Lecture5 microprocessor (Microprocessor).ppt
- 1. Computer Fundamentals Lecture # 5: Microprocessor
- 2. Today’s Objectives: To study Microprocessor and its various Subsystems
- 3. Microprocessor: The Brain of the computer Silicon Chip (IC) Latest Pentium-4 has around 125 million transistors Performs Billions of Instructions per second Combines with other devices such as Memory and I/O to form a “Microprocessor system”
- 4. Microprocessor Models: The “Calculator” Model Should be able to Take Data Decode Execute Give Results
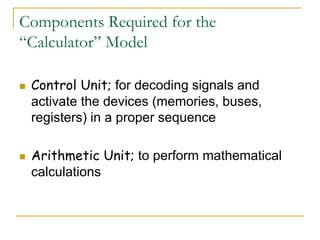
- 5. Components Required for the “Calculator” Model Control Unit; for decoding signals and activate the devices (memories, buses, registers) in a proper sequence Arithmetic Unit; to perform mathematical calculations
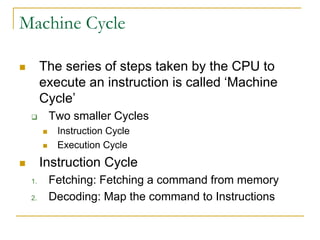
- 6. Machine Cycle The series of steps taken by the CPU to execute an instruction is called ‘Machine Cycle’ Two smaller Cycles Instruction Cycle Execution Cycle Instruction Cycle 1. Fetching: Fetching a command from memory 2. Decoding: Map the command to Instructions
- 7. Machine Cycle Execution Cycle 1. Executing: CPU converts the instructions into microcode and carries them out 2. Storing: (Optional) The CPU stores the result somewhere in the memory
- 8. Components of a Microprocessor Memory; stores data and instructions Bus Interface Unit; transfers data in and out of the Processor, instructions into the Processor Instruction Decoder; Decodes Instructions Arithmetic and Logic Unit; Performs Math, Comparisons and Logical Operations on Integers Control Unit; Controls and Manages all the Processing
- 9. The Memory Bottleneck: Accessing RAM for Data/Instructions is slow Solution: Registers attached to the ALU (for data currently in use) Cache Memory (for most frequently used data) Internal Cache (on processor chip) Instruction Cache Data Cache External Cache (on motherboard)
- 10. The “Real Numbers” Processing: Real Numbers Use in Computing Floating Point Unit; Processes the Real Numbers faster than an ALU
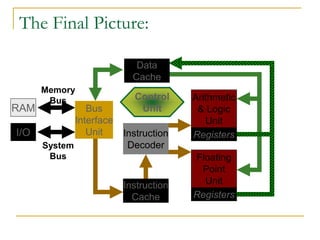
- 11. The Final Picture: Registers Registers Instruction Cache Arithmetic & Logic Unit Control Unit Bus Interface Unit Data Cache Instruction Decoder I/O RAM Memory Bus System Bus Floating Point Unit
- 12. The Instruction Set: A Microprocessor’s Language; Low-Level, Single Step Instructions Also called Program code, Binary code or Machine code Difficult to change after implementation Architecture dependant Design Issues: Silicon Real Estate Cost Expandability Legacy Support Complexity Power Consumption Deign Types CISC (Complex Instruction Set Computer) RISC (Reduced Instruction Set Computer)
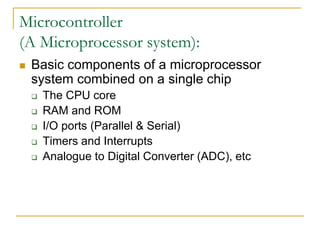
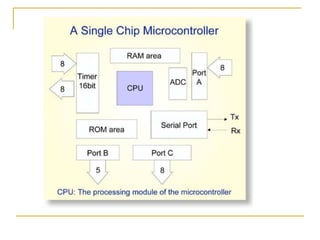
- 13. Microcontroller (A Microprocessor system): Basic components of a microprocessor system combined on a single chip The CPU core RAM and ROM I/O ports (Parallel & Serial) Timers and Interrupts Analogue to Digital Converter (ADC), etc
- 14. Microcontrollers Used in Autonomous Systems ovens, ATMs, vehicles Advantage: Compact integrated design on single chip Reduced interface
- 16. Microprocessor, Yesterday and Today: Busicom’s Desk Calculators 1971, Intel’s 1st Microprocessor-4004 2250 Transistors 740 KHz, 60,000 Op/sec 16 pins 10 Microns As Powerful as ENIAC 2001, Intel’s P4 – Today’s Processor 55 Million Transistors 32-bit Word size 2.2 GHz 2 ALUs 128 bit FPU 0.13 Micron
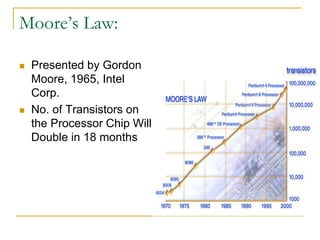
- 17. Moore’s Law: Presented by Gordon Moore, 1965, Intel Corp. No. of Transistors on the Processor Chip Will Double in 18 months
- 18. Better Future Processors? Capabilities should Include: Higher Clock Frequency Greater Word Width More Functioning Units Better Caching Algorithm Right Cache Size What else?