Queues.ppt
- 1. Queues CS 308 – Data Structures
- 2. What is a queue? • It is an ordered group of homogeneous items of elements. • Queues have two ends: – Elements are added at one end. – Elements are removed from the other end. • The element added first is also removed first (FIFO: First In, First Out).
- 3. Queue Specification • Definitions: (provided by the user) – MAX_ITEMS: Max number of items that might be on the queue – ItemType: Data type of the items on the queue • Operations – MakeEmpty – Boolean IsEmpty – Boolean IsFull – Enqueue (ItemType newItem) – Dequeue (ItemType& item)
- 4. Enqueue (ItemType newItem) • Function: Adds newItem to the rear of the queue. • Preconditions: Queue has been initialized and is not full. • Postconditions: newItem is at rear of queue.
- 5. Dequeue (ItemType& item) • Function: Removes front item from queue and returns it in item. • Preconditions: Queue has been initialized and is not empty. • Postconditions: Front element has been removed from queue and item is a copy of removed element.
- 6. Implementation issues • Implement the queue as a circular structure. • How do we know if a queue is full or empty? • Initialization of front and rear. • Testing for a full or empty queue.
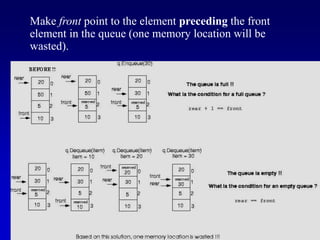
- 9. Make front point to the element preceding the front element in the queue (one memory location will be wasted).
- 10. Initialize front and rear
- 11. Queue is empty now!! rear == front
- 12. Queue Implementation template<class ItemType> class QueueType { public: QueueType(int); QueueType(); ~QueueType(); void MakeEmpty(); bool IsEmpty() const; bool IsFull() const; void Enqueue(ItemType); void Dequeue(ItemType&); private: int front; int rear; ItemType* items; int maxQue; };
- 13. Queue Implementation (cont.) template<class ItemType> QueueType<ItemType>::QueueType(int max) { maxQue = max + 1; front = maxQue - 1; rear = maxQue - 1; items = new ItemType[maxQue]; }
- 14. Queue Implementation (cont.) template<class ItemType> QueueType<ItemType>::~QueueType() { delete [] items; }
- 15. Queue Implementation (cont.) template<class ItemType> void QueueType<ItemType>:: MakeEmpty() { front = maxQue - 1; rear = maxQue - 1; }
- 16. Queue Implementation (cont.) template<class ItemType> bool QueueType<ItemType>::IsEmpty() const { return (rear == front); } template<class ItemType> bool QueueType<ItemType>::IsFull() const { return ( (rear + 1) % maxQue == front); }
- 17. Queue Implementation (cont.) template<class ItemType> void QueueType<ItemType>::Enqueue (ItemType newItem) { rear = (rear + 1) % maxQue; items[rear] = newItem; }
- 18. Queue Implementation (cont.) template<class ItemType> void QueueType<ItemType>::Dequeue (ItemType& item) { front = (front + 1) % maxQue; item = items[front]; }
- 19. Queue overflow • The condition resulting from trying to add an element onto a full queue. if(!q.IsFull()) q.Enqueue(item);
- 20. Queue underflow • The condition resulting from trying to remove an element from an empty queue. if(!q.IsEmpty()) q.Dequeue(item);
- 21. Example: recognizing palindromes • A palindrome is a string that reads the same forward and backward. Able was I ere I saw Elba • We will read the line of text into both a stack and a queue. • Compare the contents of the stack and the queue character-by-character to see if they would produce the same string of characters.
- 23. Example: recognizing palindromes #include <iostream.h> #include <ctype.h> #include "stack.h" #include "queue.h“ int main() { StackType<char> s; QueType<char> q; char ch; char sItem, qItem; int mismatches = 0; cout << "Enter string: " << endl; while(cin.peek() != 'n') { cin >> ch; if(isalpha(ch)) { if(!s.IsFull()) s.Push(toupper(ch)); if(!q.IsFull()) q.Enqueue(toupper(ch)); } }
- 24. while( (!q.IsEmpty()) && (!s.IsEmpty()) ) { s.Pop(sItem); q.Dequeue(qItem); if(sItem != qItem) ++mismatches; } if (mismatches == 0) cout << "That is a palindrome" << endl; else cout << That is not a palindrome" << endl; return 0; } Example: recognizing palindromes
- 25. Case Study: Simulation • Queuing System: consists of servers and queues of objects to be served. • Simulation: a program that determines how long items must wait in line before being served.
- 26. Case Study: Simulation (cont.) • Inputs to the simulation: (1) the length of the simulation (2) the average transaction time (3) the number of servers (4) the average time between job arrivals
- 27. Case Study: Simulation (cont.) • Parameters the simulation must vary: (1) number of servers (2) time between arrivals of items • Output of simulation: average wait time.
- 28. Exercises (Chapt 4) • 26, 29-34, 39-41, 46, 47.











![Queue Implementation (cont.)
template<class ItemType>
QueueType<ItemType>::QueueType(int
max)
{
maxQue = max + 1;
front = maxQue - 1;
rear = maxQue - 1;
items = new ItemType[maxQue];
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/queues-220729131404-79460a32/85/Queues-ppt-13-320.jpg)
![Queue Implementation (cont.)
template<class ItemType>
QueueType<ItemType>::~QueueType()
{
delete [] items;
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/queues-220729131404-79460a32/85/Queues-ppt-14-320.jpg)


![Queue Implementation (cont.)
template<class ItemType>
void QueueType<ItemType>::Enqueue
(ItemType newItem)
{
rear = (rear + 1) % maxQue;
items[rear] = newItem;
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/queues-220729131404-79460a32/85/Queues-ppt-17-320.jpg)
![Queue Implementation (cont.)
template<class ItemType>
void QueueType<ItemType>::Dequeue
(ItemType& item)
{
front = (front + 1) % maxQue;
item = items[front];
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/queues-220729131404-79460a32/85/Queues-ppt-18-320.jpg)









