet.size(); i++)
if(it.hasNext()) {{
if(it.hasNext())
dstSet.add(it.next());
dstSet.add(it.next());
}}
}}
System.out.println(dstSet);ผลลัพ ธ์ท ไ ด้จ ากการรัน โปรแก
System.out.println(dstSet); ี่
}}
[Java, Pascal, C#]
}}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter8-130103205430-phpapp01/85/Java-Programming-8-12-Arrays-and-Collection-39-320.jpg)



![ตัว อย่า งโปรแกรม
import java.util.*;
import java.util.*;
public class SampleEnumeration {
public class SampleEnumeration {
public static void main(String args[]) {
public static void main(String args[]) {
Vector v = new Vector();
Vector v = new Vector();
v.add("C#");
v.add("C#");
v.add("Java");
v.add("Java");
v.add("Pascal");
v.add("Pascal");
Enumeration e = v.elements();
Enumeration e = v.elements();
while (e.hasMoreElements()) {
while (e.hasMoreElements()) {
System.out.print(e.nextElement()+" ");
System.out.print(e.nextElement()+" ");
}}
}}
}}
ผลลัพ ธ์ท ไ ด้จ ากการรัน โปรแกรม Java
ี่ C# Pascal](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter8-130103205430-phpapp01/85/Java-Programming-8-12-Arrays-and-Collection-43-320.jpg)



