Mule
- 1. Mule Enterprise Service Bus
- 3. 3 Why we use Enterprise Service Bus? ESB as Single Point of Access ESB as Transaction Manager ESB as Security Manager
- 4. 4 Why we use Mule Enterprise Service Bus? Support for more than 30 protocols and technologies Simplified POJO-based programming model leveraging existing developer skill-sets for fast deployment Support for multiple access points such as JMS, JDBC, and SOAP No reliance on vendor-specific proprietary protocols Ease of use – services can be configured easily in one configuration file. Extensive data transformations out of the box Small footprint: memory and disk, no application server required Integration platform model: highly modular, easily extensible codebase - implement proven patterns and build streamlined solutions to unique challenges The open source advantage: large community of real-world integration experts and developers using Mule and contributing to codebase
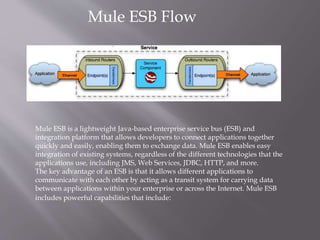
- 5. Mule ESB Flow Mule ESB is a lightweight Java-based enterprise service bus (ESB) and integration platform that allows developers to connect applications together quickly and easily, enabling them to exchange data. Mule ESB enables easy integration of existing systems, regardless of the different technologies that the applications use, including JMS, Web Services, JDBC, HTTP, and more. The key advantage of an ESB is that it allows different applications to communicate with each other by acting as a transit system for carrying data between applications within your enterprise or across the Internet. Mule ESB includes powerful capabilities that include:
- 6. 6 Software Requirement for Mule Application Operating System- Windows XP SP2, Windows 2000, Windows 2003 Server (32- bit if using the Java Service Wrapper), Linux, Solaris, AIX, HP-UX, and Mac OSX. Application Servers- Tomcat, JBoss,WebSphere, WebLogic, and Jetty. Messaging- Any JMS vendor; users have reported integration via Active MQ, Open MQ, TIBCO EMS, TIBCO Rendezvous, Oracle AQ, and IBM Web Sphere MQ Java- JDK 1.5 and 1.6
- 7. Mule use to transport to receive and send message from and to all kind of source including Java Messaging service (JMS), HTTP, FTP, TCP/IP,SMTP,POP3 and file. Another important concept of mule is the service definitions which consist some specific layers that can be solve the integration of multiple protocol and application’s communication problems. Application Channel Message Receiver Connector Transformers Inbound Routers Component Outbound Routers Message Dispatcher Mule Component Overview
- 8. Flow is a Message Source followed by a chain of message processors Each processors is invoked in a sequence Processor operate a message
- 9. What is Message Processor Message processors are responsible for processing the received message. These message processors are categorized by function: Components: perform business logic & are typically application specific Transformers: transform the message Filters: accept/reject messages Routers: control the message flow Endpoints: send/receive messages over a transport
- 10. What is Sub Flow Sub flow is a private flow which is not visible outside the current flow A sub flow will not have a Message Source.
- 11. Mule Message The Data received from an endpoint is packaged into an object that implements Mule Message interface A Message contains: A series of properties that vary depending on the transport Variables – Session and Flow The data as the payload of the Mule Message. If required, a series of attachments that can accompany the message.
- 12. Mule Message Structure The Mule message is the data that passes through an application via one or more flows. It consists of two main parts: The message header, which contains metadata about the message The message payload, which contains your business-specific data.
- 13. Mule Message Properties and Variables Message header consists of properties which provide useful information about the message variables represent data about a message Properties have two main scopes: inbound and outbound.Inbound Property
- 14. Inbound Message properties are immutable Automatically generated by the message source and cannot be set or manipulated by the user. They contain metadata specific to the message source that prevents scrambling of data formats or other processing mishaps later in the message's lifecycle. A message retains its inbound properties only for the duration of the flow; when a message passes out of a flow, its inbound properties do not follow it Inbound Message properties
- 15. They contain metadata similar to that of an inbound property, but an outbound property is applied after the message enters the flow Outbound properties can be set automatically by Mule or a user can set them by manually inserting one or more transformer elements in the flow. If the message is passed to a new flow via a flow- ref rather than a connector, the outbound properties remain outbound properties rather than being converted to inbound properties Outbound Message Properties