Normalization
- 1. Normalization By Jason Park Fall 2005 CS157A
- 2. Database Normalization Database normalization is the process of removing redundant data from your tables in to improve storage efficiency, data integrity, and scalability. In the relational model, methods exist for quantifying how efficient a database is. These classifications are called normal forms (or NF ), and there are algorithms for converting a given database between them. Normalization generally involves splitting existing tables into multiple ones, which must be re-joined or linked each time a query is issued.
- 3. History Edgar F. Codd first proposed the process of normalization and what came to be known as the 1st normal form in his paper A Relational Model of Data for Large Shared Data Banks Codd stated: “ There is, in fact, a very simple elimination procedure which we shall call normalization. Through decomposition nonsimple domains are replaced by ‘ domains whose elements are atomic (nondecomposable) values.’”
- 4. Normal Form Edgar F. Codd originally established three normal forms: 1NF, 2NF and 3NF. There are now others that are generally accepted, but 3NF is widely considered to be sufficient for most applications. Most tables when reaching 3NF are also in BCNF (Boyce-Codd Normal Form).
- 5. Table 1 Title Author1 Author2 ISBN Subject Pages Publisher Database System Concepts Abraham Silberschatz Henry F. Korth 0072958863 MySQL, Computers 1168 McGraw-Hill Operating System Concepts Abraham Silberschatz Henry F. Korth 0471694665 Computers 944 McGraw-Hill
- 6. Table 1 problems This table is not very efficient with storage. This design does not protect data integrity. Third, this table does not scale well.
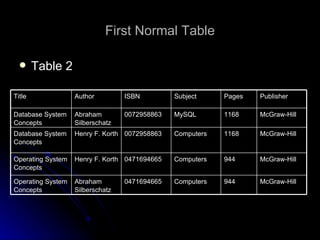
- 7. First Normal Form In our Table 1, we have two violations of First Normal Form: First, we have more than one author field, Second, our subject field contains more than one piece of information. With more than one value in a single field, it would be very difficult to search for all books on a given subject.
- 8. First Normal Table Table 2 Title Author ISBN Subject Pages Publisher Database System Concepts Abraham Silberschatz 0072958863 MySQL 1168 McGraw-Hill Database System Concepts Henry F. Korth 0072958863 Computers 1168 McGraw-Hill Operating System Concepts Henry F. Korth 0471694665 Computers 944 McGraw-Hill Operating System Concepts Abraham Silberschatz 0471694665 Computers 944 McGraw-Hill
- 9. We now have two rows for a single book. Additionally, we would be violating the Second Normal Form… A better solution to our problem would be to separate the data into separate tables- an Author table and a Subject table to store our information, removing that information from the Book table:
- 10. Subject Table Author Table Book Table Subject_ID Subject 1 MySQL 2 Computers Author_ID Last Name First Name 1 Silberschatz Abraham 2 Korth Henry ISBN Title Pages Publisher 0072958863 Database System Concepts 1168 McGraw-Hill 0471694665 Operating System Concepts 944 McGraw-Hill
- 11. Each table has a primary key, used for joining tables together when querying the data. A primary key value must be unique with in the table (no two books can have the same ISBN number), and a primary key is also an index, which speeds up data retrieval based on the primary key. Now to define relationships between the tables
- 12. Relationships Book_Author Table Book_Subject Table ISBN Author_ID 0072958863 1 0072958863 2 0471694665 1 0471694665 2 ISBN Subject_ID 0072958863 1 0072958863 2 0471694665 2
- 13. Second Normal Form As the First Normal Form deals with redundancy of data across a horizontal row, Second Normal Form (or 2NF) deals with redundancy of data in vertical columns. As stated earlier, the normal forms are progressive, so to achieve Second Normal Form, the tables must already be in First Normal Form. The Book Table will be used for the 2NF example
- 14. 2NF Table Publisher Table Book Table Publisher_ID Publisher Name 1 McGraw-Hill ISBN Title Pages Publisher_ID 0072958863 Database System Concepts 1168 1 0471694665 Operating System Concepts 944 1
- 15. 2NF Here we have a one-to-many relationship between the book table and the publisher. A book has only one publisher, and a publisher will publish many books. When we have a one-to-many relationship, we place a foreign key in the Book Table, pointing to the primary key of the Publisher Table. The other requirement for Second Normal Form is that you cannot have any data in a table with a composite key that does not relate to all portions of the composite key.
- 16. Third Normal Form Third normal form (3NF) requires that there are no functional dependencies of non-key attributes on something other than a candidate key. A table is in 3NF if all of the non-primary key attributes are mutually independent There should not be transitive dependencies
- 17. Boyce-Codd Normal Form BCNF requires that the table is 3NF and only determinants are the candidate keys
- 18. END