Python business intelligence (PyData 2012 talk)
- 1. Python for Business Intelligence Štefan Urbánek ■ @Stiivi ■ stefan.urbanek@continuum.io ■ PyData NYC, October 2012
- 3. Results Q/A and articles with Java solution references (not listed here)
- 5. Why?
- 6. Overview ■ Traditional Data Warehouse ■ Python and Data ■ Is Python Capable? ■ Conclusion
- 9. Data Analysis and Extraction, Transformation, Loading Sources Presentation Data Governance Technologies and Utilities
- 10. Traditional Data Warehouse
- 11. ■ Extracting data from the original sources ■ Quality assuring and cleaning data ■ Conforming the labels and measures in the data to achieve consistency across the original sources ■ Delivering data in a physical format that can be used by query tools, report writers, and dashboards. Source: Ralph Kimball – The Data Warehouse ETL Toolkit
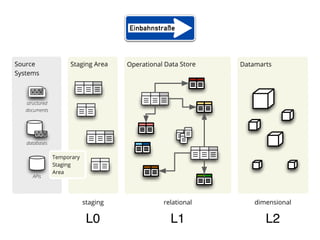
- 12. Source Staging Area Operational Data Store Datamarts Systems structured documents databases Temporary Staging Area APIs staging relational dimensional L0 L1 L2
- 13. real time = daily
- 14. Multi-dimensional Modeling
- 16. aggregation browsing slicing and dicing
- 17. business / analyst’s point of view regardless of physical schema implementation
- 18. Facts measurable fact fact data cell most detailed information
- 19. location type time dimensions
- 20. Dimension ■ provide context for facts ■ used to filter queries or reports ■ control scope of aggregation of facts
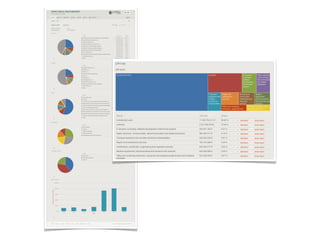
- 21. Pentaho
- 22. Python and Data community perception* *as of Oct 2012
- 24. Python
- 25. Data Analysis and Extraction, Transformation, Loading Sources Presentation Data Governance Technologies and Utilities
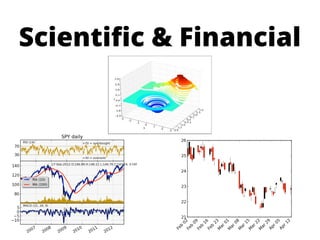
- 26. Scientific Data T1[s] T2[s] T3[s] T4[s] P1 112,68 941,67 171,01 660,48 P2 96,15 306,51 725,88 877,82 P3 313,39 189,31 41,81 428,68 P4 760,62 983,48 371,21 281,19 P5 838,56 39,27 389,42 231,12 n-dimensional array of numbers
- 27. Assumptions ■ data is mostly numbers ■ data is neatly organized... ■ … in one multi-dimensional array
- 28. Data Analysis and Extraction, Transformation, Loading Sources Presentation Data Governance Technologies and Utilities
- 29. Business Data
- 30. multiple snapshots of one source multiple representations categories are of same data changing
- 31. ❄
- 32. Is Python Capable? very basic examples
- 33. Data Pipes with SQLAlchemy Data Analysis and Extraction, Transformation, Loading Sources Presentation Data Governance Technologies and Utilities
- 34. ■ connection: create_engine ■ schema reflection: MetaData, Table ■ expressions: select(), insert()
- 35. src_engine = create_engine("sqlite:///data.sqlite") src_metadata = MetaData(bind=src_engine) src_table = Table('data', src_metadata, autoload=True) target_engine = create_engine("postgres://localhost/sandbox") target_metadata = MetaData(bind=target_engine) target_table = Table('data', target_metadata)
- 36. clone schema: for column in src_table.columns: target_table.append_column(column.copy()) target_table.create() copy data: insert = target_table.insert() for row in src_table.select().execute(): insert.execute(row)
- 38. text file (CSV) to table: reader = csv.reader(file_stream) columns = reader.next() for column in columns: table.append_column(Column(column, String)) table.create() for row in reader: insert.execute(row)
- 39. Simple T from ETL Data Analysis and Extraction, Transformation, Loading Sources Presentation Data Governance Technologies and Utilities
- 40. transformation = [ ('fiscal_year', {"w function": int, ". field":"fiscal_year"}), ('region_code', {"4 mapping": region_map, ". field":"region"}), ('borrower_country', None), ('project_name', None), ('procurement_type', None), ('major_sector_code', {"4 mapping": sector_code_map, ". field":"major_sector"}), ('major_sector', None), ('supplier', None), ('contract_amount', {"w function": currency_to_number, ". field": 'total_contract_amount'} ] target fields source transformations
- 41. Transformation for row in source: result = transform(row, [ transformation) table.insert(result).execute()
- 42. OLAP with Cubes Data Analysis and Extraction, Transformation, Loading Sources Presentation Data Governance Technologies and Utilities
- 43. Model { “name” = “My Model” “description” = .... “cubes” = [...] “dimensions” = [...] } cubes dimensions measures levels, attributes, hierarchy
- 44. logical physical ❄
- 45. 1 load_model("model.json") Application ∑ 3 model.cube("sales") 4 workspace.browser(cube) cubes Aggregation Browser backend 2 create_workspace("sql", model, url="sqlite:///data.sqlite")
- 46. browser.aggregate(o cell, . drilldown=[9 "sector"]) drill-down
- 47. for row in result.table_rows(“sector”): row.record["amount_sum"] q row.label k row.key
- 48. whole cube o cell = Cell(cube) browser.aggregate(o cell) Total browser.aggregate(o cell, drilldown=[9 “date”]) 2006 2007 2008 2009 2010 ✂ cut = PointCut(9 “date”, [2010]) o cell = o cell.slice(✂ cut) browser.aggregate(o cell, drilldown=[9 “date”]) Jan Feb Mar Apr March April May ...
- 49. How can Python be Useful
- 50. just the Language ■ saves maintenance resources ■ shortens development time ■ saves your from going insane
- 51. Source Staging Area Operational Data Store Datamarts Systems structured documents databases faster Temporary Staging Area APIs staging relational dimensional L0 L1 L2
- 52. faster advanced Data Analysis and Extraction, Transformation, Loading Sources Presentation Data Governance Technologies and Utilities understandable, maintainable
- 53. Conclusion
- 54. BI is about… people technology processes
- 56. Future who is going to fix your COBOL Java tool if you have only Python guys around?
- 57. is capable, let’s start
- 58. Thank You [t Twitter: @Stiivi DataBrewery blog: blog.databrewery.org Github: github.com/Stiivi























