Module 2 | Object Oriented Programming with C++ | Basics of C++
- 1. Module-2 C++ Basics Krishna Engineering College, Ghaziabad 1 Mr. Aditya Tandon CSE III Year Object Oriented Programming with C++ Module-2 C++ Basics 9999110872/ 9999110887/ 9999007371 aditya.tandon@krishnacollege.ac.in www.krishnacollege.ac.in
- 2. Module-2 C++ Basics Krishna Engineering College, Ghaziabad 2 Simple C++ Program
- 3. Module-2 C++ Basics Krishna Engineering College, Ghaziabad 3 I like C++ so much I will score good marks in C++ A Simple C++ Program #include <iostream> //include header file using namespace std; int main() { cout << "Hello World"; // C++ statement return 0; } iostream is just like we include stdio.h in c program. It contains declarations for the identifier cout and the insertion operator <<. iostream should be included at the beginning of all programs that use input/output statements.
- 4. Module-2 C++ Basics Krishna Engineering College, Ghaziabad 4 I like C++ so much I will score good marks in C++ A Simple C++ Program (Cont…) #include <iostream> //include header file using namespace std; int main() { cout << "Hello World"; // C++ statement return 0; } A namespace is a declarative region. A namespace is a part of the program in which certain names are recognized; outside of the namespace they’re unknown. namespace defines a scope for the identifies that are used in a program. using and namespace are the keywords of C++.
- 5. Module-2 C++ Basics Krishna Engineering College, Ghaziabad 5 I like C++ so much I will score good marks in C++ A Simple C++ Program (Cont…) #include <iostream> //include header file using namespace std; int main() { cout << "Hello World"; // C++ statement return 0; } std is the namespace where ANSI C++ standard class libraries are defined. Various program components such as cout, cin, endl are defined within std namespace. If we don’t use the using directive at top, we have to add the std followed by :: in the program before identifier. std::cout << “Hello World”;
- 6. Module-2 C++ Basics Krishna Engineering College, Ghaziabad 6 I like C++ so much I will score good marks in C++ A Simple C++ Program (Cont…) #include <iostream> //include header file using namespace std; int main() { cout << "Hello World"; // C++ statement return 0; } In C++, main() returns an integer type value. Therefore, every main() in C++ should end with a return 0; statement; otherwise error will occur. The return value from the main() function is used by the runtime library as the exit code for the process.
- 7. Module-2 C++ Basics Krishna Engineering College, Ghaziabad 7 I like C++ so much I will score good marks in C++ Insertion Operator << The operator << is called the insertion operator. It inserts the contents of the variable on its right to the object on its left. The identifier cout is a predefined object that represents standard output stream in C++. Here, Screen represents the output. We can also redirect the output to other output devices. The operator << is used as bitwise left shift operator also. Output Using Insertion Operator cout << "Hello World";
- 8. Module-2 C++ Basics Krishna Engineering College, Ghaziabad 8 I like C++ so much I will score good marks in C++ Program: Basic C++ program Write a C++ Program to print following Name: Darshan City: Rajkot Country: India
- 9. Module-2 C++ Basics Krishna Engineering College, Ghaziabad 9 I like C++ so much I will score good marks in C++ Program: Basic C++ program #include <iostream> using namespace std; int main() { cout << "Name: Darshan"; cout << "City: Rajkot"; cout << "Country: India"; return 0; } Output Name: DarshanCity: RajkotCountry: India
- 10. Module-2 C++ Basics Krishna Engineering College, Ghaziabad 10 I like C++ so much I will score good marks in C++ Program: Basic C++ program(Cont…) #include <iostream> using namespace std; int main() { cout << "Name: Darshann"; cout << "City: Rajkotn"; cout << "Country: India"; return 0; } Output Name: Darshan City: Rajkot Country: India #include <iostream> using namespace std; int main() { cout << "Name: Darshan"<<endl; cout << "City: Rajkot"<<endl; cout << "Country: India"<<endl; return 0; } The endl manipulator and n has same effect. Both inserts new line to output. But, difference is endl immediate flush to the output while n do not.
