Kotlin coroutines 톺아보기
- 1. Kotlin Coroutines 톺아보기 발 표 자 : 김태우(당근마켓 로컬 커머스 팀) 밋업자료 : 밋업코드 : https://github.com/gaaon/kotlin-coroutines-examples
- 2. 00 비동기에 대한 고민 01 Coroutine 소개 02 Coroutine 톺아보기 03 다음회 예고 목차 목차
- 3. - 로컬 커머스팀 백엔드 개발자 - 커머스에서 로컬의 가치를 찾는 팀 시작하기에 앞서
- 5. - 한번에 이해하기 힘들다 - 추적이 어렵다 - 에러 핸들링이 어렵다 00. 비동기에 대한 고민 userRepository.findUserByIdAsMaybe(userId) .subscribe { buyer -> addressRepository.findAddressByUserAsPublisher(buyer) .subscribe(LastItemSubscriber { address -> checkValidRegion(address) productRepository.findAllProductsByIdsAsFlux(productIds) .collectList() .subscribe { products -> check(products.isNotEmpty()) storeRepository.findStoresByProductsAsMulti(products) .collect().asList() .subscribe().with { stores -> check(stores.isNotEmpty()) orderRepository.createOrderAsFuture( buyer, products, stores, address ).whenComplete { order, _ -> emitter.success(order) } } } }) } 동기 프로그래밍과 다르다
- 6. - 어떻게 혼용해서 써야 할까? - 어떤 결과 타입을 반환해야 할까? - 또 다른 비동기 라이브러리가 추가되면? 00. 비동기에 대한 고민 다양한 비동기 라이브러리
- 7. - 우수한 가독성 - 에러 핸들링 - 동시성 처리 - Flow - Channel 00. 비동기에 대한 고민 Coroutine이 해결사? suspend fun execute(inputValues: InputValues): Order { val (userId, productIds) = inputValues // 1. 구매자 조회 val buyer = userRepository.findUserByIdAsMaybe(userId).awaitSingle() // 2. 주소 조회 및 유효성 체크 val address = addressRepository.findAddressByUserAsPublisher(buyer).awaitLast() checkValidRegion(address) // 3. 상품들 조회 val products = productRepository.findAllProductsByIdsAsFlux(productIds).asFlow().toList() check(products.isNotEmpty()) // 4. 스토어 조회 val stores = storeRepository.findStoresByProductsAsMulti(products).asFlow().toList() check(stores.isNotEmpty()) // 5. 주문 생성 val order = orderRepository.createOrderAsFuture(buyer, products, stores, address).await() return order }
- 9. - 구매자 정보 - 상품 정보 - 스토어 정보 - 배송지 01. Coroutine 소개 상품 주문
- 10. 동기 코드로
- 11. - 구매자 조회 - 주소 조회 및 유효성 체크 - 상품 목록 조회 - 스토어 목록 조회 - 주문 생성 01. Coroutine 소개 주문 생성 동기 코드 fun execute(inputValues: InputValues): Order { val (userId, productIds) = inputValues // 1. 구매자 조회 val buyer = userRepository.findUserByIdSync(userId) // 2. 주소 조회 및 유효성 체크 val address = addressRepository.findAddressByUserSync(buyer).last() checkValidRegion(address) // 3. 상품들 조회 val products = productRepository.findAllProductsByIdsSync(productIds) check(products.isNotEmpty()) // 4. 스토어 조회 val stores = storeRepository.findStoresByProductsSync(products) check(stores.isNotEmpty()) // 5. 주문 생성 val order = orderRepository.createOrderSync(buyer, products, stores, address) return order }
- 12. 비동기 코드로
- 13. - rxjava3의 Maybe - 0 .. 1, Error 01. Coroutine 소개 구매자 조회 import io.reactivex.rxjava3.core.Maybe interface UserAsyncRepository { fun findUserByIdAsMaybe(userId: String): Maybe<User> } class UserRxRepository : UserRepositoryBase(), UserAsyncRepository { override fun findUserByIdAsMaybe(userId: String): Maybe<User> { val user = prepareUser(userId) return Maybe.just(user) .delay(TIME_DELAY_MS, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS) } }
- 14. - jdk9의 Flow 사용 - item을 publish 하고 complete 이벤트로 flow 종료 01. Coroutine 소개 주소 조회 import java.util.concurrent.Flow interface AddressAsyncRepository { fun findAddressByUserAsPublisher(user: User): Flow.Publisher<Address> }
- 15. - reactor의 Flux 사용 - 0 .. n, Error 01. Coroutine 소개 상품 조회 import reactor.core.publisher.Flux interface ProductAsyncRepository { fun findAllProductsByIdsAsFlux(productIds: List<String>): Flux<Product> }
- 16. - mutiny의 Multi 사용 - 0 .. n, Error 01. Coroutine 소개 스토어 조회 import io.smallrye.mutiny.Multi interface StoreAsyncRepository { fun findStoresByProductsAsMulti(products: List<Product>): Multi<Store> }
- 17. - jdk8의 CompletableFuture - complete 되는 시점에 결과 반환 01. Coroutine 소개 주문 생성 import java.util.concurrent.CompletableFuture interface OrderAsyncRepository { fun createOrderAsFuture( buyer: User, products: List<Product>, stores: List<Store>, address: Address, ): CompletableFuture<Order> }
- 18. - subscribe는 결과를 얻은 시점에 주어진 subscriber (consumer)를 실행하는 일종의 callback - 반환값들이 아래에서 계속 필요해서 subscribe가 중첩 01. Coroutine 소개 subscribe hell fun execute(inputValues: InputValues): Mono<Order> { val (userId, productIds) = inputValues return Mono.create { emitter -> userRepository.findUserByIdAsMaybe(userId) .subscribe { buyer -> addressRepository.findAddressByUserAsPublisher(buyer) .subscribe(LastItemSubscriber { address -> checkValidRegion(address) productRepository.findAllProductsByIdsAsFlux(productIds) .collectList() .subscribe { products -> check(products.isNotEmpty()) storeRepository.findStoresByProductsAsMulti(products) .collect().asList() .subscribe().with { stores -> check(stores.isNotEmpty()) orderRepository.createOrderAsFuture( buyer, products, stores, address ).whenComplete { order, _ -> emitter.success(order) } } } }) } } }
- 19. - 각각의 비동기 함수를 Reactor로 변경 - RxJava3Adapter - JdkFlowAdapter - Flux.collectList - Flux.from - Mono.fromFuture 01. Coroutine 소개 flatMap hell fun execute(inputValues: InputValues): Mono<Order> { val (userId, productIds) = inputValues return RxJava3Adapter.maybeToMono(userRepository.findUserByIdAsMaybe(userId)) .flatMap { buyer -> JdkFlowAdapter.flowPublisherToFlux( addressRepository.findAddressByUserAsPublisher(buyer)) .last() .flatMap { address -> checkValidRegion(address) productRepository.findAllProductsByIdsAsFlux(productIds) .collectList() .flatMap { products -> check(products.isNotEmpty()) Flux.from(storeRepository.findStoresByProductsAsMulti(products) .collectList() .flatMap { stores -> check(stores.isNotEmpty()) Mono.fromFuture( orderRepository.createOrderAsFuture( buyer, products, stores, address ) ) } } } } }
- 20. Coroutine으로
