Lithospere
- 2. Lithosphere Itcomes from the ancient Greek “lithos” which means stone and “sphaira” which means sphere. Itrefers to the solid rocky crust that covers the Earth. The crust is composed of minerals.
- 3. The crust is a solid layer that floates over the mantle’s magma.It represents 1% of the Earth’s volume but it has different thickness and length. The crust is divided into tectonic plates that move over the mantle. The crust presents different shapes, lenghts, etc. Some times it appears under the oceans and others over the sea surface. This is called the Earth’s relief. The shapes of the Earth’s relief changes thanks to internal forces and external agents.
- 4. 200 million years ago all the continents were united into a single supercontinent called Pangea. Pangea broke up because of the internal forces of the mantel and the tectonic plates gradually moved apart. This theory is called continental drift. Tectonic plates slide against each other or move apart. Thus, the plate’s boundaries are unstable.
- 8. Internal forces and pressures from the mantle causes the crust to: Fold: are deformations of the Earth’s surface where rock layers bend. Fault: are breaks in rock layers wher the rock is too hard to bend. Subducts: when one rock layer from a plate sinks under the other and its materials melts into the mantle’s magma.
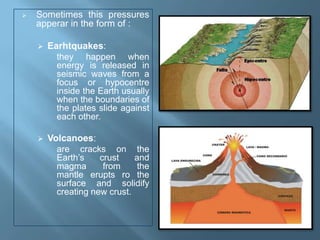
- 10. Sometimes this pressures apperar in the form of : Earhtquakes: they happen when energy is released in seismic waves from a focus or hypocentre inside the Earth usually when the boundaries of the plates slide against each other. Volcanoes: are cracks on the Earth’s crust and magma from the mantle erupts ro the surface and solidify creating new crust.
- 11. The external agents that shape the Earth’s surface are: Water Wind Vegetation They erode relief breaking it up and transporting and depositing eroded materials on a different place. Although human beings are not natural agents they also modify relief.
- 12. The crust presents different shapes, lenghts, etc. Some times it appears under the oceans and others over the sea surface. This is called the Earth’s relief. The Earth’s relief comprises the forms and shapes of the Earth’s surface.
- 13. Sometimes the Earth’s The North Pole is not a crust appears over the continent because it is sea surface and other formed by frosted times under the sea water. surface. Continents are Over the sea surface separated by oceans or there are 6 continents: seas: Africa Pacific Ocean Europe Atlantic Ocean América Indian Ocean Asia Artic Ocean Oceania Antartic Ocean or Antarctica Southern Ocean Mediterranean Sea Read Sea
- 15. Mountains: High Valley: elongated lowland elevations of the Earth’s between ranges of surface. When they are mountains or hills. grouped together it is called range. Península: land mass Plateau: high flat areas entirely surrounded by that are formed from water except in one part eroded mountains. connected with the mainland which is called Plain: low flat areas. isthmus. Alluvial plains are formed by rivers and coastal Island: a land mass plains are near the sea. entirely surrounded by water. Basins: very low areas sometimes below sea Cape: part of the coast level. that projects into the sea.
- 18. Gulf: large area of a Continental slope: the sea or ocean partially descent from the enclosed by land. continental shelf to the Bay: small area of a ocean bottom. sea or ocean partially Abyssal plain: huge enclosed by land. under water plains that Ría: long narrow inlet have an extension of the seacoast in between 3000 and which the sea occupies 7000 metres deep. the mouth of the river. Ocean trench: long Continental shelf: valley on the ocean floor great underwater that can have 11000 plateau which metres deep. correspondt to the Ocean ridge: border of a continent underwater mountain and is usually less than ranges. 400 metres deep.
- 20. Created by María Jesús Campos Chusteacher Wikiteacher