- 11. Module-2 C++ Basics Krishna Engineering College, Ghaziabad 11 I like C++ so much I will score good marks in C++ Extraction Operator >> The identifier cin is a predefined object that represents standard input stream in C++. Here, standard input stream represents the Keyboard. The operator >> is used as bitwise right shift operator also. The operator >> is called the extraction operator. It extracts (or takes) the value from keyboard and assigns it to the variable on its right. KeyBoard cin number1 Object Extraction Operator Variable >> cin >> number1;
- 12. Module-2 C++ Basics Krishna Engineering College, Ghaziabad 12 I like C++ so much I will score good marks in C++ Program: Basic C++ program #include<iostream> using namespace std; int main() { int number1,number2; cout<<"Enter First Number: "; cin>>number1; //accept first number cout<<"Enter Second Number: "; cin>>number2; //accept first number cout<<"Addition : "; cout<<number1+number2; //Display Addition return 0; }
- 13. Module-2 C++ Basics Krishna Engineering College, Ghaziabad 13 C++ Tokens
- 14. Module-2 C++ Basics Krishna Engineering College, Ghaziabad 14 I like C++ so much I will score good marks in C++ C++ Tokens The smallest individual unit of a program is known as token. C++ has the following tokens: − Keywords − Identifiers − Constants − Strings − Special Symbols − Operators #include <iostream> using namespace std; int main() { cout << "Hello World"; return 0; }
- 15. Module-2 C++ Basics Krishna Engineering College, Ghaziabad 15 I like C++ so much I will score good marks in C++ Keywords and Identifier C++ reserves a set of 84 words for its own use. These words are called keywords (or reserved words), and each of these keywords has a special meaning within the C++ language. Identifiers are names that are given to various user defined program elements, such as variable, function and arrays. Some of Predefined identifiers are cout, cin, main We cannot use Keyword as user defined identifier.
- 16. Module-2 C++ Basics Krishna Engineering College, Ghaziabad 16 I like C++ so much I will score good marks in C++ Keywords in C++ asm double new switch auto else operator template break enum private this case extern protected throw catch float public try char for register typeof class friend return union const goto short unsigned continue if signed virtual default inline sizeof void delete int static volatile do long struct while
- 17. Module-2 C++ Basics Krishna Engineering College, Ghaziabad 17 I like C++ so much I will score good marks in C++ Rules for naming identifiers in C++ 1. First Character must be an alphabet or underscore. 2. It can contain only letters(a..z A..Z), digits(0 to 9) or underscore(_). 3. Identifier name cannot be keyword. 4. Only first 31 characters are significant.
- 18. Module-2 C++ Basics Krishna Engineering College, Ghaziabad 18 I like C++ so much I will score good marks in C++ Valid, Invalid Identifiers 1) Darshan 2) A 3) Age 4) void 5) MAX-ENTRIES 6) double 7) time 8) G 9) Sue's 10) return 11) cout 12) xyz123 13) part#2 14) "char" 15) #include 16) This_is_a_ 17) _xyz 18) 9xyz 19) main 20) mutable 21) double 22) max?out Valid Valid Valid Reserved word Invalid Reserved word Valid Valid Invalid Reserved word Standard identifier Valid Invalid Invalid Invalid Valid Valid Invalid Standard identifier Reserved word Reserved word Invalid
- 19. Module-2 C++ Basics Krishna Engineering College, Ghaziabad 19 I like C++ so much I will score good marks in C++ Constants / Literals Constants in C++ refer to fixed values that do not change during execution of program. CONSTANTS INTEGER CONSTANTS i.e. 123,-321, 6543 REAL CONSTANTS i.e. 0.0083, -0.75 NUMERIC CONSTANTS SINGLE CHARACTER CONSTANTS i.e. ‘5’, ‘X’, ‘;’ STRING CONSTANTS i.e. “Hello”, “197” CHARACTER CONSTANTS
- 20. Module-2 C++ Basics Krishna Engineering College, Ghaziabad 20 C++ Operators
