Lecture 4b - Computer Elements_ Processing unit & memory.pdf
- 1. Computer Processing unit By Fidea F. Chambo
- 2. The System Unit A computer system unit, also known as a computer tower, is the main box-like structure of a computer that contains the essential components for the computer to work Many people erroneously refer to this as the CPU. The computer system unit is the housing that contains the main components of the computer. System units come in two basic varieties, the tower version, or a desktop version,
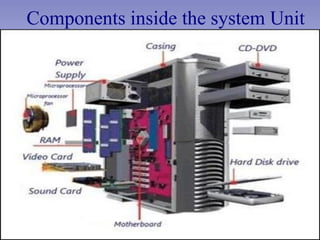
- 3. Inside the system unit, you'll find the CPU (central processing unit), the main circuit board (known as the motherboard), RAM (random access memory), and other components.
- 4. Components inside the system Unit
- 6. Main Components of a PC System Unit The main components inside the computer system unit are such as: – Central Processing Unit (CPU), – Memory Unity – Storage Unit - Hard Disk Drive/SSD, – Motherboard – Databus – Power supply – And others…
- 7. The central processing unit (CPU) Central processing unit (CPU): The "brain" of the computer that executes functions, processes, and digital instructions. Sometimes it is known as Microprocessor or Processor. The CPU is the hardware component responsible for all operations performed in the computer system, that’s why most computer users call it the brain of the computer, which is fixed on the motherboard through a slot. This is where all calculations and every instruction take place.
- 8. Processors are typically found on a single silicon chip and are often part of the Intel Pentium family. More pins indicate greater processing capability.
- 9. History of CPU Since 1823, when Baron discovered silicon, which is still the primary component used in manufacturing CPUs today, the history of the CPU has experienced numerous significant turning points. The first transistor was in December 1947. in 1958, the first working integrated circuit was built. The Intel 4004 was the company’s first microprocessor, which it unveiled in 1971. Intel released its 8008 CPU in 1972, Intel 8086 in 1976, and Intel 8088 in June 1979, The Motorola 68000, a 16/32-bit processor, was also released in 1979. The Sun also unveiled the SPARC CPU in 1987.
- 10. AMD unveiled the AM386 CPU series in March 1991. In January 1999, Intel introduced the Celeron 366 MHZ and 400 MHz processors. AMD back in April 2005 with its first dual-core processor. Intel also introduced the Core 2 Dual processor in 2006. Intel released the first Core i5 desktop processor with four cores in September 2009. In January 2010, Intel released other processors like the Core 2 Quad processor Q9500, the first Core i3 and i5 mobile processors, and the first Core i3 and i5 desktop processors. In June 2017, Intel released Core i9 desktop processor, and Intel introduced its first Core i9 mobile processor In April 2018.
- 11. Functions of CPU The key functions of a CPU are as follows − – The CPU performs all arithmetic and logic operations. – It executes all instructions provided by a program and runs the operating system as well as application software. – It constantly receives input from the user and directs the Input and output units to respond to the instructions communicated to the processor. – It contains registers, which are small storage locations within the CPU used for holding intermediate results and instructions. – The CPU conducts all data processing operations by fetching instructions from memory, decoding them, and then executing them. – Finally, it processes the data and produces output, which may be displayed on the screen.
- 12. Processor vs Core i Processor A CPU core is a single processing unit within the CPU. A core is a small CPU or processor built into a big CPU or CPU socket. It can independently perform or process all computational tasks. A core can execute only one program instruction at a time A CPU can have multiple cores, which allows it to run multiple tasks simultaneously. The more cores a CPU has, the more independent tasks the processor can run concurrently
- 13. Multi-core Processor Traditional processors, such as the Pentium processor, had only one core. In contrast, modern processors are multi-core. A multi-core processor is an integrated circuit that has two or more processor cores. These cores work together to enhance performance and reduce power consumption. Essentially, a multi-core processor is like a package containing several processors, referred to as cores, within it. These processors can execute multiple instructions simultaneously, depending on the number of cores.
