Java Web Programming [2/9] : Servlet Basic
- 1. Module 2: Servlet Basics Thanisa Kruawaisayawan Thanachart Numnonda www.imcinstitute.com
- 2. Objectives What is Servlet? Request and Response Model Method GET and POST Servlet API Specifications The Servlet Life Cycle Examples of Servlet Programs 2
- 3. What is a Servlet? Java™ objects which extend the functionality of a HTTP server Dynamic contents generation Better alternative to CGI Efficient Platform and server independent Session management Java-based 3
- 4. Servlet vs. CGI Servlet CGI Requests are handled by New process is created threads. for each request Only a single instance (overhead & low will answer all requests scalability) for the same servlet No built-in support for concurrently (persistent sessions data) 4
- 5. Servlet vs. CGI (cont.) Request CGI1 Child for CGI1 Request CGI2 CGI Based Child for CGI2 Webserver Request CGI1 Child for CGI1 Request Servlet1 Servlet Based Webserver Request Servlet2 Servlet1 JVM Request Servlet1 Servlet2 5
- 6. Single Instance of Servlet 6
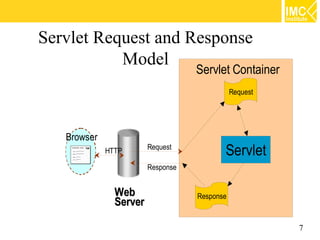
- 7. Servlet Request and Response Model Servlet Container Request Browser HTTP Request Servlet Response Web Response Server 7
- 8. What does Servlet Do? Receives client request (mostly in the form of HTTP request) Extract some information from the request Do content generation or business logic process (possibly by accessing database, invoking EJBs, etc) Create and send response to client (mostly in the form of HTTP response) or forward the request to another servlet or JSP page 8
- 9. Requests and Responses What is a request? Informationthat is sent from client to a server Who made the request Which HTTP headers are sent What user-entered data is sent What is a response? Information that is sent to client from a server Text(html, plain) or binary(image) data HTTP headers, cookies, etc 9
- 10. HTTP HTTP request contains Header Method Get: Input form data is passed as part of URL Post: Input form data is passed within message body Put Header request data 10
- 11. Request Methods getRemoteAddr() IP address of the client machine sending this request getRemotePort() Returns the port number used to sent this request getProtocol() Returns the protocol and version for the request as a string of the form <protocol>/<major version>.<minor version> getServerName() Name of the host server that received this request getServerPort() Returns the port number used to receive this request 11
- 12. HttpRequestInfo.java public class HttpRequestInfo extends HttpServlet {{ public class HttpRequestInfo extends HttpServlet :: protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)throws ServletException, IOException {{ HttpServletResponse response)throws ServletException, IOException response.setContentType("text/html"); response.setContentType("text/html"); PrintWriter out == response.getWriter(); PrintWriter out response.getWriter(); out.println("ClientAddress: "" ++ request.getRemoteAddr() ++ out.println("ClientAddress: request.getRemoteAddr() "<BR>"); "<BR>"); out.println("ClientPort: "" ++ request.getRemotePort() ++ "<BR>"); out.println("ClientPort: request.getRemotePort() "<BR>"); out.println("Protocol: "" ++ request.getProtocol() ++ "<BR>"); out.println("Protocol: request.getProtocol() "<BR>"); out.println("ServerName: "" ++ request.getServerName() ++ "<BR>"); out.println("ServerName: request.getServerName() "<BR>"); out.println("ServerPort: "" ++ request.getServerPort() ++ "<BR>"); out.println("ServerPort: request.getServerPort() "<BR>"); out.close(); out.close(); }} :: }} 12
- 13. Reading Request Header General getHeader getHeaders getHeaderNames Specialized getCookies getAuthType and getRemoteUser getContentLength getContentType getDateHeader getIntHeader 13
- 14. Frequently Used Request Methods HttpServletRequest methods getParameter() returns value of named parameter getParameterValues() if more than one value getParameterNames() for names of parameters 14
- 15. Example: hello.html <HTML> : <BODY> <form action="HelloNameServlet"> Name: <input type="text" name="username" /> <input type="submit" value="submit" /> </form> </BODY> </HTML> 15