![Scientific Data
T1[s] T2[s] T3[s] T4[s]
P1 112,68 941,67 171,01 660,48
P2 96,15 306,51 725,88 877,82
P3 313,39 189,31 41,81 428,68
P4 760,62 983,48 371,21 281,19
P5 838,56 39,27 389,42 231,12
n-dimensional array of numbers](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pythonbusinessintelligencecubes-pydata2012-121203161809-phpapp02/85/Python-business-intelligence-PyData-2012-talk-26-320.jpg)













![transformation = [
('fiscal_year', {"w function": int,
". field":"fiscal_year"}),
('region_code', {"4 mapping": region_map,
". field":"region"}),
('borrower_country', None),
('project_name', None),
('procurement_type', None),
('major_sector_code', {"4 mapping": sector_code_map,
". field":"major_sector"}),
('major_sector', None),
('supplier', None),
('contract_amount', {"w function": currency_to_number,
". field": 'total_contract_amount'}
]
target fields source transformations](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pythonbusinessintelligencecubes-pydata2012-121203161809-phpapp02/85/Python-business-intelligence-PyData-2012-talk-40-320.jpg)


![Model
{
“name” = “My Model”
“description” = ....
“cubes” = [...]
“dimensions” = [...]
}
cubes dimensions
measures levels, attributes, hierarchy](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pythonbusinessintelligencecubes-pydata2012-121203161809-phpapp02/85/Python-business-intelligence-PyData-2012-talk-43-320.jpg)


![browser.aggregate(o cell,
. drilldown=[9 "sector"])
drill-down](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pythonbusinessintelligencecubes-pydata2012-121203161809-phpapp02/85/Python-business-intelligence-PyData-2012-talk-46-320.jpg)
![for row in result.table_rows(“sector”):
row.record["amount_sum"]
q row.label k row.key](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pythonbusinessintelligencecubes-pydata2012-121203161809-phpapp02/85/Python-business-intelligence-PyData-2012-talk-47-320.jpg)
![whole cube
o cell = Cell(cube)
browser.aggregate(o cell)
Total
browser.aggregate(o cell,
drilldown=[9 “date”])
2006 2007 2008 2009 2010
✂ cut = PointCut(9 “date”, [2010])
o cell = o cell.slice(✂ cut)
browser.aggregate(o cell,
drilldown=[9 “date”])
Jan Feb Mar Apr March April May ...](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pythonbusinessintelligencecubes-pydata2012-121203161809-phpapp02/85/Python-business-intelligence-PyData-2012-talk-48-320.jpg)









