managment information system
- 1. Business Information Systems: An Overview Management Information Systems, Fifth Edition by Effy Oz
- 2. 2 Objectives • Explain why information systems are essential to business • Describe how computers process data into useful information for problem solving and decision making • Identify the functions of different types of information systems in business • Describe careers in information technology • Identify major ethical and societal concerns created by widespread use of information technology
- 3. 3 The Purpose of Information Systems • Businesses use information systems – To make sound decisions – To solve problems • Problem is any undesirable situation • Decision arises when more than one solution to problem exists
- 4. 4 The Purpose of Information Systems (continued) • Problem solving and decision making require information • Keys to success in business are – Gathering correct information – Storing information – Using information
- 5. 5 Data, Information, and Information Systems • “Data”, “information” and “system” are commonly used terms • Important to understand their similarities and differences
- 6. 6 Data vs. Information • Data: a given or fact – Can be number, statement, or picture • Information: facts or conclusions that have meaning within context – Composed of data that is manipulated
- 7. 7 Data Manipulation • Data is manipulated to make useful information • Survey is common method of collecting data • Raw data is hard to read • Information is more useful to business than data
- 8. 8 Generating Information • A process is manipulation of data • Process usually produces information • Process may produce more data • A piece of information in one context may be considered data in another context
- 9. 9 Generating Information (continued) Figure 1.1: Input-process-output
- 10. 10 Information in Context • Not all information is useful • Useful information is – Relevant – Complete – Accurate
- 11. 11 Information in Context (continued) • Useful information is – Current – Obtained economically (in business)
- 12. 12 Information in Context (continued) Figure 1.2: Characteristics of useful information
- 13. 13 What Is a System? • System: array of components that work together to achieve goal or goals • System – Accepts input – Processes input – Produces output
- 14. 14 What is a system? (continued) • System may have multiple goals • System may contain subsystems • Subsystems have sub-goals that meet main goal • Subsystems transfer output to other subsystems
- 15. 15 What is a system? (continued) • Closed system: has no connections with other systems • Open system: interfaces and interacts with other systems – Often a subsystem of a bigger system • Information system: processes data and produces information
- 16. 16 Information and Managers • Systems thinking: thinking of an organization in terms of subsystems • Database: collection of electronic records • Information systems automate exchange among subsystems • Information map: network of information systems • Information technology: technologies that facilitate construction and maintenance of information systems
- 17. 17 The Benefits of Human-Computer Synergy • Humans are relatively slow and make mistakes • Computers cannot make decisions • Synergy: combining resources to produce greater output
- 18. 18 The Benefits of Human-Computer Synergy (Continued) Figure 1.4: Qualities of humans and computers that contribute to synergy
- 19. 19 Information Systems in Organizations • Computer-based Information system: system with computer at center • Certain trends have made information systems important in business • Organizations lag behind if they do not use information systems
- 20. 20 Components of information systems Figure 1.5: Components of an information system
- 21. 21 The Four Stages of Processing • Input: collect and introduce data to system – Transaction: a business event, usually entered as input • Data processing: perform calculations on input • Output: what is produced by the information system • Storage: vast amounts of data stored on optical discs
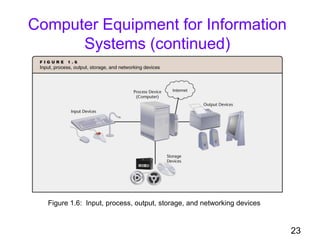
- 22. 22 Computer Equipment for Information Systems • Input devices: receive input • Computer: process data • Output: displays information • Storage devices: store data • Network devices: transfer data
- 23. 23 Computer Equipment for Information Systems (continued) Figure 1.6: Input, process, output, storage, and networking devices
- 24. 24 From Recording Transactions to Providing Expertise: Types of Information Systems • Many types of information systems • Capabilities of applications have been combined and merged • Management Information System: supports planning, control, and making decisions
- 25. 25 Transaction Processing Systems • Most widely used type of system • Records data collected at point where organization interacts with other parties • Encompasses cash registers, ATMs and purchase order systems
