Lecture 2 Software Development Process and SDCL models.pptx
- 1. LECTURE 2 SOFTWARE DEVELOPMENT LIFE CYCLE(SDLC) COURSE INSTRUCTOR: Akram Ali Omar Email: akram.ali.omar@gmail.com Mobile: +255778695626 The State University Of Zanzibar 1 DINF 0122 & DCS 0122 :SYSTEM ANALYSIS AND DESIGN
- 2. 2 What is the System Development Cycle? • Structured step-by-step approach for developing information systems • It describe the process of planning, building, using, and updating an information system. • Provides overall framework for managing systems development process
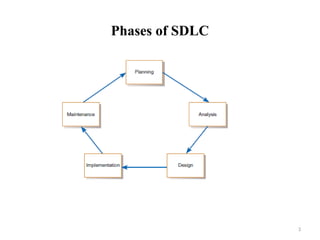
- 4. 4 Phases of SDLC • Project planning – initiate, ensure feasibility, plan schedule, obtain approval for project • Analysis – understand business needs and processing requirements • Design – define solution system based on requirements and analysis decisions • Implementation – construct, test, train users, and install new system • Support – keep system running and improve
- 5. 5 SDLC Models • The followings are most common SDLC Models: – Waterfall Model – Iterative Model – Spiral Model – V – model – Prototyping Models – Agile Model – Big Bang Model – Rapid Application Development
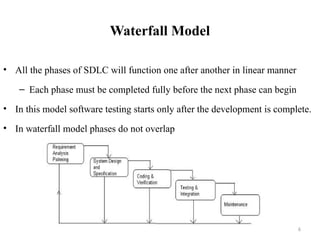
- 6. 6 Waterfall Model • All the phases of SDLC will function one after another in linear manner – Each phase must be completed fully before the next phase can begin • In this model software testing starts only after the development is complete. • In waterfall model phases do not overlap
- 7. 7 Waterfall Model • Requirement Gathering and analysis All possible requirements of the system to be developed are captured in this phase and documented in a requirement specification document • System Design The requirement specifications from first phase are studied in this phase and the system design is prepared. This system design helps in specifying hardware and system requirements and helps in defining the overall system architecture
- 8. 8 Waterfall Model • Implementation With inputs from the system design, the system is first developed in small programs called units, which are integrated in the next phase. Each unit is developed and tested for its functionality, which is referred to as Unit Testing • Integration and Testing All the units developed in the implementation phase are integrated into a system after testing of each unit. Finally after integration the entire system is tested for any faults and failures.
- 9. 9 Waterfall Model • Maintenance There are some issues which come up in the client environment. To fix those issues, patches are released. Also to enhance the product some better versions are released
- 10. 10 When to use Waterfall Model? • Some situations where the use of Waterfall model is most appropriate are Requirements are very well documented, clear and fixed. Product definition is stable. Technology is understood and is not dynamic. There are no ambiguous requirements. The project is short.
- 11. 11 Advantages of waterfall model • Easy to explain to the user • Stages and activities are well defined • Helps to plan and schedule the project • Verification at each stage ensures early detection of errors / misunderstanding
- 12. 12 Disadvantages of waterfall model • No working software is produced until late during the life cycle. • High amounts of risk and uncertainty. • Not a good model for complex and object-oriented projects. • Poor model for long and ongoing projects. • Not suitable for the projects where requirements are at a moderate to high risk of changing. So, risk and uncertainty is high with this process model. • It is difficult to measure progress within stages. • Cannot accommodate changing requirements. • Customers can not use anything until the entire system is complete
- 13. 13 Project Output in a Waterfall Model • Requirement document • Project plan • System design document • Detailed design document • Test plan and test report • Final code • Software manuals (user manual, installation manual etc.) • Review reports
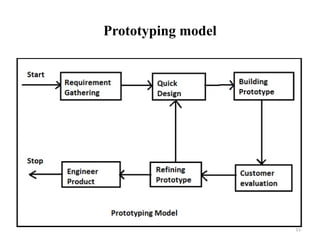
- 14. 14 Prototyping model • Prototyping model is one of the risk reduction models • It involves building a small version of the intended system called prototype • Instead of freezing the requirements before a design or coding can proceed, small version (called prototype) of the intended system is developed based on the currently known requirements • The client can get an “actual feel” of the system, since the interactions with prototype can enable the client to better understand the requirements of the desired system
- 16. 16 Advantages of Prototype model • Users are actively involved in the development • The users get a better understanding of the system being developed. • Errors can be detected much earlier. • Quicker user feedback is available leading to better solutions. • Missing functionality can be identified easily • Confusing or difficult functions can be identified • Requirements validation, Quick implementation of incomplete but functional application.