- 21. - Maybe<T>.awaitSingle - Publisher<T>.awaitLast - Flow<T>.toList - CompletableFuture<T>.await 01. Coroutine 소개 Coroutine suspend fun execute(inputValues: InputValues): Order { val (userId, productIds) = inputValues // 1. 구매자 조회 val buyer = userRepository.findUserByIdAsMaybe(userId).awaitSingle() // 2. 주소 조회 및 유효성 체크 val address = addressRepository.findAddressByUserAsPublisher(buyer).awaitLast() checkValidRegion(address) // 3. 상품들 조회 val products = productRepository.findAllProductsByIdsAsFlux(productIds).asFlow().toList() check(products.isNotEmpty()) // 4. 스토어 조회 val stores = storeRepository.findStoresByProductsAsMulti(products).asFlow().toList() check(stores.isNotEmpty()) // 5. 주문 생성 val order = orderRepository.createOrderAsFuture(buyer, products, stores, address).await() return order }
- 22. 01. Coroutine 소개 suspend fun execute(inputValues: InputValues): Order { val (userId, productIds) = inputValues // 1. 구매자 조회 val buyer = userRepository.findUserByIdAsMaybe(userId).awaitSingle() // 2. 주소 조회 및 유효성 체크 val address = addressRepository.findAddressByUserAsPublisher(buyer).awaitLast() checkValidRegion(address) // 3. 상품들 조회 val products = productRepository.findAllProductsByIdsAsFlux(productIds).asFlow().toList() check(products.isNotEmpty()) // 4. 스토어 조회 val stores = storeRepository.findStoresByProductsAsMulti(products).asFlow().toList() check(stores.isNotEmpty()) // 5. 주문 생성 val order = orderRepository.createOrderAsFuture(buyer, products, stores, address).await() return order } fun execute(inputValues: InputValues): Order { val (userId, productIds) = inputValues // 1. 구매자 조회 val buyer = userRepository.findUserByIdSync(userId) // 2. 주소 조회 및 유효성 체크 val address = addressRepository.findAddressByUserSync(buyer).last() checkValidRegion(address) // 3. 상품들 조회 val products = productRepository.findAllProductsByIdsSync(productIds) check(products.isNotEmpty()) // 4. 스토어 조회 val stores = storeRepository.findStoresByProductsSync(products) check(stores.isNotEmpty()) // 5. 주문 생성 val order = orderRepository.createOrderSync(buyer, products, stores, address) return order } 동기코드 그리고 Coroutine
- 23. 01. Coroutine 소개 Coroutine 실행 @Test fun `should return a createdOrder in coroutine`() = runBlocking { // given val userId = "user1" val productIds = listOf("product1", "product2", "product3") // when val watch = StopWatch().also { it.start() } val inputValues = CreateOrderCoroutineUseCase.InputValues(userId, productIds) val createdOrder = createOrderUseCase.execute(inputValues) watch.stop() println("Time Elapsed: ${watch.time}ms") // then println(createdOrder) } - runBlocking은 동기코드에서 coroutine을 실행할 수 있게 bridge 역할
- 26. - 경량화된 쓰레드? - 특정 지점에서 정지했다가 재개할 수 있는 쓰레드? 02. Coroutine 톺아보기 Coroutine? suspend fun execute(inputValues: InputValues): Order { val (userId, productIds) = inputValues // 1. 구매자 조회 val buyer = userRepository.findUserByIdAsMaybe(userId).awaitSingle() // 2. 주소 조회 및 유효성 체크 val address = addressRepository.findAddressByUserAsPublisher(buyer).awaitLast() checkValidRegion(address) // 3. 상품들 조회 val products = productRepository.findAllProductsByIdsAsFlux(productIds).asFlow().toList() check(products.isNotEmpty()) // 4. 스토어 조회 val stores = storeRepository.findStoresByProductsAsMulti(products).asFlow().toList() check(stores.isNotEmpty()) // 5. 주문 생성 val order = orderRepository.createOrderAsFuture(buyer, products, stores, address).await() return order }
- 27. - Finite State Machine 기반의 재귀 함수로 변환 kotlin 컴파일러가 suspend가 붙은 함수에 추가적인 코드를 추가 - Continuation 인자를 타겟 함수에 추가하고 Continuation 구현체를 생성 - 타겟 함수 내의 모든 suspend 함수에 생성한 continuation 객체를 패스 - 코드를 분리해서 switch case 안에 넣고 label을 이용해서 state를 변경 02. Coroutine 톺아보기 Kotlin Compiler
- 28. - execute 함수가 실행되면 재귀 호출을 이용해서 스스로(execute 함수)를 실행하면서 state를 변경 - state가 최종에 도달하면 값을 caller에 반환 02. Coroutine 톺아보기 FSM 기반의 재귀 함수 재귀호출 재귀호출 재귀호출 재귀호출 complete
- 29. FSM 기반의 동기 코드로
- 30. - SharedData를 통해서 여러 가지 context를 저장 - label은 state machine의 현재 state 값 - 이전 state에서 찾은 값들을 buyer, address, products, stores, order에 저장 - resumeWith로 재귀 호출을 하고 결과를 result에 저장 - 인자의 sharedData가 null이라면 생성하고 아니면 있는 sharedData를 사용 02. Coroutine 톺아보기 FSM 기반의 동기 코드 class SharedData { var label: Int = 0 lateinit var result: Any lateinit var buyer: User lateinit var address: Address lateinit var products: List<Product> lateinit var stores: List<Store> lateinit var order: Order lateinit var resumeWith: (result: Any) -> Order } fun execute( inputValues: InputValues, sharedData: SharedData? = null, ): Order { val (userId, productIds) = inputValues val that = this val shared = sharedData ?: SharedData().apply { this.resumeWith = fun (result: Any): Order { this.result = result return that.execute(inputValues, this) } }
- 31. 02. Coroutine 톺아보기 FSM 기반의 동기 코드 return when (shared.label) { 0 -> { shared.label = 1 userRepository.findUserByIdSync(userId) .let { user -> shared.resumeWith(user) } } 1 -> { shared.label = 2 shared.buyer = shared.result as User addressRepository.findAddressByUserSync(shared.buyer).last() .let { address -> shared.resumeWith(address) } } 2 -> { shared.label = 3 shared.address = shared.result as Address checkValidRegion(shared.address) productRepository.findAllProductsByIdsSync(productIds) .let { products -> shared.resumeWith(products) } } 3 -> { shared.label = 4 shared.products = shared.result as List<Product> check(shared.products.isNotEmpty()) storeRepository.findStoresByProductsSync(shared.products) .let { stores -> shared.resumeWith(stores) } } 4 -> { shared.label = 5 shared.stores = shared.result as List<Store> check(shared.stores.isNotEmpty()) orderRepository.createOrderSync( shared.buyer, shared.products, shared.stores, shared.address ).let { order -> shared.resumeWith(order) } } 5 -> { shared.order = shared.result as Order shared.order } else -> throw IllegalAccessException() }
