Lecture 02 - Development Methodologies.pptx
- 1. Software Engineering Development Methodologies Lecture 02 Asst. Prof. Sayed Elham Sadat sayed.elham@kuk.ac.in
- 2. Software Process | Development Methodologies 2 ◎ A software development methodologies also known as ○ System development methodology ○ Software development life cycle ○ Software development process ○ Software process ◎ When you work to build a product or system, it’s important to go through a series of predictable steps a road map that helps you create a timely, high-quality result. ◎ A software Process is a framework of the activities, actions and tasks that are required to build high quality software. ◎ In software engineering, a software development methodology is a division of software development work into distinct phases (or stages) containing activities with the intent of better planning and management
- 3. Software Development Methodologies cont. 3 Software development methodologies are a key concept of SE To overcome s/w crisis SE To develop a s/w product The development team must identify suitable methodology for particular project.
- 4. Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC) 4 ◎ SDLC stands for Software Development Life Cycle. SDLC is a process that consists of a series of planned activities to develop or alter the Software Products. ◎ SDLC process is used by the software industry to design, develop and test high quality software. ◎ It aims to produce the quality software that meets or exceeds customer expectations, reaches completion within time and budget. ◎ A “life-cycle” or a software process is the organizational framework for a project.
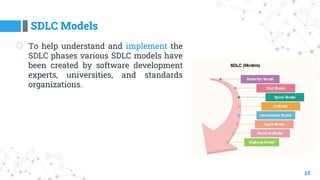
- 5. Software Development Life Cycle Models 5 ◎ There are various software development life cycle models defined and designed which are followed during the software development process. ◎ Following are the most important and popular SDLC models followed in the industry; ○ Waterfall Model ○ Incremental Model ○ Spiral Model ○ V-Model ○ Prototyping Model ◎ Other related methodologies are Agile Model, RAD Model, Big Bang Model, Iterative Model and Prototyping Models.
- 6. SDLC Phases 6 1. Planning and Requirements Analysis 2. Defining Requirements 3. Designing the Software 4. Building or Developing the Software 5. Testing the Software 6. Deployment and Maintenance
- 7. SDLC Phases Cont. 7 ◎ 1. Planning & Requirement Analysis ◎ Requirement analysis is the most important and fundamental stage in SDLC. ◎ It is performed by the senior members of the team with inputs from all the stakeholders and domain experts or SMEs in the industry. ◎ Planning for the quality assurance requirements and identification of the risks associated with the project is also done at this stage.
- 8. SDLC Phases Cont. 8 ◎ Requirement Analysis ◎ Business Requirements ◎ Stakeholder Requirements ◎ Solution Requirements ○ Functional Requirements ○ Non-functional Requirements ◎ Transition Requirements
- 9. SDLC Phases Cont. 9 ◎ 2. Defining Requirements ◎ Once the requirement analysis is done the next step is to clearly define and document the software requirements and get them approved from the project stakeholders. ◎ This is done through ‘SRS’ — Software Requirement Specification document which consists of all the product requirements to be designed and developed during the project life cycle.
- 10. SDLC Phases Cont. 10 ◎ Feasibility Study ◎ Economic: Can we complete the project within the budget or not? ◎ Legal: Can we handle this project as cyber law and other regulatory framework/compliances. ◎ Operation feasibility: Can we create operations which is expected by the client? ◎ Technical: Need to check whether the current computer system can support the software. ◎ Schedule: Decide that the project can be completed with in the given schedule or not.
- 11. SDLC Phases Cont. 11 ◎ 3. Designing the Software ◎ Based on the requirements specified in SRS, usually more than one design approach for the product architecture is proposed. ◎ Modules ◎ Use Case Diagram ◎ ERD
- 12. SDLC Phases Cont. 12 ◎ 4. Developing the Software ◎ In this stage of SDLC the actual development starts and the product is built. ◎ The programming code is generated as per DDS during this stage. ◎ Developers have to follow the coding guidelines defined by their organization and programming tools like compilers, interpreters, debuggers etc. are used to generate and implement the code.
- 13. SDLC Phases Cont. 13 ◎ 5. Testing the Software ◎ This stage is usually a subset of all the stages as in the modern SDLC models, the testing activities are mostly involved in all the stages of SDLC. ◎ However this stage refers to the testing only that stage of the software where defects are reported, tracked, fixed and retested, until the software reaches the quality standards defined in the SRS.
