lecture_8_contraceptive_methods.ppt
- 2. Contraception There are many types of contraception widely used now days for family planning purposes. Each method has its advantages and suits special cases and not necessarily suits others and the choice of contraception depends on different needs of the patients like the period of contraception and also doctor should decide which method suits needs more. No method of contraception is completely effective. Types:- 1. Natural contraception 2. Mechanical contraception 3. Hormonal contraception 4. Surgical contraception
- 3. Characteristics of ideal contraceptive: Safe 100% effective Free of side effects Easily obtainable Affordable Acceptable to the user Free of effects on future pregnancies
- 4. Types of Birth Control Hormonal Barrier IUD Methods based on information Permanent sterilization
- 5. Types of Birth Control
- 6. Types of Birth Control
- 7. Hormonal Methods Oral Contraceptives (Birth Control Pill) Injections (Depo-Provera) Implants (Norplant I & II)
- 8. Birth Control Pills Pills can be taken to prevent pregnancy Pills are safe and effective when taken properly Pills are over 99% effective
- 9. How does the pill work? Stops ovulation Thins uterine lining Thickens cervical mucus
- 10. Positive Benefits of Birth Control Pills Prevents pregnancy Eases menstrual cramps Shortens period Regulates period Decreases incidence of ovarian cysts Prevents ovarian and uterine cancer Decreases acne
- 11. Side-effects Breast tenderness Nausea Increase in headaches Moodiness Weight change
- 12. Taking the Pill Once a day at the same time everyday Use condoms for first month Use condoms when on antibiotics Use condoms for 1 week if you miss a pill or take one late The pill offers no protection from STD’s
- 13. Depo-Provera Birth control shot given once every three months to prevent pregnancy 99.7% effective preventing pregnancy No daily pills to remember
- 14. How does the shot work? The same way as the Pill! Stops ovulation Stops menstrual cycles!! Thickens cervical mucus
- 15. SIDE EFFECTS Extremely irregular menstrual bleeding and spotting for 3-6 months! NO PERIOD after 3-6 months Weight change Breast tenderness Mood change *NOT EVERY WOMAN HAS SIDE-EFFECTS!
- 16. The Patch
- 17. IMPLANTS Implants are placed in the body filled with hormone that prevents pregnancy Physically inserted in simple 15 minute outpatient procedure Plastic capsules the size of paper matchsticks inserted under the skin in the arm 99.95% effectiveness rate
- 18. Norplant I vs. Norplant II Six capsules Five years Two capsules Three years The pill works in several ways to prevent pregnancy. The pill suppresses ovulation so that an egg is not released from the ovaries, and changes the cervical mucus, causing it to become thicker and making it more difficult for sperm to swim into the womb. The pill also does not allow the lining of the womb to develop enough to receive and nurture a fertilized egg. This method of birth control offers no protection against sexually- transmitted diseases.
- 19. Norplant Considerations Should be considered long term birth control Extremely effective in pregnancy prevention > 99%
- 20. Emergency contraception pills can reduce the chance of a pregnancy by 75% if taken within 72 hours of unprotected sex! Emergency Contraception
- 21. Emergency Contraception (ECP) Must be taken within 72 hours of the act of unprotected intercourse or failure of contraception method Must receive ECP from a physician 75 – 84% effective in reducing pregnancy
- 22. ECP Floods the ovaries with high amount of hormone and prevents ovulation Alters the environment of the uterus, making it disruptive to the egg and sperm Two sets of pills taken exactly 12 hours apart
- 23. BARRIER METHODS Spermicides Male Condom Female Condom Diaphragm Cervical Cap
- 24. BARRIER METHOD Prevents pregnancy blocks the egg and sperm from meeting Barrier methods have higher failure rates than hormonal methods due to design and human error
- 25. SPERMICIDES Chemicals kill sperm in the vagina Different forms: -Jelly -Foam -Suppository Some work instantly, others require pre-insertion Only 76% effective (used alone), should be used in combination with another method i.e., condoms
- 26. MALE CONDOM Most common and effective barrier method when used properly Latex should only be used in the prevention of pregnancy and spread of STI’s (including HIV)
- 27. MALE CONDOM Typical effectiveness rate = 88% available Combining condoms with spermicides raises effectiveness levels to 99%
- 28. FEMALE CONDOM Made as an alternative to male condoms Polyurethane Physically inserted in the vagina Typical rate = 79% Woman can use female condom if partner refuses
- 29. The Female Condom The female condom is a lubricated polyurethane sheath, similar in appearance to a male condom. It is inserted into the vagina. The closed end covers the cervix. Like the male condom, it is intended for one-time use and then discarded. The sponge is inserted by the woman into the vagina and covers the cervix blocking sperm from entering the cervix. The sponge also contains a spermicide that kills sperm. It is available without a prescription.