- 32. 02. Coroutine 톺아보기 FSM 기반의 동기 코드 ; state 0 return when (shared.label) { 0 -> { shared.label = 1 userRepository.findUserByIdSync(userId) .let { user -> shared.resumeWith(user) } } 1 -> { shared.label = 2 shared.buyer = shared.result as User addressRepository.findAddressByUserSync(shared.buyer).last() .let { address -> shared.resumeWith(address) } } 2 -> { shared.label = 3 shared.address = shared.result as Address checkValidRegion(shared.address) productRepository.findAllProductsByIdsSync(productIds) .let { products -> shared.resumeWith(products) } } 3 -> { shared.label = 4 shared.products = shared.result as List<Product> check(shared.products.isNotEmpty()) storeRepository.findStoresByProductsSync(shared.products) .let { stores -> shared.resumeWith(stores) } } 4 -> { shared.label = 5 shared.stores = shared.result as List<Store> check(shared.stores.isNotEmpty()) orderRepository.createOrderSync( shared.buyer, shared.products, shared.stores, shared.address ).let { order -> shared.resumeWith(order) } } 5 -> { shared.order = shared.result as Order shared.order } else -> throw IllegalAccessException() } this.resumeWith = fun (result: Any): Order { this.result = result return that.execute(inputValues, this) }
- 33. 02. Coroutine 톺아보기 FSM 기반의 동기 코드 ; state 1 return when (shared.label) { 0 -> { shared.label = 1 userRepository.findUserByIdSync(userId) .let { user -> shared.resumeWith(user) } } 1 -> { shared.label = 2 shared.buyer = shared.result as User addressRepository.findAddressByUserSync(shared.buyer).last() .let { address -> shared.resumeWith(address) } } 2 -> { shared.label = 3 shared.address = shared.result as Address checkValidRegion(shared.address) productRepository.findAllProductsByIdsSync(productIds) .let { products -> shared.resumeWith(products) } } 3 -> { shared.label = 4 shared.products = shared.result as List<Product> check(shared.products.isNotEmpty()) storeRepository.findStoresByProductsSync(shared.products) .let { stores -> shared.resumeWith(stores) } } 4 -> { shared.label = 5 shared.stores = shared.result as List<Store> check(shared.stores.isNotEmpty()) orderRepository.createOrderSync( shared.buyer, shared.products, shared.stores, shared.address ).let { order -> shared.resumeWith(order) } } 5 -> { shared.order = shared.result as Order shared.order } else -> throw IllegalAccessException() } this.resumeWith = fun (result: Any): Order { this.result = result return that.execute(inputValues, this) }
- 34. 02. Coroutine 톺아보기 FSM 기반의 동기 코드 ; state 2 return when (shared.label) { 0 -> { shared.label = 1 userRepository.findUserByIdSync(userId) .let { user -> shared.resumeWith(user) } } 1 -> { shared.label = 2 shared.buyer = shared.result as User addressRepository.findAddressByUserSync(shared.buyer).last() .let { address -> shared.resumeWith(address) } } 2 -> { shared.label = 3 shared.address = shared.result as Address checkValidRegion(shared.address) productRepository.findAllProductsByIdsSync(productIds) .let { products -> shared.resumeWith(products) } } 3 -> { shared.label = 4 shared.products = shared.result as List<Product> check(shared.products.isNotEmpty()) storeRepository.findStoresByProductsSync(shared.products) .let { stores -> shared.resumeWith(stores) } } 4 -> { shared.label = 5 shared.stores = shared.result as List<Store> check(shared.stores.isNotEmpty()) orderRepository.createOrderSync( shared.buyer, shared.products, shared.stores, shared.address ).let { order -> shared.resumeWith(order) } } 5 -> { shared.order = shared.result as Order shared.order } else -> throw IllegalAccessException() } this.resumeWith = fun (result: Any): Order { this.result = result return that.execute(inputValues, this) }
- 35. 02. Coroutine 톺아보기 FSM 기반의 동기 코드 ; state 3 return when (shared.label) { 0 -> { shared.label = 1 userRepository.findUserByIdSync(userId) .let { user -> shared.resumeWith(user) } } 1 -> { shared.label = 2 shared.buyer = shared.result as User addressRepository.findAddressByUserSync(shared.buyer).last() .let { address -> shared.resumeWith(address) } } 2 -> { shared.label = 3 shared.address = shared.result as Address checkValidRegion(shared.address) productRepository.findAllProductsByIdsSync(productIds) .let { products -> shared.resumeWith(products) } } 3 -> { shared.label = 4 shared.products = shared.result as List<Product> check(shared.products.isNotEmpty()) storeRepository.findStoresByProductsSync(shared.products) .let { stores -> shared.resumeWith(stores) } } 4 -> { shared.label = 5 shared.stores = shared.result as List<Store> check(shared.stores.isNotEmpty()) orderRepository.createOrderSync( shared.buyer, shared.products, shared.stores, shared.address ).let { order -> shared.resumeWith(order) } } 5 -> { shared.order = shared.result as Order shared.order } else -> throw IllegalAccessException() } this.resumeWith = fun (result: Any): Order { this.result = result return that.execute(inputValues, this) }
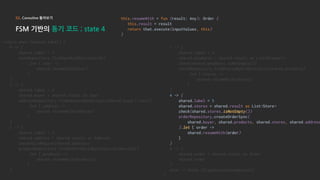
- 36. 02. Coroutine 톺아보기 FSM 기반의 동기 코드 ; state 4 return when (shared.label) { 0 -> { shared.label = 1 userRepository.findUserByIdSync(userId) .let { user -> shared.resumeWith(user) } } 1 -> { shared.label = 2 shared.buyer = shared.result as User addressRepository.findAddressByUserSync(shared.buyer).last() .let { address -> shared.resumeWith(address) } } 2 -> { shared.label = 3 shared.address = shared.result as Address checkValidRegion(shared.address) productRepository.findAllProductsByIdsSync(productIds) .let { products -> shared.resumeWith(products) } } 3 -> { shared.label = 4 shared.products = shared.result as List<Product> check(shared.products.isNotEmpty()) storeRepository.findStoresByProductsSync(shared.products) .let { stores -> shared.resumeWith(stores) } } 4 -> { shared.label = 5 shared.stores = shared.result as List<Store> check(shared.stores.isNotEmpty()) orderRepository.createOrderSync( shared.buyer, shared.products, shared.stores, shared.address ).let { order -> shared.resumeWith(order) } } 5 -> { shared.order = shared.result as Order shared.order } else -> throw IllegalAccessException() } this.resumeWith = fun (result: Any): Order { this.result = result return that.execute(inputValues, this) }
