Problem solving using Computer
- 1. Problem solving usingProblem solving using ComputersComputers By : David Livingston J Sudesh Kantila
- 2. Need for Programming LanguageNeed for Programming Language 1. We have some problem. 2. We have to solve the problem. 3. We can solve the problem, but we don’t want to repeatedly solve the similar problems. 4. We want to use the computer to do this task for us whenever required. 5. We have to tell the computer, “How to solve the problem.”
- 3. What is Problem?What is Problem? A problem is an obstacle which makes it difficult to achieve a desired goal, objective or purpose. It refers to a situation, condition, or issue that is yet unresolved. In a broad sense, a problem exists when an individual becomes aware of a significant difference between what actually is and what is desired.
- 4. What is Problem Solving?What is Problem Solving? Every problem in the real world needs to be identified and solved. Trying to find a solution to a problem is known as problem solving. Problem solving becomes a part of our day to day activity. Especially, when we use computers for performing our day to day activity.
- 5. How to solve a problem?How to solve a problem? 1. If you have a problem, either you can solve it manually or using computer. 2. If the problem is easy enough, solve it manually or else use computers. 3. Bigger problems can be sub-divided into smaller problems (sub-problems) and start solving them one by one. 4. After completing solving sub-problems, the entire big problem has been solved easily.
- 6. Algorithm – Logic to solveAlgorithm – Logic to solve If you have solved any problem already, you would have definitely used some procedure (logic) to do so. There may be many different logic that can solve a single problem. You may write this logic into small steps (easy enough) in english (or whatever language you understand). This block of steps to solve the problem is called an “Algorithm”.
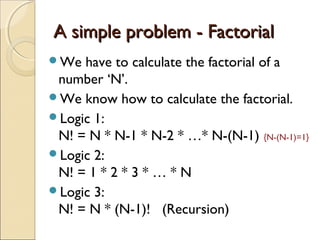
- 7. A simple problem - FactorialA simple problem - Factorial We have to calculate the factorial of a number ‘N’. We know how to calculate the factorial. Logic 1: N! = N * N-1 * N-2 * …* N-(N-1) {N-(N-1)=1} Logic 2: N! = 1 * 2 * 3 * … * N Logic 3: N! = N * (N-1)! (Recursion)
- 8. Logic 1: (Algorithm)Logic 1: (Algorithm) 1. START 2. INPUT AN INTEGER – N 3. LET F=1 4. IF N > 1 GOTO STEP 5 ELSE STEP 8 5. F = F * N 6. N = N – 1 7. GOTO STEP 4 8. OUTPUT F 9. STOP
- 9. Logic 2: (Algorithm)Logic 2: (Algorithm) 1. START 2. INPUT AN INTEGER – N 3. LET F=1, X=1 4. IF X < N GOTO STEP 5 ELSE STEP 8 5. X = X + 1 6. F = F * X 7. GOTO STEP 4 8. OUTPUT F 9. STOP
- 10. Flow Chart – Graphical AlgorithmFlow Chart – Graphical Algorithm Algorithms are written in some natural language, e.g. – English, िहिन्दी, Chinease etc. There may be some problem to understand the algorithm if a person from different region speaking a different language needs to know the logic. To overcome this problem, logic may be represented in a graphical way. This graphical representation of algorithm is called ‘Flow Chart’
- 11. Flow Chart – Logic 1Flow Chart – Logic 1 LET F=1 IF N > 1 INPUT N START OUTPUT F START F = F * N N = N - 1 Yes No
- 12. Flow Chart – Logic 2Flow Chart – Logic 2 LET F=1 X = 1 IF X < N INPUT N START OUTPUT F START X = X + 1 F = F * X No Yes
- 13. Common Flow Chart ShapesCommon Flow Chart Shapes Flow Lines Terminator Input / Output Box Process Decision Box (On Page and Off Page) Connectors Predefined Process
- 14. PseudocodePseudocode Pseudocode is a kind of structured english for describing algorithms. It allows the designer to focus on the logic of the algorithm without being distracted by details of language syntax. At the same time, the pseudocode needs to be complete. It describe the entire logic of the algorithm so that implementation becomes a rote mechanical task of translating line by line into source code (coding). Pseudocode cannot be compiled nor executed, and there are no real formatting or syntax rules.
- 15. Pseudocode – Logic 1Pseudocode – Logic 1 GET value of N SET initial value of F to 1 WHILE N > 1 F = F * N N = N – 1 ENDWHILE DISPLAY value of F
- 16. Programming (Coding) in CProgramming (Coding) in C main() { int n; long f=1; printf(“Input n to get factorial: ”); scanf(“%i”,&n); while (n > 1) { f = f * n; n = n – 1; } printf(“Factorial of %i is %li”,n,f); retrun 0; }