Normalized averaging using adaptive applicability functions with applications in image reconstruction from sparsely and randomly sampled data
- 1. Normalized averaging using adaptive applicability functions with applications in image reconstruction from sparsely and randomly sampled data Presented at SCIA 2003 Tuan Q. Pham and Lucas J. van Vliet July 17, 2009 1 Pattern Recognition Group
- 2. Overview • Normalized averaging • Local structure adaptive filtering • Experimental results • Comparison with diffusion-based image inpainting • Directions for further research July 17, 2009 2
- 3. Normalized averaging (Knutsson’93) •Weighted average filtering: r = s*a •Normalized averaging = weighted average + signal/certainty principle: •each signal s is associated with a certainty c •s & c have to be processed separately ( s . c) ∗ a r= c∗a where s :signal, c :certainty, a :filter, r :result, * :convolution input with 10% Gaussian smoothing NA with Gaussian original pixels (σ = 1) applicability (σ = 1) July 17, 2009 3
- 4. Normalized averaging: An example Reconstruction from 10% random pixels Nearest neighbor interpolation NA with adaptive applicability July 17, 2009 4
- 5. Image reconstruction using Adaptive Normalized Averaging Input Image σ=1 Normalized Output Image (sparsely & Averaging (with local randomly structure sampled) Adaptive extended into applicability missing regions) Structure Analysis July 17, 2009 5
- 6. Local structure adaptive filtering •Local structure from the structure tensor r v r r r T u ϕ rr T rr T T = ∇I ∇I = λu uu + λv vv r •orientation φ = arg(u) y = 1 κ x2 •anisotropy A = (λu - λv)/(λu + λv) 2 r •curvature κ = ∂φ /∂ v •scale rdensity = sample density •Scale-adaptive curvature-bent anisotropic Gaussian kernel with scales in 2 orthogonal directions: σ u = C (1 − A)α rdensity σ v = C (1 + A)α rdensity where C ~ SNR α ~ degree of structure enhancement kernel aligns with local structure July 17, 2009 6
- 7. Sample Density Transform •Definition: Smallest radius of a pillbox, centered at each pixel, that encompasses total certainty of at least 1 •Role: Automatic scale selection of the applicability in the NA equation to avoid unnecessary smoothing Lena with missing hole Density transform NA with Gaussian(σ=1) Adap. Norm. Avg. July 17, 2009 7
- 8. 4x4 super-resolution from 4 noisy frames • 4 input LowRes captured with fill-factor = 25%, intensity noise (σ=10), registration noise (σ=0.2 LR pitch) 1 of 4 input 64x64 LR SR using triangulation SR using adaptive NA • 16 times upsampling from only 4 frames. How is it possible: along linear structures, only 4 samples are enough for 4x super-resolution July 17, 2009 8
- 9. Orientation Anisotropy Curvature Sample density Scale along linear structures Scale in perpendicular direction July 17, 2009 9
- 10. Comparison with image inpainting • Image inpainting (Sapiro) = diffusion with level line evolution • also extending orientation into the missing regions • slow due to iterative nature • poor result for large holes input inpainting inpainting + Adapt. Norm. Avg. 110 iters (6 min) texture synthesis 0 iters (6 sec) July 17, 2009 10
- 11. Directions for Further Research • Applications • Image filtering (noise/watermark removal, edge enhancement...) • Image interpolation from sparsely and randomly sampled data (image inpainting, image fusion, super-resolution...) • Further improvements • Scale-space local structure analysis. • Detect multiple orientations using orientation space. • Robust neighborhood operator than the weighted mean. July 17, 2009 11
- 12. Image inpainting of thin scribbles input inpainting Adaptive Normalized Averaging (10 sec) July 17, 2009 12
- 13. Simultaneous geometry/texture inpainting texture input geometry Adaptive NA (1 min) July 17, 2009 13
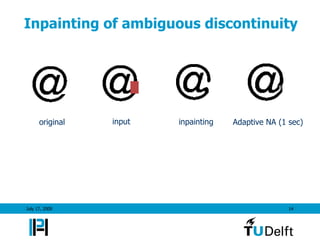
- 14. Inpainting of ambiguous discontinuity original input inpainting Adaptive NA (1 sec) July 17, 2009 14