- 21. Module-2 C++ Basics Krishna Engineering College, Ghaziabad 21 I like C++ so much I will score good marks in C++ C++ Operators All C language operators are valid in C++. 1. Arithmetic operators (+, - , *, /, %) 2. Relational operators (<, <=, >, >=, ==, !=) 3. Logical operators (&&, ||, !) 4. Assignment operators (+=, -=, *=, /=) 5. Increment and decrement operators (++, --) 6. Conditional operators (?:) 7. Bitwise operators (&, |, ^, <<, >>) 8. Special operators ()
- 22. Module-2 C++ Basics Krishna Engineering College, Ghaziabad 22 I like C++ so much I will score good marks in C++ Arithmetic Operators Operator example Meaning + a + b Addition - a – b Subtraction * a * b Multiplication / a / b Division % a % b Modulo division- remainder
- 23. Module-2 C++ Basics Krishna Engineering College, Ghaziabad 23 I like C++ so much I will score good marks in C++ Relational Operators Operator Meaning < Is less than <= Is less than or equal to > Is greater than >= Is greater than or equal to == Equal to != Not equal to
- 24. Module-2 C++ Basics Krishna Engineering College, Ghaziabad 24 I like C++ so much I will score good marks in C++ Logical Operators Operator Meaning && Logical AND || Logical OR ! Logical NOT a b a && b a || b true true true true true false false true false true false true false false false false a && b : returns false if any of the expression is false a || b : returns true if any of the expression is true
- 25. Module-2 C++ Basics Krishna Engineering College, Ghaziabad 25 I like C++ so much I will score good marks in C++ Assignment operator We assign a value to a variable using the basic assignment operator (=). Assignment operator stores a value in memory. The syntax is leftSide = rightSide ; Always it is a variable identifier. It is either a literal | a variable identifier | an expression. Literal: ex. i = 1; Variable identifier: ex. start = i; Expression: ex. sum = first + second;
- 26. Module-2 C++ Basics Krishna Engineering College, Ghaziabad 26 I like C++ so much I will score good marks in C++ Assignment Operators (Shorthand) Syntax: leftSide Op= rightSide ; Simple assignment operator Shorthand operator a = a+1 a += 1 a = a-1 a -= 1 a = a * (m+n) a *= m+n a = a / (m+n) a /= m+n a = a % b a %= b It is an arithmetic operator. Ex: x=x+3; x+=3;
- 27. Module-2 C++ Basics Krishna Engineering College, Ghaziabad 27 I like C++ so much I will score good marks in C++ Increment and Decrement Operators Increment ++ The ++ operator used to increase the value of the variable by one Decrement ─ ─ The ─ ─ operator used to decrease the value of the variable by one Example: x=100; x++; After the execution the value of x will be 101. Example: x=100; x--; After the execution the value of x will be 99.
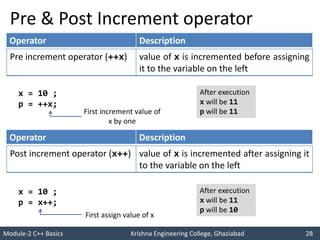
- 28. Module-2 C++ Basics Krishna Engineering College, Ghaziabad 28 I like C++ so much I will score good marks in C++ Pre & Post Increment operator Operator Description Pre increment operator (++x) value of x is incremented before assigning it to the variable on the left x = 10 ; p = ++x; After execution x will be 11 p will be 11 First increment value of x by one Operator Description Post increment operator (x++) value of x is incremented after assigning it to the variable on the left x = 10 ; p = x++; After execution x will be 11 p will be 10 First assign value of x
- 29. Module-2 C++ Basics Krishna Engineering College, Ghaziabad 29 I like C++ so much I will score good marks in C++ What is the output of this program? #include <iostream> using namespace std; int main () { int x, y; x = 5; y = ++x * ++x; cout << x << y; x = 5; y = x++ * ++x; cout << x << y; } (A) 749735 (B) 736749 (C) 367497 (D) none of the mentioned
- 30. Module-2 C++ Basics Krishna Engineering College, Ghaziabad 30 I like C++ so much I will score good marks in C++ Conditional Operator Syntax: exp1 ? exp2 : exp3 Working of the ? Operator: exp1 is evaluated first • if exp1 is true(nonzero) then - exp2 is evaluated and its value becomes the value of the expression • If exp1 is false(zero) then - exp3 is evaluated and its value becomes the value of the expression Ex: m=2; n=3; r=(m>n) ? m : n; Ex: m=2; n=3; r=(m<n) ? m : n; Value of r will be 3 Value of r will be 2