- 37. 02. Coroutine 톺아보기 FSM 기반의 동기 코드 ; state 5 return when (shared.label) { 0 -> { shared.label = 1 userRepository.findUserByIdSync(userId) .let { user -> shared.resumeWith(user) } } 1 -> { shared.label = 2 shared.buyer = shared.result as User addressRepository.findAddressByUserSync(shared.buyer).last() .let { address -> shared.resumeWith(address) } } 2 -> { shared.label = 3 shared.address = shared.result as Address checkValidRegion(shared.address) productRepository.findAllProductsByIdsSync(productIds) .let { products -> shared.resumeWith(products) } } 3 -> { shared.label = 4 shared.products = shared.result as List<Product> check(shared.products.isNotEmpty()) storeRepository.findStoresByProductsSync(shared.products) .let { stores -> shared.resumeWith(stores) } } 4 -> { shared.label = 5 shared.stores = shared.result as List<Store> check(shared.stores.isNotEmpty()) orderRepository.createOrderSync( shared.buyer, shared.products, shared.stores, shared.address ).let { order -> shared.resumeWith(order) } } 5 -> { shared.order = shared.result as Order shared.order } else -> throw IllegalAccessException() } this.resumeWith = fun (result: Any): Order { this.result = result return that.execute(inputValues, this) }
- 38. 02. Coroutine 톺아보기 FSM 기반의 동기 코드 ; 실행 @Test fun `should return a createdOrder in sync with state machine`() { // given val userId = "user1" val productIds = listOf("product1", "product2", "product3") // when val watch = StopWatch().also { it.start() } val inputValues = CreateOrderSyncStateMachineUseCase.InputValues( userId, productIds) val createdOrder = createOrderUseCase.execute(inputValues) watch.stop() println("Time Elapsed: ${watch.time}ms") // then println(createdOrder) } - execute를 실행할때, 두번째 인자를 넘기지 않아서 default value인 null로 제공
- 39. FSM 기반의 비동기 코드로
- 40. - SharedDataContinuation를 통해서 여러 가지 context를 저장 - label은 state machine의 현재 state 값 - 이전 state에서 찾은 값들을 buyer, address, products, stores, order에 저장 - resumeWith로 재귀 호출을 하여 결과를 result에 저장 - 인자의 sharedData가 SharedDataContinuation 타입이 아니라면 생성 02. Coroutine 톺아보기 FSM 기반의 비동기 코드 class SharedDataContinuation( // 실제로 continuation 구현체는 method 안에 val completion: Continuation<Any>, ) : Continuation<Any> { var label: Int = 0 lateinit var result: Any lateinit var buyer: User lateinit var address: Address lateinit var products: List<Product> lateinit var stores: List<Store> lateinit var order: Order lateinit var resume: () -> Unit override val context: CoroutineContext = completion.context override fun resumeWith(result: Result<Any>) { this.result = result this.resume() } } fun execute(inputValues: InputValues, completion: Continuation<Any>) { val (userId, productIds) = inputValues val that = this val cont = completion as? SharedDataContinuation ?: SharedDataContinuation(completion).apply { resume = fun() { // recursive self that.execute(inputValues, this)
- 41. 02. Coroutine 톺아보기 FSM 기반의 비동기 코드 class SharedDataContinuation( val completion: Continuation<Any>, ) : Continuation<Any> { var label: Int = 0 lateinit var result: Any lateinit var buyer: User lateinit var address: Address lateinit var products: List<Product> lateinit var stores: List<Store> lateinit var order: Order lateinit var resume: () -> Unit override val context: CoroutineContext = completion.context override fun resumeWith(result: Result<Any>) { this.result = result this.resume() } } fun execute(inputValues: InputValues, completion: Continuation<Any>) { val (userId, productIds) = inputValues val that = this val cont = completion as? SharedDataContinuation ?: SharedDataContinuation(completion).apply { resume = fun() { // recursive self that.execute(inputValues, this) } public interface Continuation<in T> { /** * The context of the coroutine that corresponds to this continuation. */ public val context: CoroutineContext /** * Resumes the execution of the corresponding coroutine passing a successful or failed [result] as the * return value of the last suspension point. */ public fun resumeWith(result: Result<T>) }
- 42. 02. Coroutine 톺아보기 FSM 기반의 비동기 코드 ; 실행 - testContinuation을 생성해서 execute 함수에 주입 @Test fun `should return a createdOrder in async with state machine`() { // given val userId = "user1" val productIds = listOf("product1", "product2", "product3") // when val watch = StopWatch().also { it.start() } val lock = CountDownLatch(1) val testContinuation = object : Continuation<Any> { override val context = EmptyCoroutineContext override fun resumeWith(result: Result<Any>) { watch.stop() lock.countDown() println("Time Elapsed: ${watch.time}ms") println(result.getOrThrow()) } } val inputValues = CreateOrderAsyncStateMachine3UseCase.InputValues(userId, productIds) createOrderUseCase.execute(inputValues, testContinuation) // then lock.await(3000, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS) }