- 14. The Core "i" name processors, such as i5 and i7, serve as a way to categorize and differentiate processors within a specific generation but not refer to the number of cores inside the processor. For instance, a Core i7 processor typically has between 6 to 20 cores, while a Core i5 processor usually has between 4 to 14 cores. The following is the Intel Core Processor Family and possible number of cores
- 15. Intel® Core Processor Family Intel® Core i9 Processors: Delivering up to 24 cores Intel® Core i7 Processors: This CPU packs the power of up to 20 cores. Intel® Core i5 Processors: PCs with up to 14 cores Intel® Core i3 Processors: processors deliver outstanding performance for everyday tasks. Intel® Core Processors: For casual gaming, multitasking,
- 16. Processor Speed CPU speed, also known as clock speed, refers to the number of cycles a CPU can execute in one second. It is measured in hertz (Hz). Clock speed represents how many times per second a circuit operates, or the speed at which a microprocessor can execute instructions. Hertz (Hz) measures the number of electronic pulses generated by the clock per second; which relates to the frequency at which the CPU operates or the number of cycles the processor executes each second. Understanding the type and speed of your computer's processor is important.
- 17. CPU usually expressed in megahertz (MHz) or gigahertz (GHz), determines how fast your computer will run. The faster the processor in a computer, the more quickly the computer will perform operations For example, a CPU with a clock speed of 3.0 GHz can process 3 billion cycles per second, where 3.0 MHz can execute 3 million cycles per second Higher processor speeds, combined with the number of cores, enhance computing capabilities for various user needs such as gaming or business tasks.
- 18. Types of CPU Single Core CPU: These CPUs only have a single core that performs different operations. The oldest type of CPU was used in the 1970s. Dual-Core CPU: Dual-Core CPUs contain a single Integrated Circuit with two cores. Dual-core CPUs can work faster than single-core processors. Quad-Core CPU: A quad-core processor contains a chip with four independent cores. These cores read and execute various instructions provided by the CPU.
- 19. What Makes a Good CPU Speed? When considering what’s a good CPU speed, it’s important to understand that higher numbers generally mean better performance. Here are some key points to consider: – For general use: A CPU speed of 1.6 GHz to 2.5 GHz is typically sufficient for tasks like web browsing, word processing, and basic multimedia. – For gaming: Generally, a speed of 3.5 GHz to 4.0 GHz is considered good for gaming. – For professional use: Content creators, data analysts, and other professionals might need speeds of 4.0 GHz and above, depending on their specific applications.
- 20. Choosing the Right Processor for Your Needs When selecting a CPU, consider your use case: For everyday computing: Look for multi-core processors with speeds around 2.5 GHz to 3.5 GHz, such as Intel Core i5. For gaming: Aim for processors with speeds of 3.5 GHz to 4.0 GHz or higher, like Intel Core i7. For professional use: Consider high-end processors with speeds of 4.0 GHz and above, such as Intel Core i9 Remember, the best processor for you balances speed, core count, and price according to your needs.
- 21. Components of CPU The processor itself is made up of components such as the arithmetic logic unit (ALU) and the control unit (CU). Additionally, the processor has internal memory called a register that stores a small number (usually less than 100) that is currently being processed. This register works very closely with the main memory location called RAM, which retains active programs and data. The components of the CPU are: – Control Unit (CU) – ALU (Arithmetic Logic Unit) – Registers and – Memory Unit
- 22. 1. Control Unit (CU) CU is the part of the CPU that supervises the general operations of the computer. It controls the operations of all parts of the computer. It controls the data flow between the CPU, memory, and other peripherals. A CPU executes instructions by fetching them from memory, decodes them, and then executes them. Also, the CPU reads and writes data to and from the memory system and transfers data to and from the I/O devices. A major role of a control unit is fetching instructions from the main memory, decoding them, executing them, and transferring data to and from the I/O devices.
- 23. Functions of Control Unit Instruction Fetch − A CU fetches instructions from RAM (Random Access Memory). Instruction Decoding − It decodes the fetched instructions to operate. Instruction Execution − A CU sends control signals to perform arithmetic and logical operations. Control Flow Management − It controls the flow of instructions from software. Exception Handling − A control unit effectively manages exceptions like hardware failures.