- 31. Module-2 C++ Basics Krishna Engineering College, Ghaziabad 31 I like C++ so much I will score good marks in C++ Bitwise Operator Operator Meaning & Bitwise AND | Bitwise OR ^ Bitwise exclusive OR << Shift left >> Shift right
- 32. Module-2 C++ Basics Krishna Engineering College, Ghaziabad 32 I like C++ so much I will score good marks in C++ Bitwise Operator Examples 8 = 1000 (In Binary) 6 = 0110 (In Binary) Bitwise & (AND) int a=8,b=6,c; c = a & b; cout<<"Output ="<< c; Output = 0 Bitwise | (OR) int a=8,b=6,c; c = a | b; cout<<"Output ="<< c; Output = 14 Bitwise << (Shift Left) int a=8,b=6,c; c = a << 1; cout<<"Output ="<< c; Output = 16 left shifting is the equivalent of multiplying a by a power of two Bitwise >> (Shift Right) int a=8,b=6,c; c = a >> 1; cout<<"Output ="<< c; Output = 4 right shifting is the equivalent of dividing a by a power of two
- 33. Module-2 C++ Basics Krishna Engineering College, Ghaziabad 33 I like C++ so much I will score good marks in C++ New Operators in C++ :: Scope Resolution ::* Pointer-to-member declarator ->* Pointer-to-member operator .* Pointer-to-member operator delete Memory release operator endl Line feed operator new Memory allocation operator setw Field width operator It allows to access to the global version of variable Declares a pointer to a member of a class To access pointer to class members To access pointer to data members of class Deallocates memory at run time It is a manipulator causes a linefeed to be inserted Allocates memory at run time It is a manipulator specifies a field width for printing value
- 34. Module-2 C++ Basics Krishna Engineering College, Ghaziabad 34 Scope Resolution Operator
- 35. Module-2 C++ Basics Krishna Engineering College, Ghaziabad 35 I like C++ so much I will score good marks in C++ Scope Resolution Operator(::) .... .... { int x=10; .... .... { int x=1; .... .... } .... } Block-2 Block-1 Declaration of x in inner block hides declaration of same variable declared in an outer block. Therefore, in this code both variable x refers to different data. In C language, value of x declared in Block-1 is not accessible in Block-2. In C++, using scope resolution operator (::), value of x declared in Block-1 can be accessed in Block-2.
- 36. Module-2 C++ Basics Krishna Engineering College, Ghaziabad 36 #include <iostream> using namespace std; int m=10; int main() { int m=20; { int k=m; int m=3; cout<<"we are in inner blockn"; cout<<"k="<<k<<endl; cout<<"m="<<m<<endl; cout<<"::m="<<::m<<endl; } cout<<"we are in outer blockn"; cout<<"m="<<m<<endl; cout<<"::m="<<::m<<endl; return 0; } Global declaration of variable m variable m declared , local to main variable m declared again local to inner block Output: we are in inner block k=20 m=3 ::m=10 we are in outer block m=20 ::m=10 Scope resolution example
- 37. Module-2 C++ Basics Krishna Engineering College, Ghaziabad 37 C++ Data Types
- 38. Module-2 C++ Basics Krishna Engineering College, Ghaziabad 38 I like C++ so much I will score good marks in C++ Basic Data types C++ datatypes User-defined Built-in Derived Integral Void Floating structure union class enumeration array function pointer reference int char float double
- 39. Module-2 C++ Basics Krishna Engineering College, Ghaziabad 39 I like C++ so much I will score good marks in C++ Built in Data types Data Type Size (bytes) Range char 1 -128 to 127 unsigned char 1 0 to 255 short or int 2 -32,768 to 32,767 unsigned int 2 0 to 65535 long 4 -2147483648 to 2147483647 unsigned long 4 0 to 4294967295 float 4 3.4e-38 to 3.4e+308 double 8 1.7e-308 to 1.7e+308 long double 10 3.4e-4932 to 1.1e+4932
- 40. Module-2 C++ Basics Krishna Engineering College, Ghaziabad 40 Type Conversion
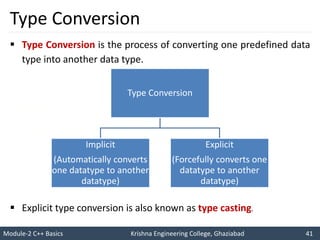
- 41. Module-2 C++ Basics Krishna Engineering College, Ghaziabad 41 I like C++ so much I will score good marks in C++ Type Conversion Type Conversion is the process of converting one predefined data type into another data type. Type Conversion Implicit (Automatically converts one datatype to another datatype) Explicit (Forcefully converts one datatype to another datatype) Explicit type conversion is also known as type casting.