- 43. 02. Coroutine 톺아보기 FSM 기반의 비동기 코드 when (cont.label) { 0 -> { cont.label = 1 userRepository.findUserByIdAsMaybe(userId) .subscribe { user -> cont.resumeWith(Result.success(user)) } } 1 -> { cont.label = 2 cont.buyer = (cont.result as Result<User>).getOrThrow() addressRepository.findAddressByUserAsPublisher(cont.buyer) .subscribe(LastItemSubscriber { address -> cont.resumeWith(Result.success(address)) }) } 2 -> { cont.label = 3 cont.address = (cont.result as Result<Address>).getOrThrow() checkValidRegion(cont.address) productRepository.findAllProductsByIdsAsFlux(productIds) .collectList() .subscribe { products -> cont.resumeWith(Result.success(products)) } } 3 -> { cont.label = 4 cont.products = (cont.result as Result<List<Product>>).getOrThrow() check(cont.products.isNotEmpty()) storeRepository.findStoresByProductsAsMulti(cont.products) .collect().asList() .subscribe().with { stores -> cont.resumeWith(Result.success(stores)) } } 4 -> { cont.label = 5 cont.stores = (cont.result as Result<List<Store>>).getOrThrow() check(cont.stores.isNotEmpty()) orderRepository.createOrderAsFuture( cont.buyer, cont.products, cont.stores, cont.address ).whenComplete { order, _ -> cont.resumeWith(Result.success(order)) } } 5 -> { cont.order = (cont.result as Result<Order>).getOrThrow() cont.completion.resumeWith(Result.success(cont.order)) } else -> throw IllegalAccessException()
- 44. 02. Coroutine 톺아보기 FSM 기반의 비동기 코드 ; state 0 when (cont.label) { 0 -> { cont.label = 1 userRepository.findUserByIdAsMaybe(userId) .subscribe { user -> cont.resumeWith(Result.success(user)) } } 1 -> { cont.label = 2 cont.buyer = (cont.result as Result<User>).getOrThrow() addressRepository.findAddressByUserAsPublisher(cont.buyer) .subscribe(LastItemSubscriber { address -> cont.resumeWith(Result.success(address)) }) } 2 -> { cont.label = 3 cont.address = (cont.result as Result<Address>).getOrThrow() checkValidRegion(cont.address) productRepository.findAllProductsByIdsAsFlux(productIds) .collectList() .subscribe { products -> cont.resumeWith(Result.success(products)) } } override fun resumeWith(result: Result<Any>) { this.result = result that.execute(inputValues, this) } 3 -> { cont.label = 4 cont.products = (cont.result as Result<List<Product>>).getOrThrow() check(cont.products.isNotEmpty()) storeRepository.findStoresByProductsAsMulti(cont.products) .collect().asList() .subscribe().with { stores -> cont.resumeWith(Result.success(stores)) } } 4 -> { cont.label = 5 cont.stores = (cont.result as Result<List<Store>>).getOrThrow() check(cont.stores.isNotEmpty()) orderRepository.createOrderAsFuture( cont.buyer, cont.products, cont.stores, cont.address ).whenComplete { order, _ -> cont.resumeWith(Result.success(order)) } } 5 -> { cont.order = (cont.result as Result<Order>).getOrThrow() cont.completion.resumeWith(Result.success(cont.order)) } else -> throw IllegalAccessException()
- 45. 02. Coroutine 톺아보기 FSM 기반의 비동기 코드 ; state 1 when (cont.label) { 0 -> { cont.label = 1 userRepository.findUserByIdAsMaybe(userId) .subscribe { user -> cont.resumeWith(Result.success(user)) } } 1 -> { cont.label = 2 cont.buyer = (cont.result as Result<User>).getOrThrow() addressRepository.findAddressByUserAsPublisher(cont.buyer) .subscribe(LastItemSubscriber { address -> cont.resumeWith(Result.success(address)) }) } 2 -> { cont.label = 3 cont.address = (cont.result as Result<Address>).getOrThrow() checkValidRegion(cont.address) productRepository.findAllProductsByIdsAsFlux(productIds) .collectList() .subscribe { products -> cont.resumeWith(Result.success(products)) } } override fun resumeWith(result: Result<Any>) { this.result = result that.execute(inputValues, this) } 3 -> { cont.label = 4 cont.products = (cont.result as Result<List<Product>>).getOrThrow() check(cont.products.isNotEmpty()) storeRepository.findStoresByProductsAsMulti(cont.products) .collect().asList() .subscribe().with { stores -> cont.resumeWith(Result.success(stores)) } } 4 -> { cont.label = 5 cont.stores = (cont.result as Result<List<Store>>).getOrThrow() check(cont.stores.isNotEmpty()) orderRepository.createOrderAsFuture( cont.buyer, cont.products, cont.stores, cont.address ).whenComplete { order, _ -> cont.resumeWith(Result.success(order)) } } 5 -> { cont.order = (cont.result as Result<Order>).getOrThrow() cont.completion.resumeWith(Result.success(cont.order)) } else -> throw IllegalAccessException()
- 46. 02. Coroutine 톺아보기 FSM 기반의 비동기 코드 ; state 2 when (cont.label) { 0 -> { cont.label = 1 userRepository.findUserByIdAsMaybe(userId) .subscribe { user -> cont.resumeWith(Result.success(user)) } } 1 -> { cont.label = 2 cont.buyer = (cont.result as Result<User>).getOrThrow() addressRepository.findAddressByUserAsPublisher(cont.buyer) .subscribe(LastItemSubscriber { address -> cont.resumeWith(Result.success(address)) }) } 2 -> { cont.label = 3 cont.address = (cont.result as Result<Address>).getOrThrow() checkValidRegion(cont.address) productRepository.findAllProductsByIdsAsFlux(productIds) .collectList() .subscribe { products -> cont.resumeWith(Result.success(products)) } } override fun resumeWith(result: Result<Any>) { this.result = result that.execute(inputValues, this) } 3 -> { cont.label = 4 cont.products = (cont.result as Result<List<Product>>).getOrThrow() check(cont.products.isNotEmpty()) storeRepository.findStoresByProductsAsMulti(cont.products) .collect().asList() .subscribe().with { stores -> cont.resumeWith(Result.success(stores)) } } 4 -> { cont.label = 5 cont.stores = (cont.result as Result<List<Store>>).getOrThrow() check(cont.stores.isNotEmpty()) orderRepository.createOrderAsFuture( cont.buyer, cont.products, cont.stores, cont.address ).whenComplete { order, _ -> cont.resumeWith(Result.success(order)) } } 5 -> { cont.order = (cont.result as Result<Order>).getOrThrow() cont.completion.resumeWith(Result.success(cont.order)) } else -> throw IllegalAccessException()
