OFDMA.ppt
- 1. Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiple Access (OFDMA) Khaja Mohammad Shazzad
- 2. 2 Outline 1. Background Multiple Access (MA) Methods 2. Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing (OFDM) Based Multiple Access (OFDMA) Orthogonality Principle OFDM OFDM-FDMA 3. Advantages and Disadvantages of OFDMA 4. Conclusion
- 3. Multiple Access (MA) General wireless cellular systems are multi-users systems Radio resource are limited – Limited Bandwidth – Limited number of channels The radio resource must be shared among multiple users Multiple Access Control (MAC) needed – Contention-based – Non-contention-based
- 4. 4 Contention-based Multiple Access(MA) Contention-based – Each terminal transmits in a decentralized way – No central controller (Base stations or access points) – Example: ALOHA Carrier Sensing Multiple Access (CSMA) Standard: – GSM [l] uses the slotted ALOHA in the terminal’s initial access process – IEEE 802.11 uses CSMA/CA based contention access scheme
- 5. Non-contention-based Multiple Access (MA) A logic controller (BS or AP) is needed to coordinate the transmissions of all the terminals The controller informs each device when and on which channel it can transmit Collisions can be avoided entirely Two Subdivisions 1. Non-channelization 2. Channelization
- 6. Non-channelization Non-contention-based MA Terminals transmit sequentially using the same channel Example: – Polling based medium access Standard: – IEEE 802.15(WPAN) – IEEE 802.11(WLAN)
- 7. Channelization Non-contention-based MA Terminals transmit simultaneously using different channels Most commonly used protocols in cellular systems Example: – 1. Time Division Multiple Access (TDMA) – 2. Code Division Multiple Access( CDMA) – 1. Frequency Division Multiple Access (FDMA) Standard – 1. GSM (TDMA) – 2. IS-95 (CDMA) – 3. American Mobile Phone System, AMPS (FDMA)
- 8. 8 Time Division Multiple Access (TDMA) GSM – Time slot 0.577 ms – Frame 4.6 ms – 8 time slots per frame – Frequency band 20 KHz
- 9. Code Division Multiple Access (CDMA) IS-95 – Orthogonal Walsh codes – 64 codes (channels) – One pilot channel – Seven paging channels – 55 traffic channels – Each carrier 1.25 MHz
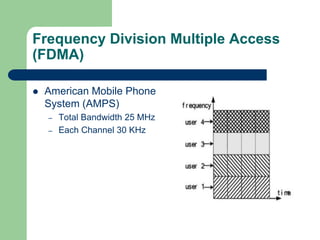
- 10. Frequency Division Multiple Access (FDMA) American Mobile Phone System (AMPS) – Total Bandwidth 25 MHz – Each Channel 30 KHz
- 11. Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing (OFDM) Based Multiple Access (OFDMA) Orthogonality Principle OFDM OFDM-FDMA
- 12. 12 Orthogonality Principle Vector space – A, B and C vectors in space are orthogonal to each other – A.B=B.C=C.A=0 – (A+B+C).A=(mod A)^2 – (A+B+C).B=(mod B)^2 – (A+B+C).C=(mod C)^2 A B C
- 13. Orthogonality Principle cont.. Real Function space 0 ) ( ) ( ) cos( ) ( ) sin( ) ( 0 ) ( ) ( ) cos( ) ( ) sin( ) ( 2 1 2 1 dt t f t f nwt N t f mwt M t f dt t f t f wt B t f wt A t f n T m n m T
- 14. Orthogonality Principle cont.. ) 2 sin( ) sin( ) ( wt wt t f T 0 0 s(nwt)dt sin(mwt)co n m where T 0 0 n(nwt)dt sin(mwt)si Ν m.n Here mw and nw are called m-th and n-th harmonics of w respectively
- 15. 15 Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing(OFDM) It is a special kind of FDM The spacing between carriers are such that they are orthogonal to one another Therefore no need of guard band between carriers. One example makes the thing clear
- 16. Example of OFDM Lets we have following information bits – 1, 1, -1, -1, 1, 1, 1, -1, 1, -1, -1, -1, -1, 1, -1, -1, … Just converts the serials bits to parallel bits C1 C2 C3 C4 1 1 -1 -1 1 1 1 -1 1 -1 -1 -1 -1 1 -1 -1 -1 1 1 -1 -1 -1 1 1
- 17. Example of OFDM cont.. Modulated signal for C1 Modulated signal for C2 Modulated signal for C3 Modulated signal for C4 Modulate each column with corresponding sub-carrier using BPSK
- 18. Example of OFDM cont.. Final OFDM Signal = Sum of all signal ) 2 sin( ) ( ) ( 1 0 nt t I t V N n n Generated OFDM signal, V(t) V(t)
- 19. OFDM-FDMA (OFDMA) Each terminal occupies a subset of sub-carriers Subset is called an OFDMA traffic channel Each traffic channel is assigned exclusively to one user at any time user1 user2 user3 user4
- 20. OFDM-FDMA (OFDMA) The IEEE 802.16e/ WiMax use OFDMA as Multiple access technique – Bandwidth options 1.25, 5, 10, or 20 MHz – Entire bandwidth divided into 128, 512, 1024 or 2048 sub carriers – 20 MHz bandwidth with 2048 sub carriers has 9.8 KHz spacing between sub carriers
- 22. 22 Advantages of OFDMA Multi-user Diversity – broadband signals experience frequency selective fading – OFDMA allows different users to transmit over different portions of the broadband spectrum (traffic channel) – Different users perceive different channel qualities, a deep faded channel for one user may still be favorable to others
- 23. Advantages of OFDMA cont.. Multi-user Diversity
- 24. Advantages of OFDMA cont.. Efficient use of Spectrum 4/3 Hz per symbol 6/5 Hz per symbol
- 25. Advantages of OFDMA cont.. Receiver Simplicity – It eliminates the intra-cell interference avoiding CDMA type of multi-user detection – Orthogonality of code destroyed by selective fading – Only FFT processor is required Bit Error Rate performance is better only in Fading environment
- 26. Disadvantages of OFDMA Peak to average power ratio (PAPR) avg P t x PAPR 2 ) ( The large amplitude variation increases in-band noise and increases the BER when the signal has to go through amplifier nonlinearities.
- 27. 27 Disadvantages of OFDMA cont.. Synchronization – Tight Synchronization between users are required for FFT in receiver – Pilot signals are used for synchronizations Co-channel interference – Dealing with this is more complex in OFDM than in CDMA – Dynamic channel allocation with advanced coordination among adjacent base stations
- 28. 28 Research issues and Conclusion Future works – Peak-to-average power reduction in OFDM – Timing and Frequency Synchronization – Efficient digital signal processing Implementation of OFDM – Multiple input/Multiple output (MIMO) OFDM Conclusion – Different variations of OFDMA are proposed and have different pros and cons




![4
Contention-based
Multiple Access(MA)
Contention-based
– Each terminal transmits in a decentralized way
– No central controller (Base stations or access points)
– Example:
ALOHA
Carrier Sensing Multiple Access (CSMA)
Standard:
– GSM [l] uses the slotted ALOHA in the terminal’s initial
access process
– IEEE 802.11 uses CSMA/CA based contention access
scheme](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ofdma-230731174336-8d7a5709/85/OFDMA-ppt-4-320.jpg)