- 42. Module-2 C++ Basics Krishna Engineering College, Ghaziabad 42 I like C++ so much I will score good marks in C++ Type Conversion(Cont…) int a; double b=2.55; a = b; // implicit type conversion cout << a << endl; // this will print 2 a = int(b); //explicit type conversion cout << a << endl; // this will print 2
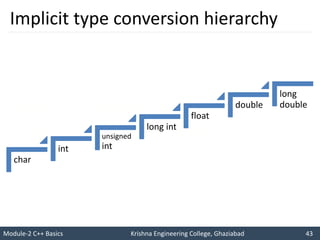
- 43. Module-2 C++ Basics Krishna Engineering College, Ghaziabad 43 I like C++ so much I will score good marks in C++ Implicit type conversion hierarchy char int unsigned int long int float double long double
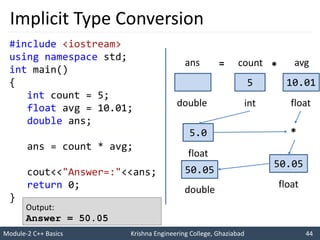
- 44. Module-2 C++ Basics Krishna Engineering College, Ghaziabad 44 I like C++ so much I will score good marks in C++ Implicit Type Conversion #include <iostream> using namespace std; int main() { int count = 5; float avg = 10.01; double ans; ans = count * avg; cout<<"Answer=:"<<ans; return 0; } Output: Answer = 50.05 5 10.01 * = double int float ans count avg 5.0 float 50.05 float 50.05 double *
- 45. Module-2 C++ Basics Krishna Engineering College, Ghaziabad 45 I like C++ so much I will score good marks in C++ Type Casting In C++ explicit type conversion is called type casting Syntax type-name (expression) //C++ notation Example average = sum/(float) i; //C notation average = sum/float (i); //C++ notation
- 46. Module-2 C++ Basics Krishna Engineering College, Ghaziabad 46 #include <iostream> using namespace std; int main() { int a, b, c; a = 19.99 + 11.99; b = (int) 19.99 + (int) 11.99; c = int (19.99) + int (11.99); cout << "a = " << a << ", b = " << b; cout << ", c = " << c << endl; char ch = 'Z'; cout << "The code for " << ch << " is "; cout << int(ch) << endl; return 0; } Output: a = 31, b = 30, c = 30 The code for Z is 90 Type Casting Example //adds the values as float // then converts the result to int // old C syntax // new C++ syntax //print as char //print as int
- 47. Module-2 C++ Basics Krishna Engineering College, Ghaziabad 47 Reference Variable
- 48. Module-2 C++ Basics Krishna Engineering College, Ghaziabad 48 I like C++ so much I will score good marks in C++ Reference Variable A reference provides an alias or a different name for a variable. One of the most important uses for references is in passing arguments to functions. int a=5; int &ans = a; cout<<"a="<<a<<endl; cout<<"&a="<<&a<<endl; cout<<"ans="<<ans<<endl; cout<<"&ans="<<&ans<<endl; ans++; cout<<"a="<<a<<endl; cout<<"ans="<<ans<<endl; declares variable a declares ans as reference to a OUTPUT a=5 &a=0x6ffe34 ans=5 &ans=0x6ffe34 a=6 ans=6 Its necessary to initialize the Reference at the time of declaration
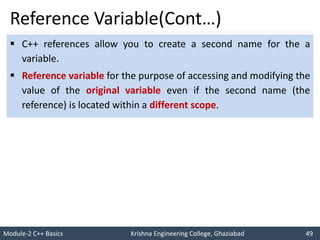
- 49. Module-2 C++ Basics Krishna Engineering College, Ghaziabad 49 I like C++ so much I will score good marks in C++ Reference Variable(Cont…) C++ references allow you to create a second name for the a variable. Reference variable for the purpose of accessing and modifying the value of the original variable even if the second name (the reference) is located within a different scope.