- 30. Vaginal Ring (NuvaRing) 95-99% Effective A new ring is inserted into the vagina each month Does not require a "fitting" by a health care provider, does not require spermicide, can make periods more regular and less painful, no pill to take daily, ability to become pregnant returns quickly when use is stopped. Nuva Ring is a flexible plastic (ethylene-vinyl acetate copolymer) ring that releases a low dose of a progestin and an estrogen over 3 weeks.
- 31. DIAPRAGHM Typical Effectiveness Rate = 80% Latex barrier placed inside vagina during intercourse Fitted by physician Spermicidal jelly before insertion Inserted up to 18 hours before intercourse and can be left in for a total of 24 hours
- 32. DIAPHRAGM
- 33. CERVICAL CAP Latex barrier inserted in vagina before intercourse “Caps” around cervix with suction Fill with spermicidal jelly prior to use Can be left in body for up to a total of 48 hours Must be left in place six hours after sexual intercourse Perfect effectiveness rate = 91% Typical effectiveness rate = 80%
- 34. Cervical Cap The cervical cap is a flexible rubber cup-like device that is filled with spermicide and self-inserted over the cervix prior to intercourse. The device is left in place several hours after intercourse. The cap is a prescribed device fitted by a health care professional and can be more expensive than other barrier methods, such as condoms.
- 35. Sponge The sponge is inserted by the woman into the vagina and covers the cervix blocking sperm from entering the cervix. The sponge also contains a spermicide that kills sperm. It is available without a prescription
- 36. INTRAUTERINE DEVICES (IUD) T-shaped object placed in the uterus to prevent pregnancy Must be on period during insertion A Natural childbirth required to use IUD Extremely effective without using hormones > 97 % The intrauterine device (IUD) shown uses copper as the active contraceptive, others use progesterone in a plastic device. IUDs are very effective at preventing pregnancy (less than 2% chance per year for the progesterone IUD, less than 1% chance per year for the copper IUD). IUDs come with increased risk of ectopic pregnancy and perforation of the uterus and do not protect against sexually transmitted disease. IUDs are prescribed and placed by health care providers.
- 37. INTRAUTERINE DEVICES (IUD) T-shaped object placed in the uterus to prevent pregnancy Must be on period during insertion Extremely effective without using hormones > 97 %
- 38. Copper T vs.. Progestasert 10 years 99.2 % effective Copper on IUD acts as spermicide, IUD blocks egg from implanting 1 year 98% effective T shaped plastic that releases hormones over a one year time frame Thickens mucus, blocking egg
- 39. STERILIZATION Procedure performed on a man or a woman permanently sterilizes Female = Tubal Ligation Male = Vasectomy
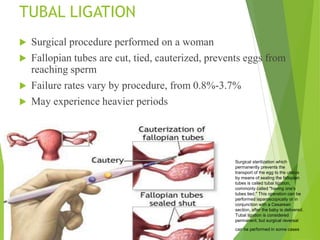
- 40. TUBAL LIGATION Surgical procedure performed on a woman Fallopian tubes are cut, tied, cauterized, prevents eggs from reaching sperm Failure rates vary by procedure, from 0.8%-3.7% May experience heavier periods Surgical sterilization which permanently prevents the transport of the egg to the uterus by means of sealing the fallopian tubes is called tubal ligation, commonly called "having one's tubes tied." This operation can be performed laparoscopically or in conjunction with a Cesarean section, after the baby is delivered. Tubal ligation is considered permanent, but surgical reversal can be performed in some cases
- 42. VASECTOMY Male sterilization procedure Ligation of Vas Deferens tube Faster and easier recovery than a tubal ligation Failure rate = 0.1%, more effective than female sterilization
- 43. During a vasectomy (“cutting the vas”) a urologist cuts and ligates (ties off) the ductus deferens. Sperm are still produced but cannot exit the body. Sperm eventually deteriorate and are phagocytized. A man is sterile, but because testosterone is still produced he retains his sex drive and secondary sex characteristics.
- 44. METHODS BASED ON INFORMATION Withdrawal Natural Family Planning Fertility Awareness Method Abstinence
- 45. Natural Family Planning & Fertility Awareness Method Women take a class on the menstrual cycle to calculate more fertile times NFP abstains from sex during the calculated fertile time FAM uses barrier methods during fertile time Perfect effectiveness rate = 91% Typical effectiveness rate = 75% No 100% safe day-irregular periods
- 46. EXCELLENT REFERENCE : www.plannedparenthood.org/bc Hatcher, Robert, MD Contraceptive Technology ,17ed. (2001)