- 24. 2. Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU) Arithmetic logic unit (ALU) is a circuit embedded within a computer’s central processing unit (CPU), which performs mathematical and logical operations using electrical transistors that convey signals in 0s and 1s. As the name implies, the Arithmetic and Logical Unit (or ALU) performs arithmetic and logical functions. The arithmetic functions are addition, subtraction, multiplication division, and comparisons, whereas the logical functions mainly include selecting, comparing, and merging the data.
- 25. Functions of ALU Arithmetic Operations: The ALU can perform basic arithmetic operations. It executes arithmetic operations such as addition, subtraction, and multiplication. Logic operations: The ALU can also perform logical operations like AND, OR, NOT, XOR, and bit-shifting
- 26. 3. Memory Unit Memory refers to the temporary internal storage areas within a computer where data that need to be processed and instructions required for processing are stored. Memory is used to store the information (programs and data) that the computer is currently using. It is sometimes called main or primary memory. The memory unit supplies the data to other units of the computer whenever it is required to do so. There are two types of memory in the computer, which are primary memory and secondary memory.
- 27. Primary Memory Primary storage or memory is also known as the main memory, which is the part of the computer that stores current data, programs, and instructions. Primary memory is a segment of computer memory that can be accessed directly by the processor. In a hierarchy of memory, primary memory has access time less than secondary memory. Generally, primary memory has a storage capacity lesser than secondary memory. In order to enhance the efficiency of the system, memory is organized in such a way that access time for the ready process is minimized.
- 28. The following approach is followed to minimize access time for the ready process. All programs, files, and data are stored in secondary storage that is larger, to execute any process operating system loads the process in primary memory which is smaller and can be accessed directly by the CPU and hence has greater access time.. Since only those processes are loaded in primary memory which is ready to be executed, the CPU can access those processes efficiently and this optimizes the performance of the system.
- 29. Classification of Primary Memory Primary memory can be broadly classified into two parts: 1. Random Access Memory (RAM) 2. Read-Only Memory (ROM)
- 30. RAM (Random Access Memory) Random Access Memory (RAM) is also known as an internal storage unit or main memory, it is the main ‘working’ memory used by the computer which holds only those data and instructions on which the computer is currently working. RAM is volatile, which means RAM store data temporarily and data stored in it is lost when we switch off the computer or if there is a power failure. The contents of RAM are necessary for the computer to process data. A computer cannot run without primary memory
- 31. The RAM within your computer is where the operating system is loaded to when you switch on your computer. Any process in the system which needs to be executed is loaded in RAM which is processed by the CPU as per Instructions in the program. The units which are used to measure computer memory are bytes. RAM has limited capacity, currently , PCs typically have 1GB to 32GB of RAM. While RAM is used for short-term storage, the more things you open on your computer, the more GB of RAM you need.
- 32. How much RAM do you need? The size of RAM affects speed, power and capability of a computer system. As a rule of thumb, the more RAM you have installed in your computer the better. Generally, it is recommended to have – 4-8GB of RAM for casual computer usage and internet browsing, – 8-16GB for spreadsheets and other office programs, and – at least 32GB for gamers and multimedia creators. How you use your computer influences how much RAM you need, so use this as a guideline.
- 33. ROM (Read Only Memory ) Read-Only Memory (ROM) is a type of primary memory from which information can only be read. ROM is a special type of memory chip which holds software which can be read but not written to it. ROM can be directly accessed by the Central Processing Unit. But, the data and instructions stored in ROM are retained even when the computer is switched off. This type of memory is non-volatile. Means, the information is stored permanently in such memories during manufacture.
- 34. ROM is typically used to store programs and data that are required to start up (boot) a computer system. This operation is referred to as bootstrap. Another use of ROM, is to store operating systems subprograms for carrying out I/O and other activities. Any data which need not be altered are stored in ROM. ROM includes those programs which run on booting of the system (known as a bootstrap program that initializes OS) along with data like algorithm required by OS. Anything stored in ROM cannot be altered or changed.
- 35. ROM chips are not only used in the computer but also in other electronic items like washing machine and microwave oven. Also, network cards and video cards contain ROM chips. A good example is the ROM-BIOS chip, which contains read-only software for Basic I/O devices.
