Presentation Anton Hemerijck
- 1. SOCIAL INVESTMENT: THE EU’S NEW SKILLS, JOBS AND CARE AGENDA ANTON HEMERIJCK, VRIJE UNIVERSITEIT AMSTERDAM/LONDON SCHOOL OF ECONOMICS (LSE) AMSTERDAM, 16 FEBRUARY 2016
- 2. 2 Faculteit der Sociale Wetenschappen OUTLINE 1. Angela Merkel 2013 and the post-neoliberal paradox 1. Social investment policy analysis 2. VET systems and welfare complementarities 1. Where there is way, there is a will
- 3. 3 Faculteit der Sociale Wetenschappen 1. ANGELA MERKEL (2013) The European Union accounts for 7% of the world’s population and 25% of its GDP, but over 50% of its welfare spending. …. We are not competitive!
- 4. 4 Faculteit der Sociale Wetenschappen GOOD NEWS AND WORRYING TRENDS We live longer We are richer We go to school longer We work more We spend more on social policy than ever Welfare states can adapt, mitigate shocks and are popular, but Growing inequality between young and old (Southern Europe) Rising inequality between work-rich and work-poor households (Northern-Europa) High youth and long-term unemployment Low growth Too little private and public investment (education especially)
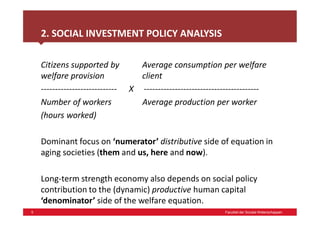
- 5. 5 Faculteit der Sociale Wetenschappen 2. SOCIAL INVESTMENT POLICY ANALYSIS Citizens supported by Average consumption per welfare welfare provision client --------------------------- X ----------------------------------------- Number of workers Average production per worker (hours worked) Dominant focus on ‘numerator’ distributive side of equation in aging societies (them and us, here and now). Long-term strength economy also depends on social policy contribution to the (dynamic) productive human capital ‘denominator’ side of the welfare equation.
- 6. 6 Faculteit der Sociale Wetenschappen ACCOUNTING IN A LIFE COURSE PERSPECTIVE -300 000 -200 000 -100 000 0 100 000 200 000 300 000 400 000 500 000 600 000 0 5 10 15 20 25 30 35 40 45 50 55 60 65 70 75 80 85 90 95 100 Net savings Public sector Within households Income from labour Between households
- 7. 7 Faculteit der Sociale Wetenschappen THREE CORE WELFARE FUNCTIONS • Social insurance (over the life course) – Piggy Bank • Risk sharing and risk insurance • Redistribution (between rich and poor) – Robin Hood • Fighting poverty • Reduce inequality • Counter social exclusion • Capacitation (services devolution) – Social investment • Human capital development • Easing labour market transitions • Regional economic policy
- 8. 8 Faculteit der Sociale Wetenschappen “CARRYING CAPACITY” THROUGH RAISING ‘STOCKS’, EASING ‘FLOWS AND UNIVERSALIZING ‘BUFFERS’ Social risks of the life course and the labor market have become less predictable – and therefore less insurable by social protection only. 1. Raising the quality of human capital ‘stock’ over the life course from the young to the old (cumulative returns) 2. Easing the ‘flow’ of contemporary labour market transitions in line with (gendered) life course dynamics 3. Upkeeping/upgrading strong minimum-income universal safety nets as social (income) protection and macro-economic stabilization ‘buffers’ over risky transitions From remedial social insurance to preventive life course insurance
- 9. 9 Faculteit der Sociale Wetenschappen FUNCTIONAL OVERLAP AND INSTITUTIONAL COMPLEMENTARITIES Stock Flow Buffer Stock Skill development to complement existing human capital stock and further learning Skills to enter and change jobs in competitive labour markets Skills to live healthy and safe during risky transitions of inactivity Flow Facilitates transitions from training to work and vice versa Facilitates labour market transitions in sync with work-life balance Facilitates transitions to secure market income (including social insurance requalification) Buffer Provides income security to uphold skills. Provides income security necessary for “innovative risk taking” in training Provides income security to enable successful job search and risk- taking Provides income security in inactivity rehabilitation and/or care obligations and job search