- 17. 17 Disadvantages of Prototype model • Leads to implementing and then repairing way of building systems. • Practically, this methodology may increase the complexity of the system as scope of the system may expand beyond original plans. • Incomplete application may cause application not to be used as the full system was designed • Incomplete or inadequate problem analysis.
- 18. 18 When to use Prototype model • When the desired system needs to have a lot of interaction with the end users. • Typically, online systems, web interfaces have a very high amount of interaction with end users, are best suited for Prototype model
- 19. Iterative & Incremental model • The whole requirement is divided into various builds • Multiple development (“multi-waterfall”) cycles take place here • Cycles are divided up into smaller, more easily managed modules • Each module passes through the requirements, design, implementation and testing phases • A working version of software is produced during the first module • Each subsequent release of the module adds function to the previous release. • The process continues till the complete system is achieved. • For example 19
- 20. Iterative & Incremental model 20
- 21. Advantages of Iterative & Incremental model • Generates working software quickly and early during the software life cycle. • This model is more flexible – less costly to change scope and requirements. • It is easier to test and debug during a smaller iteration. • In this model customer can respond to each built. • Lowers initial delivery cost. • Easier to manage risk because risky pieces are identified and handled during it’s iteration.
- 22. Disadvantages of Iterative & Incremental model • Needs good planning and design. • Needs a clear and complete definition of the whole system before it can be broken down and built incrementally. • Total cost is higher than waterfall.
- 23. When to use the Iterative & Incremental model • This model can be used when the requirements of the complete system are clearly defined and understood. • Major requirements must be defined; however, some details can evolve with time. • There is a need to get a product to the market early. • A new technology is being used • Resources with needed skill set are not available • There are some high risk features and goals
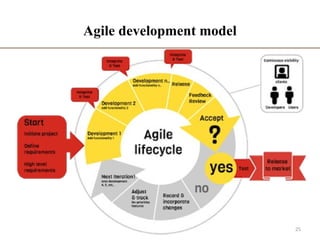
- 24. Agile development model • Is also a type of Incremental model • Breaks tasks into small increments with minimal planning • Iterations are short time frames that typically last from one to four weeks • Each iteration involves planning, requirements analysis, design, coding, unit testing, and acceptance testing • At the end of the iteration a working product is demonstrated to stakeholders 24
- 26. Advantages of Agile model • Customer satisfaction by rapid, continuous delivery of useful software. • People and interactions are emphasized rather than process and tools. • Customers, developers and testers constantly interact with each other. • Working software is delivered frequently (weeks rather than months). • Face-to-face conversation is the best form of communication. • Close, daily cooperation between business people and developers. • Regular adaptation to changing circumstances. • Even late changes in requirements are welcomed 26
- 27. Disadvantages of Agile model • In case of some software deliverables, especially the large ones, it is difficult to assess the effort required at the beginning of the software development life cycle. • There is lack of emphasis on necessary designing and documentation. • The project can easily get taken off track if the customer representative is not clear what final outcome that they want. • Only senior programmers are capable of taking the kind of decisions required during the development process. Hence it has no place for newbie programmers, unless combined with experienced resources. 27
- 28. Choosing the right Software development life cycle model • Selecting the right SDLC is a process in itself that organization can implement internally or consult for • Steps to get the right selection. STEP 1: Learn the about SDLC Models - already covered STEP 2: Assess the needs of Stakeholders STEP 3: Define the criteria STEP 4: Decide 28
