Mental_emotional PHYSICIAL PSYCHOLOGICAL.pptx
- 2. WHAT IS HEALTH?? Health The combination of your mental/emotional, physical, and social well-being Wellness Overall state of well-being or total health. Heredity Traits that are passed along biologically from both parents to child Culture Beliefs, customs, and behaviors
- 3. 3 ELEMENTS OF HEALTH Physical Health Mental/Emotional Health Social Health
- 4. PHYSICAL HEALTH Parts and systems of your body working together. If you are physically healthy: Helps you cope with stress Have more ENERGY!! Helps you cope with changes What can you do to improve or maintain physical health? Exercise Eat right Sleep
- 5. MENTAL/EMOTIONAL HEALTH The way one feels about self, relates with others and meets the demands of daily life. If you are mentally/emotionally healthy: You are in touch with your feelings and express them in an appropriate way. What can you do to improve or maintain your mental/emotional health? Journal writing Spending time with family Talking to trusted friends Be optimistic Doing well in school
- 6. SOCIAL HEALTH The way one works with others If you are socially healthy: You make friends You keep friends You cooperate with others (school, work, play, etc) You communicate! – Verbal vs. Non-verbal What can you do to improve or maintain your social health? Communicate!! Look at people when you communicate. Be positive – smile a lot! Have good friends
- 7. LIFESTYLE FACTORS Get between 7 & 8 hours of sleep per night. Eat nutritious food from the various food groups each day. Refrain from smoking and using tobacco products. EAT BREAKFAST! Do 60-90 minutes of activity every day. Do not use alcohol or other drugs Maintain your recommended weight for your height and age.
- 8. SELF-ESTEEM How one feels about ones self. Self-loving behavior: a behavior that shows a person believes him/herself to be worthwhile and loveable. “If you can’t love yourself how in the heck are you going to love somebody else.” Self-centered behavior: Fulfilling needs and wishes with little regard for any one else. Self-destructive behavior: behavior in which a person harms him-herself. How do we build our self-esteem??
- 9. DEVELOPING POSITIVE SELF-ESTEEM Set goals and make plans to reach them. Develop a skill or talent. Make a list of things you do well. Work to do your best in school. Be involved in school clubs and community activities. Develop a trusting relationship with at least one adult. Choose friends who encourage others to do their best. Spend time with friends and adults who provide support. Volunteer to help another person. Keep a neat appearance.
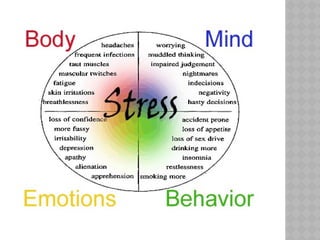
- 10. STRESS Definition: The body’s response to a demand It depends on how you react to it! Eustress When stress results from something good and you react in a positive manner. “Positive stress” Provides energy and motivation Makes you more creative, alert, assertive & dedicated to a task Makes you feel good about yourself Distress When stress is caused by something bad or if you react in a negative manner. “Negative stress” Interferes with schoolwork, home life, relationships with peers. Leads to health problems
- 11. STRESSORS Situations that cause stress Family relationships School work Peer groups Fatigue Discrimination Injury Sickness ETC. HOW WILL YOU REACT?
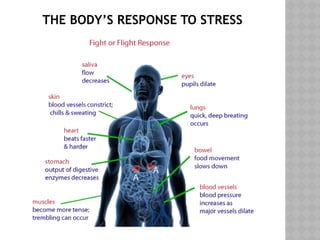
- 12. REACTING TO STRESS Physical reactions to stress Fight-or-flight response Natural protective mode of your body Adrenaline Chemical that gives you energy to perform physical acts in an emergency. Stress causes body functions to change Blood circulation increases Nutrients (energy) in the blood increases. Muscles are strengthened Breathing becomes more rapid to provide more oxygen Senses become more alert. e.g. pupils dilate to sharpen vision.
- 13. THE BODY’S RESPONSE TO STRESS
- 15. STRESS MANAGEMENT Develop resistance to stress Get fit! Get enough sleep Develop a good nutritional diet Stay away from sugar and caffeine Develop strategies to reduce stress Don’t sweat the small stuff! Set goals Practice time management
- 16. STRESS MANAGEMENT Develop positive coping strategies Practice self-talk “Is it worth it?” “Getting angry never solves anything.” “Don’t do something you’ll regret.” Seek temporary relief Exercise, yoga, daydreaming, etc. Recognize symptoms of stress Identify stressful situations Support groups are helpful Parents, friends, teachers, coaches, counselors, etc. Progressive relaxation “Untense” your muscles
- 17. STRESS MANAGEMENT Negative Coping Techniques Being overemotional Fighting “It’s not my fault” Blurting out negative statements Impatience Avoidance Being afraid to talk it out Shyness Not volunteering Avoid speaking in front of people Drugs and alcohol Causes mental and physical problems Habit forming Lose efficiency and motivation Only covers up stress; the problem is still there.
- 18. For each of the following stressful situations, find out if this is Eustress or Distress. What types of stressors you think can cause this stress. What are 2 positive coping strategies and 2 negative coping strategies related to this specific stress? How would you handle this stressful situations?
- 19. 1) You and your family are moving away from home because one of your parents got a fantastic new job on the east coast. You have to move within the month and it is your Freshman year of high school.
- 20. 2) You have an older sibling and they just get engaged and want you to be their best man or bridesmaid.
- 21. 3) You and your two best friends are in turmoil. One of them is mad at the other because they decided to hang out with a different group from a class instead of hanging out with you both. You don’t mind but your other friend is super mad over it. They aren’t talking to each other and are looking to you to mend things.
- 22. 4) Grade checks just came in for your sport and you have a 64 percent in your class. Your coach tells you if you don’t get your grades up in 3 days you are not going to be able to play in the championship game.
- 23. 5) Even though you aren’t 18, you won 25,000$ in the lottery. Your parents want you to think about putting the money towards something good, you don’t know what you want to do because your friends all think you should just go on a shopping spree and spend it all.