Popliteal Fossa.ppt
- 1. Back of Thigh & Popliteal Fossa Dr. Mujahid Khan
- 2. Skin & Cutaneous Nerves The posterior cutaneous nerve of thigh is a branch of the sacral plexus Leaves the gluteal region by emerging from beneath the lower border of the gluteus maximus Descends on the back of thigh In the popliteal fossa it pierces the deep fascia and supplies the skin Gives off branches to the skin on the back of the thigh and upper part of leg
- 4. Superficial Veins Many small veins curve around the medial and lateral aspects of the thigh They drain into the great saphenous vein Superficial veins form in the lower part of the back of thigh join small saphenous vein in the popliteal fossa Lymph from the skin and superficial fascia drain into the vertical group of superficial inguinal lymph nodes
- 5. Contents Muscles: Biceps femoris, semitendinosus, semimembranosus, and a small part of the adductor magnus Blood Supply: Branches of the profunda femoris artery Nerve Supply: Sciatic Nerve
- 6. Biceps Femoris Origin: The long head from the ischial tuberosity Short head from the linea aspera and the lateral supracondylar ridge of the shaft of the femur Insertion: Two heads unite just above the knee joint and insert into the head of the fibula Nerve Supply: Long head by the tibial part of the sciatic, short head by the common peroneal part of sciatic Action: Flexes and laterally rotates the leg at the knee joint, long head extends the thigh at the hip joint
- 8. Semitendinosus Origin: From the ischial tuberosity Insertion: By a long tendon into the upper part of the medial surface of the shaft of the tibia Nerve Supply: The tibial portion of sciatic nerve Action: Flexes and medially rotates the leg at the knee, extends the thigh at the hip joint
- 9. Semimembranosus Origin: From the ischial tuberosity Insertion: Into the posteromedial surface of the medial condyle of the tibia It sends a fibrous expansion on the back of the knee joint called oblique popliteal ligament Nerve Supply: Tibial part of the sciatic nerve Action: Flexes and medially rotates the leg at the knee joint, extends thigh at the hip joint
- 10. Adductor Magnus (Hamstring Portion) Origin: Ischial tuberosity Insertion: Adductor tubercle of femur Nerve Supply: Tibial portion of sciatic nerve Action: Extends thigh at hip joint
- 11. Blood Supply The four perforating branches of the profunda femoris artery provide a rich blood supply to this compartment The profunda femoris vein drains the greater part of the blood from the compartment
- 12. Sciatic Nerve It is a branch of sacral plexus It leaves the gluteal region as it descends in the midline of the thigh It is overlapped posteriorly by the adjacent margins of the biceps femoris and semimembranosus muscles It lies on the posterior aspect of the adductor magnus muscle
- 14. Sciatic Nerve In the lower third of the thigh it ends by dividing into the tibial and common peroneal nerves Occasionally, the sciatic nerve divides into its two terminal parts at a higher level, in the upper part of the thigh, the gluteal region, or even inside the pelvis
- 15. Branches of Sciatic Nerve Tibial Nerve: It enters the popliteal fossa Common Peroneal Nerve: It enters the popliteal fossa on the lateral side of the tibial nerve Muscular Branches: To the long head of the biceps femoris, the semitendinosus, the semimembranosus, and the hamstring part of the adductor magnus, These branches arise from the tibial component and run medially
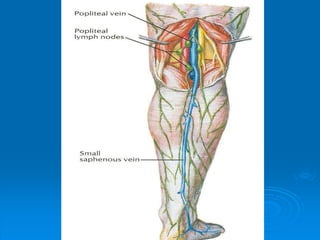
- 16. Popliteal Fossa Popliteal fossa is a diamond-shaped intermuscular space situated at the back of the knee It is more prominent when the knee is flexed It contains the popliteal vessels, the small saphenous vein, the common peroneal and tibial nerves, the posterior cutaneous nerve of the thigh, the genicular branch of the obturator nerve, connective tissue and lymph nodes
- 17. Boundaries of Popliteal Fossa Laterally: Biceps femoris above and the lateral head of gastrocnemius and plantaris below Medially: the semimembranosus and the semitendinosus above and the medial head of the gastrocnemius below