- 16. HelloNameServlet.java public class HelloNameServlet extends HttpServlet {{ public class HelloNameServlet extends HttpServlet :: protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {{ throws ServletException, IOException response.setContentType("text/html"); response.setContentType("text/html"); PrintWriter out == response.getWriter(); PrintWriter out response.getWriter(); out.println("Hello "" ++ request.getParameter("username")); out.println("Hello request.getParameter("username")); out.close(); out.close(); }} :: }} 16
- 17. Result 17
- 18. HTTP GET and POST The most common client requests HTTP GET & HTTP POST GET requests: User entered information is appended to the URL in a query string Can only send limited amount of data .../chap2/HelloNameServlet?username=Thanisa POST requests: User entered information is sent as data (not appended to URL) Can send any amount of data 18
- 19. TestServlet.java import javax.servlet.*; import javax.servlet.http.*; import java.io.*; public class TestServlet extends HttpServlet { public void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException { response.setContentType("text/html"); PrintWriter out = response.getWriter(); out.println("<h2>Get Method</h2>"); } } 19
- 20. Steps of Populating HTTP Response Fill Response headers Get an output stream object from the response Write body content to the output stream 20
- 21. Example: Simple Response Public class HelloServlet extends HttpServlet { public void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException { // Fill response headers response.setContentType("text/html"); // Get an output stream object from the response PrintWriter out = response.getWriter(); // Write body content to output stream out.println("<h2>Get Method</h2>"); } } 21
- 23. Servlet Interfaces & Classes Servlet GenericServlet HttpSession HttpServlet ServletRequest ServletResponse HttpServletRequest HttpServletResponse 23
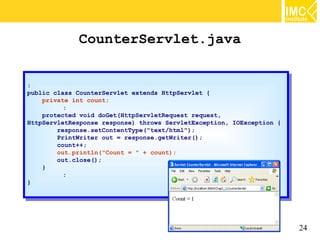
- 24. CounterServlet.java :: public class CounterServlet extends HttpServlet {{ public class CounterServlet extends HttpServlet private int count; private int count; :: protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {{ HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException response.setContentType("text/html"); response.setContentType("text/html"); PrintWriter out == response.getWriter(); PrintWriter out response.getWriter(); count++; count++; out.println("Count == "" ++ count); out.println("Count count); out.close(); out.close(); }} :: }} 24
- 25. Servlet Life-Cycle Is Servlet Loaded? Http request Load Invoke No Http response Yes Run Servlet Servlet Container Client Server 25
- 26. Servlet Life Cycle Methods service( ) init( ) destroy( ) Ready Init parameters doGet( ) doPost( ) Request parameters 26
- 27. The Servlet Life Cycle init executed once when the servlet is first loaded Not call for each request Perform any set-up in this method Setting up a database connection destroy calledwhen server delete servlet instance Not call after each request Perform any clean-up Closing a previously created database connection 27
- 28. doGet() and doPost() Methods Server HttpServlet subclass doGet( ) Request Service( ) Response doPost( ) Key: Implemented by subclass 28
- 29. Servlet Life Cycle Methods Invoked by container Container controls life cycle of a servlet Defined in javax.servlet.GenericServlet class or init() destroy() service() - this is an abstract method javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet class doGet(), doPost(), doXxx() service() - implementation 29
- 30. Implementation in method service() protected void service(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException { String method = req.getMethod(); if (method.equals(METHOD_GET)) { ... doGet(req, resp); ... } else if (method.equals(METHOD_HEAD)) { ... doHead(req, resp); // will be forwarded to doGet(req, resp) } else if (method.equals(METHOD_POST)) { doPost(req, resp); } else if (method.equals(METHOD_PUT)) { doPut(req, resp); } else if (method.equals(METHOD_DELETE)) { doDelete(req, resp); } else if (method.equals(METHOD_OPTIONS)) { doOptions(req,resp); } else if (method.equals(METHOD_TRACE)) { doTrace(req,resp); } else { ... } 30 }
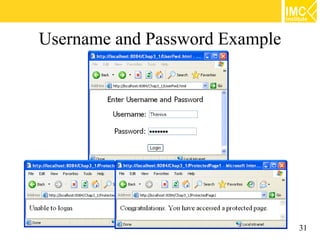
- 31. Username and Password Example 31
- 32. Acknowledgement Some contents are borrowed from the presentation slides of Sang Shin, Java™ Technology Evangelist, Sun Microsystems, Inc. 32
- 33. Thank you thananum@gmail.com www.facebook.com/imcinstitute www.imcinstitute.com 33