- 26. 26 Supply Chain Management Systems • Supply chain: sequence of activities involved in producing products – Activities include marketing, purchasing raw materials, manufacturing, shipping, billing, collecti on, and after-sale services
- 27. 27 Customer Relationship Management Systems • Customer relationship management: managing relations with customers – Used in combination with telephones to provide customer service – Often linked to Web applications that track online transactions
- 28. 28 Business Intelligence Systems • Business Intelligence: gather data to help organization compete – Often contains statistical models – Access large pools of data • Data warehouse: large database that usually store transactional records
- 29. 29 Decision Support and Expert Systems • Decision support system: supports decision- making – Relies on models to produce tables – Extrapolates data to predict outcomes • Expert system: supports knowledge-intensive decision-making – Uses artificial intelligence
- 30. 30 Geographic Information Systems • Geographic information system: ties data to physical locations • Represents data on a map in different formats • May reflect demographic information in addition to geographic • May use information from GPS satellites
- 32. 32 Information Systems in Business Functions • Functional business area: services within a company that support main business – Includes accounting, finance, marketing, and human resources – Part of a larger enterprise system
- 33. 33 Accounting • Information systems help record transactions • Produce periodic statements • Create required reports for law • Create supplemental reports for managers
- 34. 34 Finance • Finance systems facilitate financial planning and business transactions • Tasks include organizing budgets, managing cash flow, analyzing investments, and making decisions
- 35. 35 Marketing • Pinpoint likely customers and promote products • Marketing information systems analyze demand for products in regions and demographic groups – Identify trends in demand for products/services • Web provides opportunity to collect marketing data
- 36. 36 Human Resources • Human resource management systems aid record-keeping – Must keep accurate records – Aids recruiting, selection, placement, and reward analysis • Performance evaluation systems provide grading utilities
- 37. 37 Web Empowered Enterprises • E-commerce: Buying and selling goods and services through Internet • Internet is a vast network of computers connected globally • Web has a profound impact on information systems
- 38. 38 Careers in Information Systems • Information technology professionals are increasingly in demand • Networking, system analyst, software engineering, and database administrator jobs are increasing in demand
- 39. 39 Systems Analyst • System analyst: designs and updates information systems • Involves analyzing system requirements, documenting development efforts, and providing specifications for programmers • Requires communication and presentation skills
- 40. 40 Database Administrator • Database administrator: responsible for databases – Develops and acquires database applications – Must protect privacy of customers and employees – Responsible for securing the database
- 41. 41 Network Administrator • Network administrator: acquires, implements, manages, maintains, trou bleshoots networks • Implements security – Firewalls – Access codes
- 42. 42 Webmaster • Webmaster: creates and maintains Web site • Designs and codes the page • Demand for Webmasters grows as more businesses use Web
- 43. 43 Chief Security Officer • Chief security officer: supervises security of information system • Position exists due to growing threat to information security • Reports to chief information officer
- 44. 44 Chief Information Officer and Chief Technology Officer • Chief information officer: responsible for all aspects of information system – Often the vice president • Chief technology officer: has similar duties as CIO
- 45. 45 Chief Information Officer and Chief Technology Officer (continued) Figure 1.7: Traits of a successful CIO
- 46. 46 Summary • Computer-based information systems pervade almost every aspect of our lives • A system is a set of components that work together to achieve a common goal • Subsystem: a system performs a limited task that produces an end result, which must be combined with other products from other systems to reach an ultimate goal • Data processing has four stages
- 47. 47 Summary (continued) • Any IS that helps in management is a management information system (MIS) • Many different types of MIS • Enterprise application systems (SCM or ERP) tie together different functional areas of a business • ISs are used in accounting, finance, marketing, and human resources
- 48. 48 Summary (continued) • The job prospects for IT professionals are bright • IT has created societal concerns