- 47. 02. Coroutine 톺아보기 FSM 기반의 비동기 코드 ; state 3 when (cont.label) { 0 -> { cont.label = 1 userRepository.findUserByIdAsMaybe(userId) .subscribe { user -> cont.resumeWith(Result.success(user)) } } 1 -> { cont.label = 2 cont.buyer = (cont.result as Result<User>).getOrThrow() addressRepository.findAddressByUserAsPublisher(cont.buyer) .subscribe(LastItemSubscriber { address -> cont.resumeWith(Result.success(address)) }) } 2 -> { cont.label = 3 cont.address = (cont.result as Result<Address>).getOrThrow() checkValidRegion(cont.address) productRepository.findAllProductsByIdsAsFlux(productIds) .collectList() .subscribe { products -> cont.resumeWith(Result.success(products)) } } override fun resumeWith(result: Result<Any>) { this.result = result that.execute(inputValues, this) } 3 -> { cont.label = 4 cont.products = (cont.result as Result<List<Product>>).getOrThrow() check(cont.products.isNotEmpty()) storeRepository.findStoresByProductsAsMulti(cont.products) .collect().asList() .subscribe().with { stores -> cont.resumeWith(Result.success(stores)) } } 4 -> { cont.label = 5 cont.stores = (cont.result as Result<List<Store>>).getOrThrow() check(cont.stores.isNotEmpty()) orderRepository.createOrderAsFuture( cont.buyer, cont.products, cont.stores, cont.address ).whenComplete { order, _ -> cont.resumeWith(Result.success(order)) } } 5 -> { cont.order = (cont.result as Result<Order>).getOrThrow() cont.completion.resumeWith(Result.success(cont.order)) } else -> throw IllegalAccessException()
- 48. 02. Coroutine 톺아보기 FSM 기반의 비동기 코드 ; state 4 when (cont.label) { 0 -> { cont.label = 1 userRepository.findUserByIdAsMaybe(userId) .subscribe { user -> cont.resumeWith(Result.success(user)) } } 1 -> { cont.label = 2 cont.buyer = (cont.result as Result<User>).getOrThrow() addressRepository.findAddressByUserAsPublisher(cont.buyer) .subscribe(LastItemSubscriber { address -> cont.resumeWith(Result.success(address)) }) } 2 -> { cont.label = 3 cont.address = (cont.result as Result<Address>).getOrThrow() checkValidRegion(cont.address) productRepository.findAllProductsByIdsAsFlux(productIds) .collectList() .subscribe { products -> cont.resumeWith(Result.success(products)) } } override fun resumeWith(result: Result<Any>) { this.result = result that.execute(inputValues, this) } 3 -> { cont.label = 4 cont.products = (cont.result as Result<List<Product>>).getOrThrow() check(cont.products.isNotEmpty()) storeRepository.findStoresByProductsAsMulti(cont.products) .collect().asList() .subscribe().with { stores -> cont.resumeWith(Result.success(stores)) } } 4 -> { cont.label = 5 cont.stores = (cont.result as Result<List<Store>>).getOrThrow() check(cont.stores.isNotEmpty()) orderRepository.createOrderAsFuture( cont.buyer, cont.products, cont.stores, cont.address ).whenComplete { order, _ -> cont.resumeWith(Result.success(order)) } } 5 -> { cont.order = (cont.result as Result<Order>).getOrThrow() cont.completion.resumeWith(Result.success(cont.order)) } else -> throw IllegalAccessException()
- 49. 02. Coroutine 톺아보기 FSM 기반의 비동기 코드 ; state 5 when (cont.label) { 0 -> { cont.label = 1 userRepository.findUserByIdAsMaybe(userId) .subscribe { user -> cont.resumeWith(Result.success(user)) } } 1 -> { cont.label = 2 cont.buyer = (cont.result as Result<User>).getOrThrow() addressRepository.findAddressByUserAsPublisher(cont.buyer) .subscribe(LastItemSubscriber { address -> cont.resumeWith(Result.success(address)) }) } 2 -> { cont.label = 3 cont.address = (cont.result as Result<Address>).getOrThrow() checkValidRegion(cont.address) productRepository.findAllProductsByIdsAsFlux(productIds) .collectList() .subscribe { products -> cont.resumeWith(Result.success(products)) } } override fun resumeWith(result: Result<Any>) { this.result = result that.execute(inputValues, this) } 3 -> { cont.label = 4 cont.products = (cont.result as Result<List<Product>>).getOrThrow() check(cont.products.isNotEmpty()) storeRepository.findStoresByProductsAsMulti(cont.products) .collect().asList() .subscribe().with { stores -> cont.resumeWith(Result.success(stores)) } } 4 -> { cont.label = 5 cont.stores = (cont.result as Result<List<Store>>).getOrThrow() check(cont.stores.isNotEmpty()) orderRepository.createOrderAsFuture( cont.buyer, cont.products, cont.stores, cont.address ).whenComplete { order, _ -> cont.resumeWith(Result.success(order)) } } 5 -> { cont.order = (cont.result as Result<Order>).getOrThrow() cont.completion.resumeWith(Result.success(cont.order)) } else -> throw IllegalAccessException()
- 50. 02. Coroutine 톺아보기 FSM 기반의 비동기 코드 ; 최종 class SharedDataContinuation( val completion: Continuation<Any>, ) : Continuation<Any> { var label: Int = 0 lateinit var result: Any lateinit var buyer: User lateinit var address: Address lateinit var products: List<Product> lateinit var stores: List<Store> lateinit var order: Order lateinit var resume: () -> Unit override val context: CoroutineContext = completion.context override fun resumeWith(result: Result<Any>) { this.result = result this.resume() } } fun execute(inputValues: InputValues, completion: Continuation<Any>) { val (userId, productIds) = inputValues val that = this val cont = completion as? SharedDataContinuation ?: SharedDataContinuation(completion).apply { resume = fun() { // recursive self that.execute(inputValues, this) } - completion은 외부에서 주입하는 continuation 기반의 객체
- 51. 02. Coroutine 톺아보기 FSM 기반의 비동기 코드 ; 실행 - testContinuation을 생성해서 execute 함수에 주입 @Test fun `should return a createdOrder in async with state machine`() { // given val userId = "user1" val productIds = listOf("product1", "product2", "product3") // when val watch = StopWatch().also { it.start() } val lock = CountDownLatch(1) val testContinuation = object : Continuation<Any> { override val context = EmptyCoroutineContext override fun resumeWith(result: Result<Any>) { watch.stop() lock.countDown() println("Time Elapsed: ${watch.time}ms") println(result.getOrThrow()) } } val inputValues = CreateOrderAsyncStateMachine3UseCase.InputValues(userId, productIds) createOrderUseCase.execute(inputValues, testContinuation) // then lock.await(3000, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS) }
