Lecture 4-cs648 Randomized Algorithms
- 1. Randomized Algorithms CS648 Lecture 4 • Linearity of Expectation with applications (Most important tool for analyzing randomized algorithms) 1
- 2. RECAP FROM THE LAST LECTURE 2
- 4. Expected Value of a random variable (average value) 4 Ω X= a X= b X= c
- 5. Examples 5
- 6. Can we solve these problems ? 6
- 7. Balls into Bins (number of empty bins) 7 1 2 3 … … n 1 2 3 4 5 … m-1 m This is a right but useless answer !
- 8. Randomized Quick Sort (number of comparisons) 8 We can not proceed from this point … A recursion tree associated with Randomized Quick Sort
- 9. 9 1 2 3 4 5 … m-1 m 1 2 3 … … n Balls into Bins (number of empty bins) Randomized Quick Sort (number of comparisons)
- 10. Balls into Bins (number of empty bins) 10 1 2 3 4 5 … m-1 m
- 11. 11 1 2 3 4 5 1 2 3 4 5 6 0 1 0 1 0
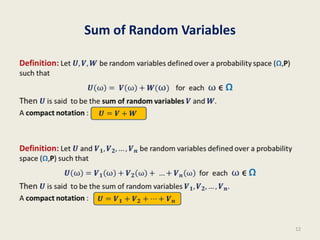
- 12. Sum of Random Variables 12
- 13. Randomized Quick Sort (number of comparisons) 13 Elements of A arranged in Increasing order of values
- 14. 14 1 0 … 0 1 1 … 0
- 15. What have we learnt till now? 15
- 16. The main question ? 16
- 17. Balls into Bins (number of empty bins) 17 1 2 3 … … n 1 2 3 4 5 … m-1 m
- 18. Randomized Quick Sort (number of comparisons) 18
- 20. Where to use Linearity of expectation ? 20
- 21. Think over the following questions? 21
- 22. Think over the following questions? 22
- 24. Some Practice problems as homework • Balls into bin problem: • What is the expected number of bins having exactly 2 balls ? • We toss a coin n times, what is the expected number of times pattern HHT appear ? • A stick has n joints. The stick is dropped on floor and in this process each joint may break with probability p independent of others. As a result the stick will be break into many substicks. – What is the expected number of substicks of length 3 ? – What is the expected number of all the substicks ? 24
- 25. PROBLEMS OF THE NEXT LECTURE 25