- 19. Boundaries of Popliteal Fossa The anterior wall or floor of the fossa is formed by the popliteal surface of the femur, the posterior ligament of the knee joint, and the popliteus muscle The roof is formed by skin, superficial fascia, and the deep fascia of the thigh
- 20. Popliteus Muscle Origin: From the lateral surface of the lateral condyle of the femur by a rounded tendon and by a few fibers from the lateral semilunar cartilage Insertion: Posterior surface of tibia, above the soleal line It arises within the capsule of the knee joint and emerges through the lower part of the capsule of the joint
- 22. Popliteus Muscle Nerve Supply: Tibial nerve Action: Medial rotation of the tibia on the femur If the foot is on the ground, lateral rotation of the femur on the tibia This action is also called unlocking of the knee joint
- 23. Popliteal Artery The popliteal artery is deeply placed It is a continuation of the femoral artery It enters the popliteal fossa through the opening in the adductor magnus It ends at the level of the lower border of the popliteus muscle by dividing into anterior and posterior tibial arteries
- 25. Relations of Popliteal Artery Anteriorly: The popliteal surface of the femur, the knee joint, and the popliteus muscle Posteriorly: The popliteal vein and the tibial nerve, fascia and skin Branches: Muscular branches and articular branches
- 26. Popliteal Vein The popliteal vein is formed by the junction of the venae comitantes of the anterior and posterior tibial arteries Forms at the lower border of the popliteus muscle On the medial side of the popliteal artery It passes through the opening in the adductor magnus to become the femoral vein
- 27. Tributaries of Popliteal Vein Veins that correspond to branches given off by the popliteal artery Small saphenous vein, perforates the deep fascia and passes between the two heads of the gastrocnemius muscle to end in the popliteal vein
- 28. Arterial Anastomosis Around Knee Joint To compensate for the narrowing of the popliteal artery which occurs during extreme flexion of the knee Around the knee joint a profuse anastomosis of small branches of the femoral artery is present It is joined by the muscular and articular branches of the popliteal artery and with branches of the anterior and posterior tibial arteries
- 30. Popliteal Lymph Nodes About six lymph nodes are embedded in the fatty connective tissue of the popliteal fossa They receive superficial lymph vessels from the lateral side of the foot and popliteal fossa They also receive lymph from the knee joint and from deep lymph vessels accompanying the anterior and posterior tibial arteries
- 32. Tibial Nerve It is the larger terminal branch of the sciatic nerve It arises in the lower third of the thigh It runs downward through the popliteal fossa Lying first on the lateral side of the popliteal artery then posterior to it It enters the posterior compartment of the leg by passing beneath the soleus muscle
- 34. Branches of Tibial Nerve Cutaneous: Usually joined by the sural communicating branch Muscular: Supply both heads of the gastrocnemius and plantaris, soleus and popliteus Articular: Supply the knee joint
- 36. Common Peroneal Nerve It is a smaller terminal branch of the sciatic nerve Arises in the lower third of the thigh Runs downward through the popliteal fossa Leaves the fossa by crossing superficially to the lateral head of the gastrocnemius muscle
- 38. Common Peroneal Nerve Passes behind the head of the fibula Winds around the neck of fibula Pierces the peroneus longus muscle Divides into two terminal branches: the superficial peroneal and deep peroneal nerves It is subcutaneous and can be rolled against the neck of the fibula
- 39. Branches of Common Peroneal Nerve Cutaneous: sural communicating branch, the lateral cutaneous nerve of the calf supplies the lateral side of the back of the leg Muscular: supply to the short head of biceps femoris Articular branches to the knee joint