Lecture 3 sql {basics ddl commands}
- 1. LECTURE -3 S T R U C T U R E D Q U E R Y L A N G U A G E D A T A D E F I N I T I O N L A N G U A G E ( D D L ) D e l i v e r e d B y : M r . S h u b h a m S h u k l a
- 2. DATA DEFINITION LANGUAGE (DDL): Three basic commands: • CREATE • DROP • ALTER
- 3. CREATE • CREATE TABLE Statement Syntax CREATE TABLE table_name ( column1 datatype [ NULL | NOT NULL ], column2 datatype [ NULL | NOT NULL ], ... column_n datatype [ NULL | NOT NULL ] );
- 4. Example: CREATE TABLE customers ( customer_id number(10) NOT NULL, customer_name varchar2(50) NOT NULL, city varchar2(50), PRIMARY KEY (customer_id) );
- 5. CREATE TABLE AS Statement: Create Table - By Copying all columns from another table Syntax CREATE TABLE new_table AS (SELECT * FROM old_table); Create Table - By Copying selected columns from another table Syntax CREATE TABLE new_table AS (SELECT column_1, column2, ... column_n FROM old_table);
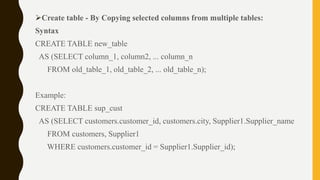
- 6. Create table - By Copying selected columns from multiple tables: Syntax CREATE TABLE new_table AS (SELECT column_1, column2, ... column_n FROM old_table_1, old_table_2, ... old_table_n); Example: CREATE TABLE sup_cust AS (SELECT customers.customer_id, customers.city, Supplier1.Supplier_name FROM customers, Supplier1 WHERE customers.customer_id = Supplier1.Supplier_id);
- 7. ALTER • ALTER TABLE Statement Add Single column in table Syntax ALTER TABLE table_name ADD column_name column-definition; Example: ALTER TABLE customers ADD customer_name varchar2(45);
- 8. Add multiple columns in table Syntax ALTER TABLE table_name ADD (column_1 column-definition, column_2 column-definition, ... column_n column_definition); For example: ALTER TABLE customers ADD (customer_name varchar2(45), city varchar2(40));
- 9. Modify column in table Syntax ALTER TABLE table_name MODIFY column_name column_type; For example: ALTER TABLE customers MODIFY customer_name varchar2(100) not null;
- 10. Modify Multiple columns in table Syntax ALTER TABLE table_name MODIFY (column_1 column_type, column_2 column_type, ... column_n column_type); For example: ALTER TABLE customers MODIFY (customer_name varchar2(100) not null, city varchar2(75));
- 11. Drop column in table Syntax ALTER TABLE table_name DROP COLUMN column_name; For example: ALTER TABLE customers DROP COLUMN customer_name;
- 12. Rename column in table Syntax ALTER TABLE table_name RENAME COLUMN old_name to new_name; For example: ALTER TABLE customers RENAME COLUMN customer_name to cname;
- 13. Rename table Syntax ALTER TABLE table_name RENAME TO new_table_name; For example: ALTER TABLE customers RENAME TO contacts;
- 14. DROP DROP TABLE Statement Syntax DROP TABLE [schema_name].table_name [ CASCADE CONSTRAINTS ] [ PURGE ]; CASCADE CONSTRAINTS: Optional. If specified, all referential integrity constraints will be dropped as well. PURGE: Optional. If specified, the table and its dependent objects will be purged from the recycle bin and you will not be able to recover the table. If not specified, the table and its dependent objects are placed in the recycle bin and can be recovered later, if needed. For example: DROP TABLE customers PURGE;
- 15. VIEW • It is a virtual table that does not physically exist. Rather, it is created by a query joining one or more tables. Create VIEW Syntax CREATE VIEW view_name AS SELECT columns FROM tables [WHERE conditions];
- 16. VIEW Example: CREATE VIEW sup_orders AS SELECT suppliers.supplier_id, orders.quantity, orders.price FROM suppliers INNER JOIN orders ON suppliers.supplier_id = orders.supplier_id WHERE suppliers.supplier_name = 'Microsoft';
- 17. Update VIEW Syntax CREATE OR REPLACE VIEW view_name AS SELECT columns FROM table WHERE conditions;
- 18. Example CREATE or REPLACE VIEW sup_orders AS SELECT suppliers.supplier_id, orders.quantity, orders.price FROM suppliers INNER JOIN orders ON suppliers.supplier_id = orders.supplier_id WHERE suppliers.supplier_name = 'Apple';
- 19. Drop VIEW Syntax DROP VIEW view_name; Example DROP VIEW sup_orders;
- 20. THANK YOU



![CREATE
• CREATE TABLE Statement
Syntax
CREATE TABLE table_name
(
column1 datatype [ NULL | NOT NULL ],
column2 datatype [ NULL | NOT NULL ],
...
column_n datatype [ NULL | NOT NULL ]
);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture3sqlbasics-ddlcommands-171108150457/85/Lecture-3-sql-basics-ddl-commands-3-320.jpg)









![DROP
DROP TABLE Statement
Syntax
DROP TABLE [schema_name].table_name
[ CASCADE CONSTRAINTS ]
[ PURGE ];
CASCADE CONSTRAINTS: Optional. If specified, all referential integrity constraints will
be dropped as well.
PURGE: Optional. If specified, the table and its dependent objects will be purged from the
recycle bin and you will not be able to recover the table. If not specified, the table and its
dependent objects are placed in the recycle bin and can be recovered later, if needed.
For example:
DROP TABLE customers PURGE;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture3sqlbasics-ddlcommands-171108150457/85/Lecture-3-sql-basics-ddl-commands-14-320.jpg)
![VIEW
• It is a virtual table that does not physically exist. Rather, it is created by a
query joining one or more tables.
Create VIEW
Syntax
CREATE VIEW view_name AS
SELECT columns
FROM tables
[WHERE conditions];](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture3sqlbasics-ddlcommands-171108150457/85/Lecture-3-sql-basics-ddl-commands-15-320.jpg)