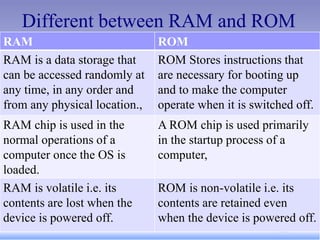
- 36. Different between RAM and ROM RAM ROM RAM is a data storage that can be accessed randomly at any time, in any order and from any physical location., ROM Stores instructions that are necessary for booting up and to make the computer operate when it is switched off. RAM chip is used in the normal operations of a computer once the OS is loaded. A ROM chip is used primarily in the startup process of a computer, RAM is volatile i.e. its contents are lost when the device is powered off. ROM is non-volatile i.e. its contents are retained even when the device is powered off.
- 37. 4. Registers A CPU register is a small piece of computer memory that stores and manipulates data while instructions are executed. It has small amount of memory associated with the CPU, which it uses to perform the operations. A register may hold an instruction, a storage address, or any kind of data (such as a bit sequence or individual characters). It is also the cache, which serves as high-speed memory where instructions can be copied to and retrieved.
- 38. The register size of a particular processor allows us to classify the processor. Depending on the processor, a register may typically store 8, 16, 32 or 64 bits. Processors with a register size of n-bits are called n- bit processors, so that processors with 8-bit registers are called 8-bit processors, similarly there are 16- bit, 32-bit and 64-bit processors etc. An n-bit processor is said to have an n-bit word size so a 32-bit processor has a 32-bit word size. The greater the number of bits the more powerful the processor is, since it will be able to process a larger unit of information in a single operation.
- 39. 32-bit vs 64-bit You’ve probably heard when you download a piece of software, the term 32-bit and 64-bit. This term is used for processor, Operating System, install a game, computer driver etc. There are two type processors exist in computing i.e. 32-bit and 64-bit. The term x86 is used for architecture of the CPUs that means x86 stands for 32 bits and it refers to the family of processors (80386 and 80486). The term x64 stands for 64 bits processors.
- 40. Data Bus DataBus is the physical connection that makes it possible to transfer data from one location in the computer system to another. It composed of a set of communication lines or wires DataBus is the channel or path that lets the parts of a computer communicate with each other. Data travels from one part of the computer to another through a bus. This is used to transfer information between all system components. A data bus is utilized to transport data from the memory to the registers and from the registers to the
- 41. An alternative method of classifying a processor is to use the width of the data bus. This means that the CPU can transfer n-bits to another device in a single operation. Databuss width is measured by using bits The data bus width is very important in a computer system, since it determines the amount of information that can be transferred to or from the CPU, in a single operation. This means, for example, if the data bus width is 16- bits, then would have to transfer two 16-bit items to the CPU to fill a 32-bit register.
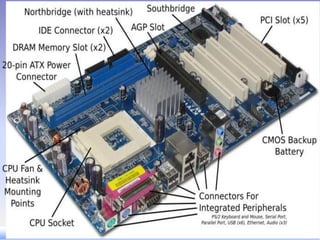
- 42. Motherboard Motherboard is the computer's main circuit board that connects all components of a microcomputer. It is also known as System board. A motherboard is often referred to as the “backbone” or “spine” of a computer. The CPU is normally housed on system board along with all the other electronic components that has connectors for attaching devices to the bus. It allocates power and allows communication between the CPU (central processing unit), RAM (random-access memory), and all other computer
- 43. There are multiple types of motherboards, designed to fit different types and sizes of computers. Each type is designed to work with specific types of processors and memory, so they don't work with every processor and type of memory. However, hard drives are mostly universal and work with most motherboards, regardless of the type or brand.
- 45. Secondary Memory Secondary storage, is a computer system's long-term storage component that stores data that's not accessed frequently. These are also known as Long term storage or Permanent Storage, and external memory or backup memory or auxiliary storage, They are non-volatile storage such that data is permanently stored even if power is switched off and can be used to store, back up, and archive data. It is slower than main memory. Contents of secondary memories are first transferred to main memory, and then CPU can access it. CPU does not access these memories directly instead they are accessed via input- output routines.
- 46. Secondary memory is used for different purposes, the main purposes of using secondary memory are: Permanent storage: As we know primary memory stores data only when the power supply is on. So we need a secondary memory to store data permanently even if the power supply is off. Large Storage: Secondary memory provides large storage space so that we can store large data like videos, images, audio, files, etc permanently. Portable: Some secondary devices are removable. So, we can easily store or transfer data from one computer or device to another.