- 52. Coroutine으로
- 53. 02. Coroutine 톺아보기 FSM 기반의 Coroutines ; 시작 when (cont.label) { 0 -> { cont.label = 1 userRepository.findUserByIdAsMaybe(userId) .subscribe { user -> cont.resumeWith(Result.success(user)) } } 1 -> { cont.label = 2 cont.buyer = (cont.result as Result<User>).getOrThrow() addressRepository.findAddressByUserAsPublisher(cont.buyer) .subscribe(LastItemSubscriber { address -> cont.resumeWith(Result.success(address)) }) } 2 -> { cont.label = 3 cont.address = (cont.result as Result<Address>).getOrThrow() checkValidRegion(cont.address) productRepository.findAllProductsByIdsAsFlux(productIds) .collectList() .subscribe { products -> cont.resumeWith(Result.success(products)) } } 3 -> { cont.label = 4 cont.products = (cont.result as Result<List<Product>>).getOrThrow() check(cont.products.isNotEmpty()) storeRepository.findStoresByProductsAsMulti(cont.products) .collect().asList() .subscribe().with { stores -> cont.resumeWith(Result.success(stores)) } } 4 -> { cont.label = 5 cont.stores = (cont.result as Result<List<Store>>).getOrThrow() check(cont.stores.isNotEmpty()) orderRepository.createOrderAsFuture( cont.buyer, cont.products, cont.stores, cont.address ).whenComplete { order, _ -> cont.resumeWith(Result.success(order)) } } 5 -> { cont.order = (cont.result as Result<Order>).getOrThrow() cont.completion.resumeWith(Result.success(cont.order)) } else -> throw IllegalAccessException()
- 54. 02. Coroutine 톺아보기 FSM 기반의 Coroutines ; extension function fun <T: Any> Maybe<T>.awaitSingle(cont: Continuation<Any>) { this.subscribe { user -> cont.resumeWith(Result.success(user)) } } fun <T: Any> Flow.Publisher<T>.awaitLast(cont: Continuation<Any>) { this.subscribe(LastItemSubscriber { address -> cont.resumeWith(Result.success(address)) }) } fun <T: Any> Flux<T>.toList(cont: Continuation<Any>) { this.collectList() .subscribe { products -> cont.resumeWith(Result.success(products)) } } fun <T: Any> Multi<T>.toList(cont: Continuation<Any>) { this.collect() .asList() .subscribeAsCompletionStage() .whenComplete { stores, _ -> cont.resumeWith(Result.success(stores)) } } fun <T: Any> CompletionStage<T>.awaitSingle(cont: - 각각의 비동기 라이브러리에서 사용하는 객체에 대한 extension function 생성 - (Flux.toList, Multi.toList, CompletionStage.awaitSingle 은 실제와 달라요)
- 55. 02. Coroutine 톺아보기 FSM 기반의 Coroutines ; extension function when (cont.label) { 0 -> { cont.label = 1 userRepository.findUserByIdAsMaybe(userId) .subscribe { user -> cont.resumeWith(Result.success(user)) } } 1 -> { cont.label = 2 cont.buyer = (cont.result as Result<User>).getOrThrow() addressRepository.findAddressByUserAsPublisher(cont.buyer) .subscribe(LastItemSubscriber { address -> cont.resumeWith(Result.success(address)) }) } 2 -> { cont.label = 3 cont.address = (cont.result as Result<Address>).getOrThrow() checkValidRegion(cont.address) productRepository.findAllProductsByIdsAsFlux(productIds) .collectList() .subscribe { products -> cont.resumeWith(Result.success(products)) } } 3 -> { cont.label = 4 cont.products = (cont.result as Result<List<Product>>).getOrThrow() check(cont.products.isNotEmpty()) storeRepository.findStoresByProductsAsMulti(cont.products) .collect().asList() .subscribe().with { stores -> cont.resumeWith(Result.success(stores)) } } 4 -> { cont.label = 5 cont.stores = (cont.result as Result<List<Store>>).getOrThrow() check(cont.stores.isNotEmpty()) orderRepository.createOrderAsFuture( cont.buyer, cont.products, cont.stores, cont.address ).whenComplete { order, _ -> cont.resumeWith(Result.success(order)) } } 5 -> { cont.order = (cont.result as Result<Order>).getOrThrow() cont.completion.resumeWith(Result.success(cont.order)) } else -> throw IllegalAccessException() }
- 56. 02. Coroutine 톺아보기 FSM 기반의 Coroutines ; extension function when (cont.label) { 0 -> { cont.label = 1 userRepository.findUserByIdAsMaybe(userId).awaitSingle(cont) } 1 -> { cont.label = 2 cont.buyer = (cont.result as Result<User>).getOrThrow() addressRepository.findAddressByUserAsPublisher(cont.buyer) .awaitLast(cont) } 2 -> { cont.label = 3 cont.address = (cont.result as Result<Address>).getOrThrow() checkValidRegion(cont.address) productRepository.findAllProductsByIdsAsFlux(productIds) .toList(cont) } 3 -> { cont.label = 4 cont.products = (cont.result as Result<List<Product>>).getOrThrow() check(cont.products.isNotEmpty()) storeRepository.findStoresByProductsAsMulti(cont.products) .toList(cont) } 4 -> { cont.label = 5 cont.stores = (cont.result as Result<List<Store>>).getOrThrow() check(cont.stores.isNotEmpty()) orderRepository.createOrderAsFuture( cont.buyer, cont.products, cont.stores, cont.address ).awaitSingle(cont) } 5 -> { cont.order = (cont.result as Result<Order>).getOrThrow() cont.completion.resumeWith(Result.success(cont.order)) } else -> throw IllegalAccessException() }
- 57. 02. Coroutine 톺아보기 FSM 기반의 Coroutines ; when 제거 when (cont.label) { 0 -> { cont.label = 1 userRepository.findUserByIdAsMaybe(userId).awaitSingle(cont) } 1 -> { cont.label = 2 cont.buyer = (cont.result as Result<User>).getOrThrow() addressRepository.findAddressByUserAsPublisher(cont.buyer) .awaitLast(cont) } 2 -> { cont.label = 3 cont.address = (cont.result as Result<Address>).getOrThrow() checkValidRegion(cont.address) productRepository.findAllProductsByIdsAsFlux(productIds) .toList(cont) } 3 -> { cont.label = 4 cont.products = (cont.result as Result<List<Product>>).getOrThrow() check(cont.products.isNotEmpty()) storeRepository.findStoresByProductsAsMulti(cont.products) .toList(cont) } 4 -> { cont.label = 5 cont.stores = (cont.result as Result<List<Store>>).getOrThrow() check(cont.stores.isNotEmpty()) orderRepository.createOrderAsFuture( cont.buyer, cont.products, cont.stores, cont.address ).awaitSingle(cont) } 5 -> { cont.order = (cont.result as Result<Order>).getOrThrow() cont.completion.resumeWith(Result.success(cont.order)) } else -> throw IllegalAccessException() }
