Presentation1 stepper and servomotor12
- 1. CENTRE FOR ADVANCED STUDIES, AKTU LUCKNOW PRESENTED BY SHUBHAM KUMAR SINGH PRESENTATION ON STEPPER AND SERVO MOTOR
- 2. TABLE OF CONTENT 1.Basic Introduction Of Stepper Motor 2.Fundamentals Of Operation 3.Working Of Stepper Motor 4.Types Of Stepper Motor (a)Permanent Magnet Stepper Motor (b) Variable Recluctance Stepper Motor (c)Hybrid Synchronus Motor 5.Two Phase Stepper Motor (a)Unipolar Motor (b)Bipolar Motor 6.Applications 7.Refrences
- 3. TABLE OF CONTENT 1.Introduction Of Servo Motor 2.Types Of Servo Motor (a)DC Servo Motor (b)AC Servo Motor (c)Positional Rotation Servo Motor (d)Continuous Rotation Servo Motor (e)Linear Servo Motor 3.Servo Motor Working Principle 4.Applications Of Servo Motor 5.Refrences
- 4. BASIC INTRODUCTION OF STEPPER MOTOR • A stepper motor, also known as step motor or stepping motor, is a brushless DC electric motor that divides a full rotation into a number of equal steps. • The motor's position can then be commanded to move and hold at one of these steps without any position sensor for feedback (an open-loop controller), as long as the motor is carefully sized to the application in respect to torque and speed.
- 5. FUNDAMENTALS OF OPERATION • Brushed DC motors rotate continuously when DC voltage is applied to their terminals. The stepper motor is known by its property of converting a train of input pulses (typically square wave pulses) into a precisely defined increment in the shaft position. Each pulse moves the shaft through a fixed angle. • Stepper motors effectively have multiple "toothed" electromagnets arranged around a central gear-shaped piece of iron.
- 6. • The electromagnets are energized by an external driver circuit or a micro controller. To make the motor shaft turn, first, one electromagnet is given power, which magnetically attracts the gear's teeth. • When the gear's teeth are aligned to the first electromagnet, they are slightly offset from the next electromagnet. This means that when the next electromagnet is turned on and the first is turned off, the gear rotates slightly to align with the next one. From there the process is repeated. Each of those rotations is called a "step", with an integer number of steps making a full rotation. In that way, the motor can be turned by a precise angle.
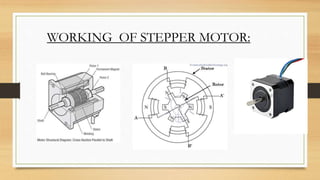
- 7. WORKING OF STEPPER MOTOR:
- 8. TYPES OF STEPPER MOTORS: There are three main types of stepper motors: 1. Permanent magnet stepper 2. Variable reluctance stepper 3. Hybrid synchronous stepper
- 9. Applications 1. Computer controlled stepper motors are a type of motion- control positioning system. They are typically digitally controlled as part of an open loop system for use in holding or positioning applications. 2. In the field of lasers and optics they are frequently used in precision positioning equipment such as linear actuators, linear stages, rotation stages, goniometers, and mirror mounts. Other uses are in packaging machinery, and positioning of valve pilot stages for fluid control systems.
- 10. 3. Commercially, stepper motors are used in floppy disk drives, flatbed scanners, computer printers, plotters, slot machines, image scanners, compact disc drives, intelligent lighting, camera lenses, CNC machines and, more recently, in 3D printers. Advantages: 1.Low cost for control achieved 2.High torque at startup and low speeds 3.Ruggedness 4.Simplicity of construction 5.Can operate in an open loop control system 6.Low maintenance
- 11. References 1. Liptak, Bela G. (2005). Instrument Engineers' Handbook: Process Control and Optimization. CRC Press. p. 2464. ISBN 978-0-8493-1081-2. 2.Tarun, Agarwal. "Stepper Motor – Types, Advantages & Application". 3. See "Friction and the Dead Zone" by Douglas W Jones https://homepage.divms.uiowa.edu/~jones/step/physics.html 4."electricmotors.machinedesign.com". 5. zaber.com, microstepping 6. "Microstepping: Myths and Realities - MICROMO". www.micromo.com. 7. More on what is an IP65 step motor: http://www.applied- motion.com.
- 12. Introduction Of Servo Motor The servo motor is most commonly used for high technology devices in the industrial application like automation technology. It is a self contained electrical device, that rotate parts of a machine with high efficiency and great precision. The output shaft of this motor can be moved to a particular angle. Servo motors are mainly used in home electronics, toys, cars, airplanes, etc
- 13. Types of Servo Motor: 1. DC Servo Motor 2. AC Servo Motor 3. Positional Rotation Servo Motor 4. Continuous Rotation Servo Motor 5. Linear Servo Motor
- 14. Servo Motor Working Principle: A unique design for servo motors are proposed in controlling the robotics and for control applications. They are basically used to adjust the speed control at high torques and accurate positioning. Parts required are motor position sensor and a highly developed controller.
- 15. Applications of Servo Motor:
- 16. Servo Motor in Packaging Machine
- 17. References 1.Baldor Electric Company – Servo Control Facts. Accessed 25 September 2013. 2.BusinessDictionary.com definition. Accessed 25 September 2013 3. Andrew Betts Brown. 4.Eugine L. Ragonnet, Controlling Mechanism for Locomotives, U.S. Patent 930,225, Aug. 9, 1909. 5.IEEE Industry Applications Magazine March/April 1996, pg 74. 6.G. W. Younkin, Industrial Servo Control Systems – Fundamentals and Applications – Second Edition, Taylor and Francis, 2007.
- 18. THANK YOU!