- 47. Three main types of secondary storage Magnetic storage: Uses magnetized fields to store data in binary form on a metal disk or magnetic tape. Hard disk drives (HDDs) and magnetic tape are examples of magnetic storage. Solid state storage: Uses silicon microchips with transistors to store data. Solid-state drives (SSDs) and USB memory sticks are examples of solid-state storage. Faster read and write speeds than HDDs and optical storage devices, and consume less power and generate less heat. USB flash drives are compact and portable, while SSDs are more commonly installed internally within a computer. Optical storage: Uses microscopic light reflected off a metal or plastic disk to store data. CDs, DVDs, and Blu-ray discs are examples of optical storage. Portable, durable, and low-cost.
- 48. Magnetic storage devices Magnetic storage devices are storage devices that use mechanical and binary technology to record information. This is because they use a moving part to mark and read information on a magnetic surface. Magnetic storage devices use magnetization process to write, rewrite and access data. Data gets saved here in binary form. These devices store data in the form of tiny, magnetized dots. The dots are created, read and erased using magnetic fields created by very tiny electromagnets. Magnetic storage is one of the most affordable ways to store large amounts of data.
- 49. Magnetic storage are of two categories Magnetic tape and Magnetic Discs In the magnetic tape the dots are arranged along the length of a long plastic strip which has been coated with a magnetizable layer (audio and video tapes use a similar technology). In the magnetic discs the dots are arranged in circles on the surface of a plastic, metal or glass disc that has a magnetizable coating(e.g. floppy disc or hard-drive), . Some of the most common magnetic storage devices include: – Magnetic Tapes. – Hard Disk Drives (HDDs) – Floppy Disks.
- 50. 1. Magnetic Tape Magnetic tape storage is a method of storing digital data on a thin plastic strip with a magnetic coating. It contains thin plastic ribbon coated with magnetic oxide. It was a primary storage medium for early computers and is still used today for data backup and archiving Magnetic tape is made up of a thin, magnetizable coating on a long, narrow strip of plastic film. Devices that record and play audio and video using magnetic tape are tape recorders and videotape recorders. A device that stores computer data on magnetic tape is known as a tape drive.
- 51. In magnetic tape only one side of the ribbon is used for storing data. It uses 'serial access' to find a piece of data. This means that to find a specific piece of data, the tape reader has to start at the beginning of the tape and continue fast forwarding until it gets to the piece of data that needed. Serial access makes it fairly slow to find and retrieve data. Data read/write speed is slower because of sequential access. However, magnetic tape is excellent for archiving data i.e. data not likely to be needed instantly. Tape data storage is used more for system backup, data archive and data exchange. The low cost of tape has kept it viable for long-term storage and archive
- 52. Advantages and Disadvantages of Magnetic Tape Advantages : These are inexpensive, i.e., low cost memories. It provides backup or archival storage. It is a reusable memory. It is compact and easy to store on racks. Disadvantages : Sequential access, means it does not allow access randomly or directly. It requires caring to store, i.e., vulnerable humidity, dust free, and suitable environment. It’s stored data cannot be easily updated or modified, i.e., difficult to make updates on data.
- 53. 2. Hard Disk Drive (HDD) Hard Disk Drives (HDDs) are the most common magnetic storage devices found in computers and data centers. Hard- drives have a very large storage capacity (up to 1TB). An HDD is composed of several circular disks, called platters, which store data on their magnetic surfaces. These platters spin at high speeds, allowing the read-write head to access the stored data. The surface of a disk is divided into tracks and each track is divided into sectors (blocks). Disk storage is the most popular form of secondary storage. It is more versatile than tape storage.
- 54. Hard-drives are random access devices and data access speeds are very fast. It is faster to access, as information can be accessed (direct access) quickly, independently of its position on the disk. Its disadvantage is that it is more expensive than tape storage. It is measured in a Byte, they can be used to store vast amounts of data. For example, a modern 2TB HDD can store millions of text documents, hundreds of hours of high- definition videos, or thousands of high-resolution images. This is the main, large data storage area within your computer.