- 29. STEP 2: Assess the needs of Stakeholders • We must study the business domain, stakeholders concerns and requirements, business priorities, our technical capability and ability, and technology constraints to be able to choose the right SDLC against their selection criteria. 29
- 30. STEP 3: Define the criteria • Some of the selection criteria or arguments that you may use to select an SDLC are: Is the SDLC suitable for the size of our team and their skills? Is the SDLC suitable for the selected technology we use for implementing the solution? Is the SDLC suitable for client and stakeholders concerns and priorities? Is the SDLC suitable for the geographical situation (distributed team)? Is the SDLC suitable for the size and complexity of our software? Is the SDLC suitable for the type of projects we do? Is the SDLC suitable for our software engineering capability? 30
- 31. Some Recommended criteria 31 Factors Waterfall V-Shaped Prototyping Spiral Iterative & Incremental Agile Unclear User Requirement Poor Poor Good Excellent Good Excellent Unfamiliar Technology Poor Poor Excellent Excellent Good Poor Complex System Good Good Excellent Excellent Good Poor Reliable system Good Good Poor Excellent Good Good Short Time Schedule Poor Poor Good Poor Excellent Excellent Strong Project Management Excellent Excellent Excellent Excellent Excellent Excellent Cost limitation Poor Poor Poor Poor Excellent Excellent Visibility of Stakeholders Good Good Excellent Excellent Good Excellent Skills limitation Good Good Poor Poor Good Poor Documentation Excellent Excellent Good Good Excellent Poor Component reusability Excellent Excellent Poor Poor Excellent Poor
- 32. Software Development Approaches to SDLC • Two common approaches in software development 1. Traditional Approach(structured approach) 2. object-oriented (OO) approach 32
- 33. Traditional Approach(structured approach) • It adopts a formal step-by-step approach to the SDLC phases and activities • The activities of one phase must be completed before moving to the next phase • At the completion of each activity or phase, a document is produced that must be approved by the stakeholders before moving to the next activity or phase. • This is necessary as teams of developers with varying skills and responsibilities 33
- 34. Traditional Approach(structured approach) • The structured approach looks at a system from a top-down view • The center of the structured approach is the process model, which depicts the business processes of a system, and the primary model that presents the processes is the data-flow diagram (DFD) 34
- 35. Structured approach to SDLC (Waterfall Model) • The activities of the software development process represented in the waterfall model. • There are several other models to represent this process. 35
- 36. The Object-Oriented Approach • It is a new way of thinking about problems using models based on real world concepts • The object-oriented methodology views a system as a bottom-up approach to systems development. • The basic construct is object which combines both data structure and behavior in a single entity 36
- 37. Object-Oriented Analysis and Design • Analysis model is built to abstract essential aspects of application domain which contains objects found in application, their properties and behavior. • Then design model is made to describe and optimize the implementation. • Finally the design model is implemented in a programming language, database or hardware. • Graphical notation is used for expressing object-oriented models. 37
- 38. Structured vs. OO Methodology Structured Methodology Object Oriented (Unified Process) Use of development activities (Planning, Analysis..) Each activity covers a whole phase All activities run in each phase, several times (iterations) Names of development phases Planning, Analysis, Design, Implementation, Installation/Testing Inception, Elaboration, Construction, Transition Appropriate to use When system goals certain, static IT When system goals less certain, dynamic IT Modeling technique Data Flow Diagrams, Entity-Relationship Diagrams Diagrams defined by Unified Modeling Language (Use Cases, Class Diagrams…) Relation to reality Predictive Adaptive 38
- 39. 39 END!