- 14. SDLC Phases Cont. 14 ◎ 5. Deployment and Maintenance ◎ Once the software is tested and no bugs or errors are reported then it is deployed. ◎ Then based on the feedback, the software may be released as it is or with suggested enhancements in the target segment. ◎ After the software is deployed then its maintenance starts. ◎ Maintenance ○ Bug fixing - bugs are reported because of some scenarios which are not tested at all ○ Upgrade - Upgrading the application to the newer versions of the Software ○ Enhancement - Adding some new features into the existing software
- 15. SDLC Models 15 ◎ To help understand and implement the SDLC phases various SDLC models have been created by software development experts, universities, and standards organizations.
- 16. Reasons for Using SDLC Models 16 ◎ Provides the base for project planning, estimating & scheduling. ◎ Provides framework for standard set of terminologies, activities & deliverables. ◎ Provides mechanism for project tracking & control. ◎ Increases visibility of project progress to all stakeholders.
- 17. Advantages of Choosing an appropriate SDLC Models 17 ◎ Increased development speed ◎ Increased product quality ◎ Improved tracking & control ◎ Improved client relations ◎ Decreased project risk ◎ Decreased project management overhead
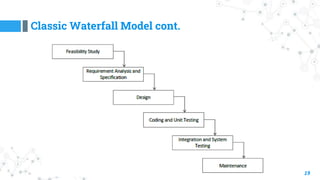
- 18. Classic Waterfall Model 18 ◎ Oldest and most well-known SDLC model. ◎ Follows a sequential step-by-step process from requirements analysis to maintenance. ◎ The waterfall Model shows the software development process in a linear sequential flow. This means that any phase in the development process begins only if the previous phase is complete. - no turning back. ◎ Invented in 1970. The waterfall model, sometimes called the classic life cycle ◎ Systems that have well-defined and understood requirements are a good fit for the Waterfall Model.
- 19. Classic Waterfall Model cont. 19
- 20. Classic Waterfall Model cont. 20 ◎ Advantages: ◎ Easy to understand, easy to use ◎ Provides structure to inexperienced staff ◎ Milestones are well understood ◎ Sets requirements stability ◎ Good for management control (plan, staff, track) ◎ Process and results are well documented. ◎ Works well when quality is more important than cost or schedule
- 21. Classic Waterfall Model cont. 21 ◎ Disadvantages: ◎ No feedback ◎ No parallelism ◎ High Risk ◎ Poor model for long and ongoing projects. ◎ 60% efforts in Maintenance
- 22. Classic Waterfall Model cont. 22 ◎ When to use : ◎ Requirements are very well known ◎ Product definition is stable ◎ Technology is understood ◎ There are no ambiguous requirements ◎ New version of an existing product
- 23. Iterative Waterfall Model 23 ◎ Iterative waterfall allows you to return to the previous phase and adjust requirements and, if necessary, some modifications. ◎ In the iterative waterfall model, the next phase can only begin when the previous phase is completed as the waterfall model.
- 24. Iterative Waterfall Model cont. 24
- 25. Iterative Waterfall Model cont. 25 ◎ Advantages: ◎ Feedback Path: Iterative waterfall allows the mechanism of error connection because there is a feedback path from one phase to its preceding phase which it lacks in the Waterfall Model. ◎ Simple: Iterative waterfall model is simple to understand and use. It is the most widely used software development model evolved so far. ◎ Parallel development: In the iterative waterfall model, parallel development can be done.
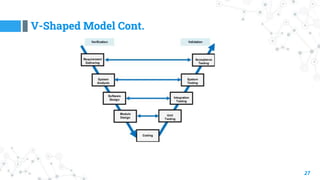
- 26. V-Shaped Model 26 ◎ A variation in the representation of the waterfall model is called the V- model. ◎ Also known as Verification and Validation Model. ◎ Testing is associated with every phase of lifecycle. ◎ Verification Phase (Requirement analysis, System Design, Architecture Design, Module Design). ◎ Validation phase (Unit testing, Integration, System, Acceptance Testing).