- 55. Internal Hard Disk Internal Hard disks are the main data storage area within your computer and are used to store your operating system, your application programs (i.e. your word processor, games etc) and your data. They are much faster than CD-ROMs and floppy disks and can also hold much more data. Hard disks are installed within the system unit of your computer.
- 56. External hard disks External Hard Drives are similar to internal HDDs, external hard drives are portable devices that house an HDD in an external casing, allowing users to store and transfer data between multiple computers with ease. They also offer varying capacities, from gigabytes to terabytes. Some external hard disks will plug into the USB port (connector) located at the back of your computer. Other external hard disks require the installation of a special card within your computer which allows the connection of the external hard disk to the computer unit. Normally slower than internal disks, but more
- 57. 3. Floppy disk A floppy disk is a flexible removable storage device also known as a diskette. It is a type of disk storage composed of a thin and flexible disk of a magnetic storage medium in a square or nearly square plastic enclosure lined with a fabric that removes dust particles from the spinning disk. It has a flexible plastic disk covered with a thin layer of a magnetic substance, onto which digital data can be recorded and stored. It is the oldest portable storage devices that was commonly used to store computer files from the 1970s to the 1990s but are not used that much now due to their limited storage capacity. They are very slow compared to hard disks, and hold relatively small amounts of data (1.44 Mbytes).
- 58. Comparison Type Storage Capacity Access Method Primary Use Hard Disk Drives GB to TB Random Access Data Storage in Computers and Data Centers Floppy Disks KB to MB Random Access Portable Data Storage (Historical) Magnetic Tapes GB to TB Sequential Access Backup and Archivi
- 59. Solid state storage (SSD) STORAGE Solid-state drive (SSD) is a solid-state storage device that uses integrated circuit assemblies as memory to store data. SSD stores the data on flash memory chips making it faster and more efficient than a traditional hard disk drive (HDD) There are no moving mechanical components in SSD. This makes them different from conventional electromechanical drives such as Hard Disk Drives (HDDs) or floppy disks, which contain movable read/write heads and spinning disks. That's why they are called solid-state drives
- 60. SSDs have lower latency compared to electromechanical devices they are more resistant to physical shock, run silently, and have quicker access time. As a result, SSDs offer advantages such as reduced boot times, quicker file transfers, and advanced system overall performance. SSDs may be constructed from random-access memory (RAM) for applications requiring fast access but not necessarily data persistence after power loss. Batteries can be employed as integrated power sources in such devices to retain data for a certain amount of time after external power is lost.
- 61. Advantages of SSD Faster Read/Write Speeds: SSDs offer significantly faster read and write speeds than traditional hard disk drives (HDDs), which use spinning disks and mechanical read/write heads. Lower Power Consumption: SSDs consume less power than HDDs, making them ideal for use in laptops, tablets, and other mobile devices that rely on battery power. No Moving Parts: SSDs have no moving parts. This makes them more resistant to shock and vibration, and less prone to mechanical failure. Higher Reliability: Because SSDs have no moving parts, they are generally more reliable than HDDs, SSDs also have a lower rate of data loss due to read/write errors. Lower Noise and Heat Output: SSDs generate less noise and heat than HDDs,
- 62. Disadvantages of SSD Cost: SSDs are more expensive than regular hard drives. Limited Lifespan: Each memory cell in an SSD has a limited number of write cycles before it degrades. Storage choices: Because of the expense, SSDs are often sold in smaller sizes. Performance: SSDs’ performance degrades over time due to write cycle limitations.
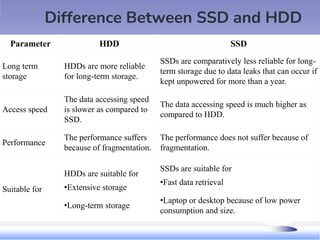
- 63. Difference Between SSD and HDD Parameter HDD SSD Long term storage HDDs are more reliable for long-term storage. SSDs are comparatively less reliable for long- term storage due to data leaks that can occur if kept unpowered for more than a year. Access speed The data accessing speed is slower as compared to SSD. The data accessing speed is much higher as compared to HDD. Performance The performance suffers because of fragmentation. The performance does not suffer because of fragmentation. Suitable for HDDs are suitable for •Extensive storage •Long-term storage SSDs are suitable for •Fast data retrieval •Laptop or desktop because of low power consumption and size.
