Lipds
- 1. Lipids Chemical Composition Elements: C, H , and O . E.g. Fats/neutral fats/triglycerides (butter, lard), oils, waxes, steroids (estrogen, progesterone, testosterone), cholesterol, aldosterone, prostaglandins, glycolipids and phospholipids in the CM. Fat soluble, and water insoluble Non-polar, dissolve in solvents such as alcohol, gasoline, and paint thinner, i.e. the hydrocarbon chains make neutral fats non-polar; thus they do not interact with water.
- 3. Locations and Functions of the Three Classes of Lipids
- 4. 1.) Neutral fats (also referred to as triglycerides ) Stored as adipose tissue under skin, around kidneys, within abdomen, in breasts. Long term energy source/long term energy storage . Provide insulation (prevent heat loss) and provide protection around organs.
- 5. 2.) Phospholipids Structural component of CM, and membrane-bound organelles within the cell. Regulates the amount of materials going in/out of cells. Provides flexibility and fluidity to CM allowing vesicle formation .
- 6. 3.) Steroids Ovaries, testes and adrenal gland; liver and fatty sheath around nerve cells, i.e. cholesterol. Maintains sexual characteristics , homeostasis and provides stability / fluidity to the cell membrane ; precursor for hormones and vitamins (A, D, E, K).
- 7. Monomers 1 glycerol and 3 fatty acids . Glycerol:
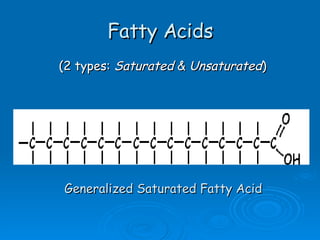
- 8. Fatty Acids (2 types: Saturated & Unsaturated ) Generalized Saturated Fatty Acid
- 9. Saturated Fatty Acid: Stearic acid (18:0) Obtained from animal fat; found in soaps, candles, cosmetics, lotions, moisturizers, creams, lotions, food packaging, deodorant, toothpaste, cocoa butter etc.
- 10. Unsaturated Fatty Acid: Oleic acid (18:1) (Mostly makes up olive oil, grapeseed oil, avacado, almonds, Macademia nuts)
- 11. What is a fatty acid? A fatty acid is a long chain of C’s and H’s to make a backbone (usually 14-24 C’s) and has an attached COOH (carboxyl group) at the end.
- 12. Formation Formation of a lipid polymer through dehydration synthesis ( -H 2 0 ). E.g. Neutral fat/triglyceride, phospholipid, steroid, cholesterol, estrogen, testosterone, aldosterone etc. Bonds form between the joining of glycerol and the fatty acids/monomers.
- 13. Going the other way! Formation of a lipid monomer through hydrolysis ( +H 2 0 ). E.g. Glycerol, saturated or unsaturated fatty acids. Bonds between the glycerol and fatty acids are destroyed within the lipid polymer.
- 14. (Animations) http://trc.ucdavis.edu/biosci10v/bis10v/media/ch02/triglyceride.html http://www2.nl.edu/jste/lipids.htm
- 16. Basic layout
- 18. Saturated and Unsaturated Fatty Acids - There are 2 types of fatty acids: Saturated Unsaturated
- 19. Saturated Contains a single covalent bond between the C’s. “ Saturated” with all the H atoms it can hold. E.g. Butter and lard.
- 20. Unsaturated Contains one or more double bonds between C’s. E.g. Vegetable oils, fish oils
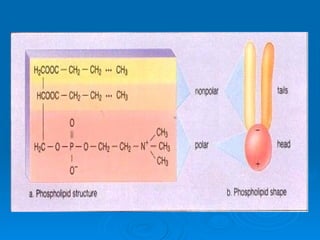
- 21. Phospholipids Composed of C, H, O, N , and phosphate groups . The phosphorus containing polar head is hydrophilic (“water-loving”) and the fatty acid chains of non-polar tails are hydrophobic (“water-fearing”).
- 22. Phospholipids 1 fatty acid is saturated and the other is unsaturated with a significant bend in the tail. Third fatty acid is replaced with N and a phosphate group
- 27. Functions: - Structural component of CM, which helps to regulate molecules in/out of cell -Provides flexibility and fluidity to CM allowing vesicle formation
- 29. Steroids A class of compounds that includes cholesterol, hormones, bile acids and vitamin D Contains a backbone of four fused C-H rings with different atoms attached to rings; non-polar. Testosterone (sex hormone)
- 30. Functions Many are hormones synthesized from cholesterol : i) Estrogen and progesterone produced in ovaries , maintain sex characteristics and the uterine lining in females. ii) Testosterone produced in testes , maintain sex characteristics in males. iii) Aldosterone produced in adrenal gland , regulates sodium and potassium (Na+/K+) in the kidneys.
- 31. Functions continued Others are cholesterol , which is a major constituent in the cell membrane providing stability (see Cell Structures, B1) and is the precursor of several steroids such as testosterone and estrogen.
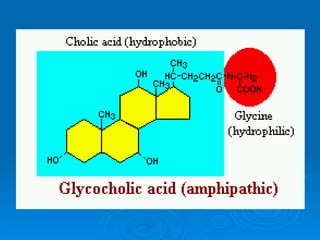
- 36. Bile! Bile , a modified cholesterol molecule (bile acids), is produced in the liver , (stored in the gall bladder & later released) Function: Emulsifies neutral fats into fat droplets (an emulsion) in the small intestine (this increases the surface area for lipase to break down the fat droplets; see Digestion, C1).
- 39. Bile! Note: Having the liver synthesize bile accounts for the majority of cholesterol breakdown in the body. In humans, roughly 500 mg of cholesterol are converted to bile acids and eliminated in bile every day! Bile acts like a ‘detergent’ on fat molecules since it has hydrophilic & hydrophobic ends
- 40. Emulsification Emulsification Physical break-up of molecules Provides greater surface area for enzymatic reactions
- 42. mmmmmm……. A poor patient with an extreme case of gallstones!
- 44. Something of interest…..a connection with bile & sea lampreys of the Great Lakes! These creatures parasitise other fish and have invaded the Great Lakes in North America, with devastating effects on the fishing industry. Weiming Li of Michigan State University was looking at spawning to develop new lamprey controls and discovered that males release a pheromone which can attract the attention of females at least 65 metres downstream. Analysis revealed that this pheromone is a bile acid , and it must have evolved specifically for this purpose because adult lampreys do not eat and therefore have no need for digestion!
- 45. Where does that food come from? The gummy, chewy texture of Gummy Bears, Worms & marshmallows is due to gelatin, a thickening agent derived from collagen protein in animal connective tissue.