- 28. V-Shaped Model Cont. 28 ◎ Advantages: ◎ Time Saving ◎ Good understanding of project in the beginning ◎ Every component must be testable ◎ Progress can be tracked easily
- 29. V-Shaped Model Cont. 29 ◎ Disadvantages: ◎ No feedback so less scope of changes ◎ Risk analysis is not done. ◎ Not good for big projects
- 30. Incremental Model 30 ◎ Module by Module development ◎ In incremental model the whole requirement is divided into various builds. Multiple development cycles take place here, making the life cycle a “multi-waterfall” cycle. ◎ Cycles are divided up into smaller, more easily managed modules. ◎ Each subsequent release of the system adds function to the previous release, until all designed functionality has been implemented. ◎ Maximum customer intraction
- 32. Incremental Model Cont. 32 ◎ Advantages: ◎ Generates working software quickly and early during the software life cycle. ◎ This model is more flexible – less costly to change scope and requirements. ◎ It is easier to test and debug during a smaller iteration. ◎ In this model customer can respond to each built. ◎ Lowers initial delivery cost. ◎ Easier to manage risk because risky pieces are identified and handled during it’d iteration.
- 33. Incremental Model Cont. 33 ◎ Disadvantages: ◎ Needs good planning and design. ◎ Needs a clear and complete definition of the whole system before it can be broken down and built incrementally. ◎ Total cost is higher than waterfall.
- 34. Incremental Model Cont. 34 ◎ When to use the Incremental model: ◎ This model can be used when the requirements of the complete system are clearly defined and understood. ◎ Major requirements must be defined; however, some details can evolve with time. ◎ There is a need to get a product to the market early. ◎ A new technology is being used ◎ Resources with needed skill set are not available ◎ There are some high risk features and goals.
- 35. Prototype Model 35 ◎ The Software Prototyping refers to building software application prototypes which displays the functionality of the product under development, but may not actually hold the exact logic of the original software. ◎ Customer is not clear with idea. ◎ Throwing away model ◎ Developers build a prototype during the requirements phase ◎ Prototype is evaluated by end users ◎ Users give corrective feedback ◎ Developers further refine the prototype ◎ When the user is satisfied, the prototype code is brought up to the standards needed for a final product. ◎ Good for technical and requirement risks
- 37. Prototype Model cont. 37 ◎ Advantages: ◎ Customers can “see” the system requirements as they are being gathered ◎ Developers learn from customers ◎ A more accurate end product ◎ Allows for flexible design and development ◎ Unexpected requirements accommodated
- 38. Prototype Model cont. 38 ◎ Disadvantages: ◎ Time-consuming ◎ Increase in cost of development ◎ Customer can confuse between the actual product and prototype. ◎ Change in the requirement usually expand the scope of the product beyond its original plan and thus increase the complexity.
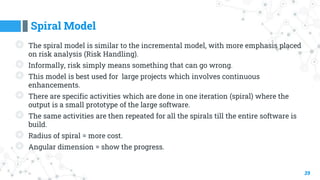
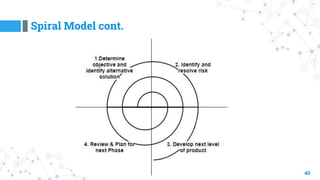
- 39. Spiral Model 39 ◎ The spiral model is similar to the incremental model, with more emphasis placed on risk analysis (Risk Handling). ◎ Informally, risk simply means something that can go wrong. ◎ This model is best used for large projects which involves continuous enhancements. ◎ There are specific activities which are done in one iteration (spiral) where the output is a small prototype of the large software. ◎ The same activities are then repeated for all the spirals till the entire software is build. ◎ Radius of spiral = more cost. ◎ Angular dimension = show the progress.
- 41. Spiral Model cont. 41 ◎ Advantages: ◎ Risk Handling ◎ Large Projects ◎ Flexible – new changes can occur. ◎ Customer satisfaction
- 42. Spiral Model cont. 42 ◎ Disadvantages: ◎ Complex ◎ Expensive ◎ Too much risk analysis ◎ Budget and time can not be define in start ◎ Time ◎ Knowledgeable and experienced staff is required.
- 43. 43 Thank You!
Editor's Notes
- #13: Details design specification (DDS).
- #27: Verification and validation is done in testing phase. Verification step by step verifying Whether the product is created well or not. Validation – when the whole system is develop we check that the system is good or not. System Design – means full system design like whole house design Architecture design – means design of system modules like floors in house Module Design – Means sub modules like rooms in first floor.