- 64. Flash Disks Compact Flash (USB drives), memory sticks and other compact media (e.g., micro SD cards) are increasing versatile and vary in capacity. They are very useful to have and can fit in your wallet or on a keychain. These attach through USB or special drives. Prices vary with the capacity (amount of storage space); you can get a relatively inexpensive one that can hold a lot of data.
- 65. Optical disks storage Optical disk storage is a method of storing digital data on flat, circular discs using lasers to read and write information. Optical disks are a popular storage format for many applications, including archival storage and data backup Optical disk is a storage device that uses reflecting surfaces and laser technology to read and write data on a disk. With optical storage, data is burned into the storage medium using beams of laser light. The burns form patterns of small pits in the disk surface to represent data. Optical media are very durable, but they do not provide the flexibility of magnetic media for changing the data once they are stored.
- 66. i. CD-ROM (Compact Disk Read- Only Memory) CD-ROM (Compact Disk Read-Only Memory) is another form of secondary storage, that is a low-cost storage medium with a very large capacity. Unlike other disk storage, CD-ROM is a WORM (Write Once Read Many times) device i.e. it is a read only storage device. This means that like ROM, the disk comes with information already stored on it. In terms of capacity, a single CD-ROM may store up to 600 megabytes.
- 67. ii. CD-R - Recordable Also known as Recordable CDs, a CD drive unit allows you to record data, music or video to your own. (CD-R) is now becoming more widely used. This storage combines the reliability and storage capacity of CD-ROM with the flexibility of magnetic disks in that users can store their own information on them. They are still slower to access than conventional hard disks.
- 68. iii. CD-RW(Rewritable CD) This type of optical disk can be erased and use to rewrite new information. This storage combines the reliability and storage capacity of CD-ROM with the flexibility of magnetic disks in that users can store their own information on them. They can store over 200 MB of data, and speed of access to this data is faster than a floppy but slower than a hard drive. These take up much more storage space than data in character format, such as in word-processed files. They are still slower to access than conventional hard disks.
- 69. iv. DVD (Digital Video Display) DVD(Digital Video Display or Digital Versatile Disks) drives are a common option on computers. are similar to CD-ROM (but have a larger capacity) and are used for similar applications. CD-ROMs are now being replaced by DVD-ROMs. Software, especially with complex graphics (particularly games) are distributed on DVD. These are also used for distributing films as a rival to video tapes. Also allow you to watch movies on your computer screen. DVD-ROM capacity ranges from 4.7 GB upwards (4.7x 2 or 4.7 x 4 GB). A current PC will typically have a DVD drive which is also capable of reading conventional CDs.
- 70. Writing a CD It is not possible to write to a CD without special hardware, a CD writer, popularly known as a “CD burner”. However, once you have written to a CD, it cannot be erased and overwritten like a diskette, unless you buy CD’s designed for re- writing. Even re-writable CD’s are not designed for continual saving and overwriting
- 71. Computer Performance Some of the factors which impact computer’s performance, are such as: –Data Bus –CPU speed, –RAM size, and –the number of applications running Explain how these affect computer performance
- 72. Some of the factors which affect Computer Performance CPU Clock speed: – The computer clock speed governs how fast the CPU will run. The higher the clock speed the faster the computer will work for you. – The higher the MHz speed the faster the computer. RAM size: – As a rule the more memory you have the faster the PC will appear to operate. – Windows also uses the hard disk a lot, so logically the faster the hard disk can operate then again the faster the PC will appear to run.
- 73. Hard disk speed and storage: – Hard disks are also measured by their speed, defined by the disk access time, which is measured in milliseconds. – The smaller this access time the faster the hard disk will store or retrieve data. Free Hard Disk Space: – To get the most out of your Windows based PC, you not only need a fast hard disk but also a large hard disk with plenty of "spare space". – This is due to the fact Windows is constantly moving data between the hard disk and RAM (Random Access Memory).
- 74. Multitasking considerations(running more than one program): – Windows is a multitasking system, which means that it can run more than one program at a time. – However the more programs which are running at the same time, the slower each one will run. To some extent this slowing effect depends on what each program is doing. Editing a large, full color picture for instance can take up a lot of CPU time.