OOP-Advanced Programming with c++
- 3. - Procedural Programming - Focus on processes or actions that a program takes - Programs are typically a collection of functions - Data is declared separately - Data is passed as arguments into functions As Programs get larger they become more: Difficult to understand Difficult to maintain Difficult to extend Difficult to debug Difficult to code
- 4. Object Oriented Programming Object-oriented programming (OOP) is a programming paradigm based on the concept of "objects", which can contain data and code: data in the form of fields (often known as attributes or properties), and code, in the form of procedures (often known as methods). - Encapsulation - Objects contain data and operations that work on that data - Abstract Data Type ( ADT)
- 6. Object Oriented Programming “Abstraction mean Simplify The Reality”
- 7. 09:Object Oriented Programming “Just all we need about the person”
- 8. 09:Object Oriented Programming “Just all we need about the person”
- 9. Object Oriented Programming - Information - Hiding - Encapsulation - Implementation - specific logic be hidden - User of class code to be interface since they don’t need to know the implementation - More abstraction - Easier to test, debug, maintain and extend
- 10. Object Oriented Programming - Reusability - Easier to reuse classes in order application - Faster development - Higher quality
- 11. 09:Object Oriented Programming provide code reuse Code reuse is the practice of using existing code for a new function or software. This saves time, improves the features in your program, and generally makes for more cost-effective programming. Reusability is an important issue in software engineering.
- 12. Object Oriented Programming - Inheritance - Can create new classes in term of existing classes - Reusability - Polymorphic classes
- 13. Object Oriented Programming- provide Inheritance
- 15. 09:Object Oriented Programming A class is an extensible program-code-template for creating objects, although a very tiny application might need just a single class. The class must go within a pair of curly braces.
- 16. Class design like Blueprint architecture
- 17. Class design
- 18. Class design
- 19. Class design
- 20. Class design
- 21. The interface of the class(Abstraction) All you need to know to know how to use
- 22. The interface of the class(Abstraction) All you need to know to know how to use
- 24. 09:Object Oriented Programming provide code reuse Code reuse is the practice of using existing code for a new function or software. This saves time, improves the features in your program, and generally makes for more cost-effective programming. Reusability is an important issue in software engineering.
- 25. Create Class using unified modeling language UML
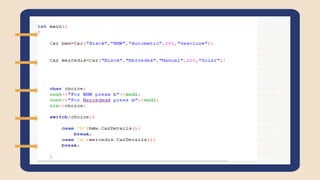
- 26. Accessing Class We can access - Class attributes - Class methods Some class members will not be accessible (more on that later) We need an object to access instance variables
- 27. Class Access Modifier - public , private and protected - public - Accessible everywhere - private - Accessible only by members or friends of the class - protected - Used with inheritance - we’ll talk about it in the next section
- 28. Class Access Modifier - public , private and protected - public - Accessible everywhere - private - Accessible only by members or friends of the class - protected - Used with inheritance - we’ll talk about it in the next section
- 29. Class Access Modifier - public , private and protected - public - Accessible everywhere - private - Accessible only by members or friends of the class - protected - Used with inheritance - we’ll talk about it in the next section
- 30. Class Access Modifier - public , private and protected - public - Accessible everywhere - private - Accessible only by members or friends of the class - protected - Used with inheritance - we’ll talk about it in the next section
- 31. Class Access Modifier - public , private and protected - public - Accessible everywhere - private - Accessible only by members or friends of the class - protected - Used with inheritance - we’ll talk about it in the next section
- 32. Class Access Modifier - public , private and protected - public - Accessible everywhere - private - Accessible only by members or friends of the class - protected - Used with inheritance - we’ll talk about it in the next section
- 33. Class Access Modifier - public , private and protected - public - Accessible everywhere - private - Accessible only by members or friends of the class - protected - Used with inheritance - we’ll talk about it in the next section
- 34. What are setters and getters? Getters and setters are used to protect your data, particularly when creating classes. For each instance variable, a getter method returns its value while a setter method sets or updates its value. Given this, getters and setters are also known as accessors and mutators, respectively.
- 35. What are setters and getters? Getters and setters are used to protect your data, particularly when creating classes. For each instance variable, a getter method returns its value while a setter method sets or updates its value. Given this, getters and setters are also known as accessors and mutators, respectively.
- 36. What is a abstract? By definition, an abstract class in C++ is a class that has at least one pure virtual function (i.e., a function that has no definition).
- 37. What is a C++ abstract class? By definition, an abstract class in C++ is a class that has at least one pure virtual function (i.e., a function that has no definition).
- 38. What is a C++ abstract class? Abstract classes are essential to providing an abstraction to the code to make it reusable and extendable. For example, a Vehicle parent class with Truck and Motorbike inheriting from it is an abstraction that easily allows more vehicles to be added. However, even though all vehicles have wheels, not all vehicles have the same number of wheels – this is where a pure virtual function is needed.
- 39. What is a C++ abstract class?
- 40. What is a C++ abstract class?
- 41. Inhertance
- 42. What is Polymorphism in C++? Polymorphism in C++ means, the same entity (function or object) behaves differently in different scenarios
- 43. What is Polymorphism in C++? 2. Runtime Polymorphism In a Runtime polymorphism, functions are called at the time the program execution. Hence, it is known as late binding or dynamic binding. Function overriding In function overriding, we give the new definition to base class function in the derived class. At that time, we can say the base function has been overridden. It can be only possible in the ‘derived class’. In function overriding, we have two definitions of the same function, one in the superclass and one in the derived class. The decision about which function definition requires calling happens at runtime. That is the reason we call it ‘Runtime polymorphism’.
- 44. What is Polymorphism in C++? 1. Compile Time Polymorphism In compile-time polymorphism, a function is called at the time of program compilation. We call this type of polymorphism as early binding or Static binding. Function overloading and operator overloading is the type of Compile time polymorphism. Function Overloading Function overloading means one function can perform many tasks. In C++, a single function is used to perform many tasks with the same name and different types of arguments. In the function overloading function will call at the time of program compilation. It is an example of compile-time polymorphism.
- 45. CREDITS: This presentation template was created by Slidesgo, including icons by Flaticon, and infographics & images by Freepik Thanks