Learn more about the concepts Functions of Python
- 2. In Python, a function is a group of related statements that performs a specific task. Functions help break our program into smaller and modular chunks. They take inputs, do some specific computation and produces output. These are logical functional blocks of code that can be reused independently from the main program. Python provides built-in functions like print(), etc. but we can also create your own functions. These functions are called user-defined functions.
- 3. Benefits of Modularizing a Program with Functions • The benefits of using functions include: • Simpler code • Code reuse • write the code once and call it multiple times • Better testing and debugging • Can test and debug each function individually • Faster development • Easier facilitation of teamwork • Different team members can write different functions
- 4. Void Functions and Value-Returning Functions • A void function: • Simply executes the statements it contains and then terminates. • A value-returning function: • Executes the statements it contains, and then it returns a value back to the statement that called it. • The input, int, and float functions are examples of value- returning functions.
- 5. Defining and Calling a Function • Functions are given names • Function naming rules: • Cannot use key words as a function name • Cannot contain spaces • First character must be a letter or underscore • All other characters must be a letter, number or underscore • Uppercase and lowercase characters are distinct
- 6. Here are simple rules to define a function in Python: • Function blocks begin with the keyword def followed by the function name and parentheses ( ( ) ). def functionname(): statements def my_function(): print("Hello World!")
- 7. Any input parameters or arguments should be placed within these parentheses. You can also define parameters inside these parentheses. These are optional. def function_name(parameter): statements return def greet(name): print("Hello, " + name + ". Good morning!") >>> greet(‘Naman')
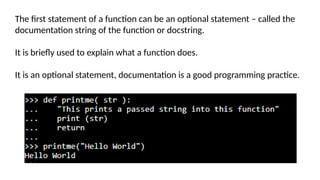
- 8. The first statement of a function can be an optional statement – called the documentation string of the function or docstring. It is briefly used to explain what a function does. It is an optional statement, documentation is a good programming practice.
- 9. The code block within every function starts with a colon (:) and is indented. The statement return [expression] exits a function, optionally passing back an expression to the caller. A return statement with no arguments is the same as return None.
- 10. Required arguments Required arguments are the arguments passed to a function in correct positional order. Here, the number of arguments in the function call should match exactly with the function definition. To call the function hello(), you definitely need to pass one argument, otherwise it gives a syntax error Def hello(str): print (str)
- 11. A default argument is an argument that assumes a default value if a value is not provided in the function call for that argument. We can provide a default value to an argument by using the assignment operator (=). Default Arguments:
- 12. Keyword arguments Keyword arguments are related to the function calls. When you use keyword arguments in a function call, the caller identifies the arguments by the parameter name. This allows us to place them out of order because the Python interpreter is able to use the keywords provided to match the values with parameters.
- 13. Arbitrary Arguments Sometimes, we do not know in advance the number of arguments that will be passed into a function. Python allows us to handle this kind of situation through function calls with an arbitrary number of arguments. In the function definition, we use an asterisk (*) before the parameter name to denote this kind of argument.
- 15. Pass by Reference or pass by value? One important thing to note is, in Python every variable name is a reference. When we pass a variable to a function, a new reference to the object is created. It means if you change what a parameter refers to within a function, the change also reflects back in the calling function.
- 16. Scope of a variable Scope of a variable is the portion of a program where the variable is recognized. Parameters and variables defined inside a function are not visible from outside the function. Hence, they have a local scope. Global variables are the one that are defined and declared outside a function and we need to use them inside a function. If there is no local num, the value from the global num will be used.
- 17. If a variable with the same name is defined inside the scope of function as well then it will print the value given inside the function only and not the global value.
- 19. Split Function
- 20. Calculate the length of the word using len() function. If the length is even, then print the word.







![The code block within every function starts with a colon (:) and is indented.
The statement return [expression] exits a function, optionally passing back
an expression to the caller.
A return statement with no arguments is the same as return None.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pythonfunctions-241129040412-b181dbfc/85/Learn-more-about-the-concepts-Functions-of-Python-9-320.jpg)










