Lecture+9+-+Dynamic+Programming+I.pdf
- 1. CIST212-Data Structures and Algorithms Lecture 9 Dynamic Programming I Prof. Boxiang Dong https://msuweb.montclair.edu/~dongb/ Office: CCIS-227E Email: dongb@montclair.edu
- 2. Review • Stack, Queue, Linked List • traverse: O(n) • search: O(n) • insertion: (1) • deletion: O(1) • Binary Search Tree • traverse: inorder, preorder, postorder O(n) • search: O(h) • minimum/maximum: O(h) • successor: O(h) • insertion: O(h) • deletion: O(h)
- 3. Dynamic Programming • Dynamic programming is a general strategy to solve computational problems, like divide-and-conquer.
- 4. Dynamic Programming • Divide-and-conquer paradigm: • Break the problem into several disjoint subproblems that are similar to the original one but smaller in size. • Solve the subproblems recursively. • Combine these solutions to create a solution to the original problem. • Dynamic programming: • Break the problem into several overlapping subproblems that are similar to the original one but smaller in size. • Solve the subproblems recursively only once. • Combine these solutions to create a solution to the original problem.
- 6. Dynamic Programming • Lets look at the rod-cutting problem. • Given a rod of length n inches and a table of prices pi for i=1,2,…,n, determine the maximum revenue rn obtainable by cutting up the rod and selling the prices.
- 8. Dynamic Programming pn: the revenue from no cut at all ri+rn-i: the revenue from cutting at the i-th place This is called the optimal substructure property: Optimal solutions to a problem incorporate optimal solutions to related subproblems, which we may solve independently.
- 9. Dynamic Programming • To make it simpler, we have Only the right-hand side of a cut at the i–th place will be cut further.
- 10. Dynamic Programming • Based on the previous formula, we derive the following recursive algorithm:
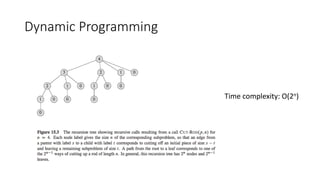
- 11. Dynamic Programming Time complexity: O(2n)
- 12. Dynamic Programming • We do not want to repeatedly calculate r2, r3, …, rn-1. • In dynamic programming, we only need to calculate them once. • The first time we calculate ri, we store it in a place. • The next time we need to use ri, we just retrieve it directly.
- 14. Dynamic Programming Key idea: 1. We use r[0,…,n] to store the maximum revenue. 2. In line 1 of MEMOIZED-CUT-ROD-AUX(p, n, r), If we find that rn is calculated before, we just return it directly; Otherwise, calculate and store it.
- 15. Dynamic Programming • MEMOIZED-CUT-ROD-AUX(p, n, r) calculates rn in a top-down fashion by recursion. • Most often, we want a bottom-up solution for two reasons: • Logically, it is easy to follow. • Faster, as it avoids recursion.
- 16. Dynamic Programming Time complexity: O(n2) Space complexity: O(n) Dynamic programming is an approach to trading space for efficiency.
- 18. Your Task • Read: Ch 15.1 (Must-be)












![Dynamic Programming
Key idea:
1. We use r[0,…,n] to store the maximum revenue.
2. In line 1 of MEMOIZED-CUT-ROD-AUX(p, n, r),
If we find that rn is calculated before, we just
return it directly;
Otherwise, calculate and store it.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture9-dynamicprogrammingi-221111020744-11ec2a00/85/Lecture-9-Dynamic-Programming-I-pdf-14-320.jpg)