- 10. 10 Faculteit der Sociale Wetenschappen SOCIAL INVESTMENT LIFE COURSE MULTIPLIER (POST- NEOLIBERAL POLICY CONSENSUS) Early childhood education and care Early childhood education and care Educational attainmentEducational attainment EmploymentEmployment Dual earnership, worklife balance (fertility) Dual earnership, worklife balance (fertility) Exit ageExit age Poverty reduction and social inclusion Poverty reduction and social inclusion
- 11. 11 Faculteit der Sociale Wetenschappen THE WELFARE STATE IN CRISIS AGAIN
- 12. 12 Faculteit der Sociale Wetenschappen YOUNG PEOPLE NOT IN EMPLOYMENT, EDUCATION OR TRAINING AGED 20–24 (% OF COHORT POPULATION)
- 13. 13 Faculteit der Sociale Wetenschappen DISTRIBUTION OF ADULT SKILLS ACROSS COUNTRIES
- 14. 14 Faculteit der Sociale Wetenschappen EDUCATION SPENDING BEFORE AND AFTER THE CRISIS
- 15. 15 Faculteit der Sociale Wetenschappen 3. COMPETITIVE ECONOMIES ARE ACTIVE WELFARE STATES WITH AGILE VET SYSTEMS IN TRANSITION (WEF) 1. Switzerland (professional VET partnership) 2. Singapore (high education spending) 3. United States 4. Germany (industry specific VET) 5. Netherlands (school based and work based VET apprenticeship) 6. Japan (firm specific VET) 7. Hong Kong 8. Finland (remedial teaching based differentiation) 9. Sweden (state based vocationalism) 10.United Kingdom (Great training robbery)
- 16. 16 Faculteit der Sociale Wetenschappen RECALIBRATING STOCKS, FLOWS AND BUFFERS I Netherlands Fighting early school leaving through ‘bridging’ activating ‘buffers’, labour market ‘flow’ job coaches, and public-private training and apprenticeships ‘stock’ rehabilitation Early selection and barriers between initial and post-initial training (for high skill groups and largely private). Layering of educational streams across learning careers good for migrant youngsters Italy and France Little modernization and bridging of ‘stocks’, ‘flows’, and ‘buffers’ results inequitable, unequal and inefficient welfare states
- 17. 17 Faculteit der Sociale Wetenschappen RECALIBRATING STOCKS, FLOWS, AND BUFFERS I Germany: Kurzarbeit ‘buffers’, expansion of low pay sector sector ‘flow’ (minijobs), intensification joint (employer-union) defense of sector sponsored VET (dualization drift) Denmark: Generous activating ‘buffers’, facilitating ‘flow’, low barriers between school-based training and firm based apprenticeships and between training for employed and unemployed through modularization and training individualization by local public administration (embedded flexibilization)
- 18. 18 Faculteit der Sociale Wetenschappen 4. CONCLUSION • ‘Contingent’ convergence toward social investment and VET emancipation (gradual transformative change) • Active, family-friendly welfare states with effective VET systems outperform others – positive lesson • Problematic policy legacies exposed (pension- biased/dualization/perverse familialism) – negative lesson • Post-neoliberal inclusive growth theory Word Bank and OECD: inequality is bad for the economy because it undermines talent development, human capital and social mobility • Bridging ‘stocks’, ‘flows’ and ‘buffers’ is the new Triple-Helix!
- 19. 19 Faculteit der Sociale Wetenschappen WHERE THERE’S A WAY, THERE’S A WILL • Asymmetric competition, social divergence, dramatic youth unemployment undermine E(M)U viability – macro lesson • Undifferentiated fiscal austerity undermines budgetary consolidation in problem countries – crisis management lesson • Insecure futures breeding ground for xenophobia – political lesson • Social investment imperative for economic, social and political reasons (education spending discounting in SGP by a Social Investment Protocol)
- 20. THANK YOU