- 50. Module-2 C++ Basics Krishna Engineering College, Ghaziabad 50 I like C++ so much I will score good marks in C++ Reference Vs Pointer Pointers int *p = &i; References int i; int &r = i; i r addr p addr A pointer is a variable which stores the address of another variable. A reference is a variable which refers to another variable.
- 51. Module-2 C++ Basics Krishna Engineering College, Ghaziabad 51 Enumeration
- 52. Module-2 C++ Basics Krishna Engineering College, Ghaziabad 52 I like C++ so much I will score good marks in C++ Enumeration (A user defined Data Type) An enumeration is set of named integer constants. Enumerations are defined much like structures. enum days{Sun,Mon,Tues,Wed,Thur,Fri,Sat}; Keyword Tag name Integer Values for symbolic constants 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 Above statement creates days the name of datatype. By default, enumerators are assigned integer values starting with 0. It establishes Sun, Mon… and so on as symbolic constants for the integer values 0-6.
- 53. Module-2 C++ Basics Krishna Engineering College, Ghaziabad 53 I like C++ so much I will score good marks in C++ Enumeration Behaviour(Cont…) enum coin { penny, nickel, dime, quarter=100, half_dollar, dollar}; The values of these symbols are penny 0 nickel 1 dime 2 quarter 100 half_dollar 101 dollar 102
- 54. Module-2 C++ Basics Krishna Engineering College, Ghaziabad 54 Enumeration Behaviour enum days{ sun, mon, tue, wed, thu, fri, sat }; days today; today = tue; today = 6; today++; today = mon + fri; int num = sat; num = 5 + mon; variable today declared of type days Valid, because tue is an enumerator. Value 2 will be assigned in today Invalid, because 6 is not an enumerator Invalid, today is of type days. We can not apply ++ to structure variable also Invalid Valid, days data type converted to int, value 6 will be assigned to num Valid, mon converted to int with value 1
- 55. Module-2 C++ Basics Krishna Engineering College, Ghaziabad 55 Control Structures
- 56. Module-2 C++ Basics Krishna Engineering College, Ghaziabad 56 I like C++ so much I will score good marks in C++ Control Structures The if statement: • Simple if statement • if…else statement • else…if ladder • if…else nested The switch statement : The do-while statement: An exit controlled loop The while Statement: An entry controlled loop The for statement: An entry controlled loop
- 57. Module-2 C++ Basics Krishna Engineering College, Ghaziabad 57 Thank You
Editor's Notes
- #4: On startup, control always start from main(). If there is no function called main() in your program, a linker error will be generated. Majority of the Statements in c++ are identical to statements in c. Iostream is morden style header which is defined by standard c++. Contains declarations for cout identifier and << operator. #include tells compiler to ass the sourcefile iostream to first.cpp file before compiling.
- #5: C++ program
- #37: :: operator means to use the global version of that variable.
- #42: Type conversion occurs when the expression has data of mixed data types. Implicit Type Conversion is the conversion performed by the compiler without programmer’s intervention. Type Conversion is the process of converting one predefined type into another type. and type Casting is the converting one predefined type into another type forcefully.
- #53: It is a way for attaching names to numbers Enum keyword automatically enumerates a list of words by assigning the values 0,1,2 and so on Here the tag name days become a new data type. By using this tag name you can declare new variables
- #57: Used when control is transferred to one point to many possible points.