Physiology of Cortex
- 2. Total surface square Thick- ness Total volume Neurons number Glyal cells 2200 сm2 1,3 to 4,5 mm 600сm3 109 - 1010 Total number unknown
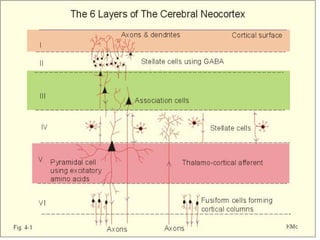
- 4. 6 LAYERS OF CORTEX I - Molecular(плексиформный) II – External stellatum III – External pyramidal IV - Internal stellatum V –Internal pyramidal VI – Layer of physiformic cells
- 5. Sponsored Medical Lecture Notes – All Subjects USMLE Exam (America) – Practice
- 6. METHODS OF CEREBRUM FUNCTIONS STUDIES A. Stimulation B. Exstirpation C. Electrophysiological prosedures D. Method of conditioned reflexes E. Method of clinical observation
- 7. Electrophysiological methods Registration of electrical activity of a group of neurons (macroelectrodes) Registration of electrical activity of single neurons (microelectrodes) EEG, electrocorticograme Caused potentials (stimulated by light or sound cortex response)
- 8. Registration of single neurons activity
- 9. Registration of caused potentials
- 11. Electroencephalography Method of registration ofvelectrical potential from the skin of the head Hanse Berger proposed this in 1929 - 1938.
- 12. EEG origin Sum of EPSPs & IPSPs Duration of EPSPs & IPSPs is from 30 tо 150 msec Amplitude depends on the frequency & synchronisation of EPSPs & IPSPs Frequency is formed by rhythmic activity of cortex neurons. Rhythmicity is due to the influence of RF of midbrain & thalamic nuclei.
- 13. EEG rhythms Аlfa – α-rhythm - 8-13 Hz - 50-100 mcV Rhythm of synchronization. Registered at the state of peaceful awakefulness at closed eyes mainly in occipital & parieto-temporal zonez. Betha – β- rhythm - 14-30 Hz - 10-30 mcV. Rhythm of desynchronization. Registered at the state of active rest with opened eyes
- 14. I - α - waves II - β - waves III - θ (theta) - waves IV - Δ (delta) - waves V - epileptic dischanges
- 15. EEG rhythms Тhеtа- θ-rhythm - 4-7 Hz - 100-150mcV Rhythm of synchronization. Registered at the state of peaceful awakefulness at closed eyes mainly in children, during sleep in adults, may be a sign of brain hypoxia. Deltа – Δ- rhythm - 0,5-4,5 Hz 150-200 mcV Rhythm of synchronization. Registered at the state of deep sleep, narcosis, at pathological states.
- 16. Synchronization - occurs at anonimous impulsation to the cortex, at closed eyes. Desynchronization – occurs at different multiply active impulsation to the cortex, at opened eyes
- 18. CLINICAL IMPORTANCE OF EEG Epilepsy diagnostics (caused potentials are preferable nowadays). Tumors localization. Cranium traumas & chronic meningitis & encephalitis Evaluation of narcosis depth (Δ rhythm at deep narcosis). To determine the state of death in some cases ( «flat» EEG).
- 19. Modern view on function localization in the cortex.
- 21. MOTOR AREA Heterotypical agranular zones Моtоr zone - precentral gyrus (pyramidal tract, voluntarily movements) Homotypical Associative areas – parietal & temporal
- 23. Сенсорно- специфические области Гетеротипические гранулярные зоны коры Зрительные – затылочная область, шпорная борозда Слуховые – височная область, извилина Гешле Соматосенсорная – постцентральная извилина - кожная чувствительность, проприоцептивная, висцеральная, чувство равновесия, вкус
- 24. Sensory specific zones of cortex AII AI nucleus Nucleus – monomodal neurons A I & A II– associative zones – polymodal neurons
- 28. Sensory zones are topically organized – receptive fields are represented in proportion to the number of afferent neurons, which form these fields, not to the square taken by the receptive field.
- 33. Sleep centers. Suprachyasmatic nuclei of hypothalamus Nuclei rhaffe in brain stem (Hess center) Serotonin Slow sleep Inhibition of pain In spinal cord
- 34. Stages of sleep Stage 0 (awake) – from lying down to falling asleep, 1-2% of sleep time, α – waves at closed eyes, β – waves at opened Stage 1 (dozing) - θ (theta) – waves on to[p of α, eye movements reduced, neck muscles relaxed, 3-6%
- 36. Stages of sleep Stage 2 (unequivocal sleep) - θ (theta) – waves with spindles, K complexes can be evoked on sensory stimulation, little eye movements , easily arrosable, 40-50% of sleep time
- 37. Stages of sleep Stage 3 (deep sleep transition)- θ (theta) – waves, Δ (delta) – waves and spindle activity, K complexes can be evoked on strong stimulation, few eye movements , not easily arrousable, 5-8% of sleep time
- 39. Stages of sleep Stage 4 (cerebral sleep)- Δ (delta) – waves predominate, K complexes can’t be evoked, fixed eyes , difficult to arrouse, 10-20% of sleep time. Night terror may occur at this time
- 40. During stages 2,3,4 heart rate and respiration are steady and muscles are relaxed Stages 3 and 4 are called slow wave sleep (SWS) REM-sleep (paradoxical)- EEG waves of all frequency, K complexes can’t be evoked, dreams and nightmares, HR and BP fluctuate, respiration is irregular, muscles are relaxed, but irregular body movements can occur occasionally Normally stages 0 to 4 and REM occur in succession over a period of 80-100 min, they are repeated cyclically