- 58. 02. Coroutine 톺아보기 FSM 기반의 Coroutines ; continuation 제거 when (cont.label) { 0 -> { cont.label = 1 val buyer = userRepository.findUserByIdAsMaybe(userId) .awaitSingle() } 1 -> { cont.label = 2 cont.buyer = (cont.result as Result<User>).getOrThrow() val address = addressRepository.findAddressByUserAsPublisher(buyer) .awaitLast() } 2 -> { cont.label = 3 cont.address = (cont.result as Result<Address>).getOrThrow() checkValidRegion(address) val products = productRepository.findAllProductsByIdsAsFlux(productIds) .toList() } 3 -> { cont.label = 4 cont.products = (cont.result as Result<List<Product>>).getOrThrow() check(products.isNotEmpty()) val stores = storeRepository.findStoresByProductsAsMulti(products) .toList() } 4 -> { cont.label = 5 cont.stores = (cont.result as Result<List<Store>>).getOrThrow() check(stores.isNotEmpty()) val order = orderRepository.createOrderAsFuture( buyer, products, stores, address ).awaitSingle() } 5 -> { cont.order = (cont.result as Result<Order>).getOrThrow() cont.completion.resumeWith(Result.success(cont.order)) return order } else -> throw IllegalAccessException() }
- 59. 02. Coroutine 톺아보기 Coroutines ; 최종 // 0 -> val buyer = userRepository.findUserByIdAsMaybe(userId).awaitSingle() // 1 -> val address = addressRepository.findAddressByUserAsPublisher(buyer) .awaitLast() checkValidRegion(address) // 2 -> val products = productRepository.findAllProductsByIdsAsFlux(productIds) .toList() check(products.isNotEmpty()) // 3 -> val stores = storeRepository.findStoresByProductsAsMulti(products) .toList() check(stores.isNotEmpty()) // 4 -> val order = orderRepository.createOrderAsFuture( buyer, products, stores, address ).awaitSingle() return order
- 60. 02. Coroutine 톺아보기 Coroutines ; 실행 @Test fun `should return a createdOrder in coroutine`() = runBlocking { // given val userId = "user1" val productIds = listOf("product1", "product2", "product3") // when val watch = StopWatch().also { it.start() } val inputValues = CreateOrderCoroutineUseCase.InputValues(userId, productIds) val createdOrder = createOrderUseCase.execute(inputValues) watch.stop() println("Time Elapsed: ${watch.time}ms") // then println(createdOrder) }
- 61. 다음회 예고 03
- 62. 03. 다음회 예고 Async를 사용한 동시성 처리 suspend fun execute(inputValues: InputValues): Order { val (userId, productIds) = inputValues // 1. 구매자 조회 val buyer = userRepository.findUserByIdAsMaybe(userId).awaitSingle() // 2. 주소 조회 및 유효성 체크 val addressDeferred = CoroutineScope(Dispatchers.IO).async { addressRepository.findAddressByUserAsPublisher(buyer) .awaitLast() } // 3. 상품들 조회 val products = productRepository.findAllProductsByIdsAsFlux(productIds).asFlow().toList() check(products.isNotEmpty()) // 4. 스토어 조회 val storesDeferred = CoroutineScope(Dispatchers.IO).async { storeRepository.findStoresByProductsAsMulti(products).asFlow().toList() } val address = addressDeferred.await() val stores = storesDeferred.await() checkValidRegion(address) check(stores.isNotEmpty()) // 5. 주문 생성 - CoroutineDispatcher - 여러 Thread를 오고가며 로직을 처리 가능
- 63. 03. 다음회 예고 try/catch를 이용한 에러 핸들링 suspend fun execute(inputValues: InputValues): Order { val (userId, productIds) = inputValues // 1. 구매자 조회 val buyer = try { userRepository.findUserByIdAsMaybe(userId).awaitSingle() } catch (e: Exception) { throw NoSuchElementException("no such user") } // 2. 주소 조회 및 유효성 체크 val address = addressRepository.findAddressByUserAsPublisher(buyer) .awaitLast() checkValidRegion(address) // 3. 상품들 조회 val products = productRepository.findAllProductsByIdsAsFlux(productIds).asFlow().toList() check(products.isNotEmpty()) // 4. 스토어 조회 val stores = storeRepository.findStoresByProductsAsMulti(products).asFlow().toList() check(stores.isNotEmpty()) // 5. 주문 생성 val order = orderRepository.createOrderAsFuture(buyer, products, stores, address).await() return order } - try/catch를 통해서 일관성 있게 에러 핸들링 가능
- 64. 03. 다음회 예고 그 외에 - Structured concurrency - Channel - Flow
- 65. QnA







































![02. Coroutine 톺아보기
FSM 기반의 비동기 코드 class SharedDataContinuation(
val completion: Continuation<Any>,
) : Continuation<Any> {
var label: Int = 0
lateinit var result: Any
lateinit var buyer: User
lateinit var address: Address
lateinit var products: List<Product>
lateinit var stores: List<Store>
lateinit var order: Order
lateinit var resume: () -> Unit
override val context: CoroutineContext = completion.context
override fun resumeWith(result: Result<Any>) {
this.result = result
this.resume()
}
}
fun execute(inputValues: InputValues, completion: Continuation<Any>) {
val (userId, productIds) = inputValues
val that = this
val cont = completion as? SharedDataContinuation
?: SharedDataContinuation(completion).apply {
resume = fun() {
// recursive self
that.execute(inputValues, this)
}
public interface Continuation<in T> {
/**
* The context of the coroutine that corresponds to this
continuation.
*/
public val context: CoroutineContext
/**
* Resumes the execution of the corresponding coroutine
passing a successful or failed [result] as the
* return value of the last suspension point.
*/
public fun resumeWith(result: Result<T>)
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/kotlincoroutinesv2-211220120736/85/Kotlin-coroutines-41-320.jpg)























