Natural science 4º a
- 1. MODULE 1. LIVING THINGS
- 3. All living things carry out on the three life processes of nutrition, interaction and reproduction but in different ways.
- 8. Sharks can fly. Birds have scales. Plants can move around. Trees are shorter than bushes. Lizards have fins. Animals make their own food.
- 11. They can´t move around. They make their own food.
- 12. Grasses+ bushes+ trees.
- 15. They can move around. They eat other living things.
- 18. They are similar to plants in that they can´t move around. They don´t make their own food. Fungi eat the reamins of living things or grow and feed on things that are still living. Mushrooms, mould and yeast are all fungi.
- 19. Mushrooms
- 23. All living things are made up of cells. Different cells have different functions. Most living things are made up of many types of different cells but some, such us bacteria, have just one cell.
- 26. 97 % of all animals are invertebrates and they live almost everywhere. Molluscs, Jellyfish, Sponges, Echinoderms, Annelids and Arthropods…
- 27. They have a soft muscular body, often protected by a hard shell. Some live on land, but most, like mussels and octopuses live in the sea.
- 29. They live in the sea. They have a soft body called umbrella and often have long tentacles.
- 30. They live in the sea. They have soft bodies covered with little holes. They stay on the seabed and take in oxygen and food through the holes.
- 32. They live in the sea. They´re are protected from predators by hard skin or spikes and are often brightly coloured.
- 33. They have a long, soft body divided into segments. A very important annelid is the earthworm.
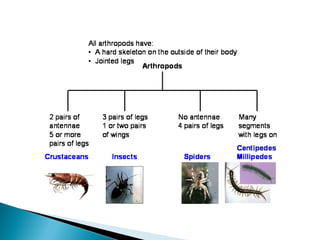
- 34. Almost all animals on Earth are arthropods, The biggest group is insects. They live in water, on land, in the air and underground. They have a head, thorax and abdomen, jointed legs and a protective exoskeleton.
- 37. Respiration, Reproduction, Nutrition.
- 41. All animals need oxygen to live. Mammals, reptiles and birds get oxygen from the air. They breathe with lungs. Fish use gills to get oxygen from the water. Amphibians have gills when they are young and live in water and later develop lungs to live on land.
- 42. Reproduction. All mammals are born directly from their mother. They are viviparous.
- 43. All other groups reproduce by laying eggs. They are oviparous.
- 46. Most vertebrate animals are omnivores or carnivores. Some mammals and fish and few birds are herbivores.
- 51. Decomposer: When and animal dies, bacteria and fungi break down the animal´s remains and turn them into nutrients.
- 52. Sexual reproduction. In sexual reproduction pollen goes from the stamen of one flower to the pistil of a different, or the same, flower.
- 56. The pollen joins an ovule to make a seed. This is called fertilisation. The pistil grows around a seed into a fruit. The fruit falls to the ground and the seed grows into a new plant.
- 57. In asexual reproduction there are no flowers or fertilisation.
- 60. Every animal, including humans, needs oxygen to live. Plants give us oxygen. Plants absorb nutrients and water from the soil and carbon dioxide from the air during the day and use these to make their own food. In this processs they release oxygen into the aire for us to breathe.
- 64. A habitat is defined by the amount of light and water, the temperature and the type of soil. The combination of the habitat and its community of living things is called an ecosystem.
- 65. Parts of a plant.
- 66. The flowers make seeds for reproduction.
- 67. Water, minerals and food pass through the stem. The stem also holds the plant up.
- 68. Roots absorb water and minerals from the soil. They also fix the plant to the soil.
- 69. Food is made in the leaves. The pistil grows around the seeds into a fruit.
- 72. Plants that produce seeds. Plants that produce spores. Mosses and ferns are non-flowering plants that produce spores.