Section 56 .ppt
- 1. Exponent Rules and Dividing Polynomials 5.6 1. Divide exponential forms with the same base. 2. Divide numbers in scientific notation. 3. Divide monomials. 4. Divide a polynomial by a monomial. 6. Simplify expressions using rules of exponents. 5. Use long division to divide polynomials.
- 2. Objective 1 Divide exponential forms with the same base.
- 3. Quotient Rule for Exponents If m and n are integers and a is a real number, where a 0, then . m m n n a a a 3 7 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 3 7 4 4 3 7 2 1 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 1 1 1 1 1 1
- 4. When an equation in one variable is solved the answer is a point on a line. Divide: 14 6 j j 3 5 u u 3 6 m m 2 2 3 5 y x y x 2 u 8 1 j 8 14 6 j j 9 3 6 m m 9 1 m y x3
- 5. Objective 2 Divide numbers in scientific notation.
- 6. Divide and write the result in scientific notation. 7 3 2.34 10 3.6 10 7 3 2.34 10 3.6 10 7 3 0.65 10 4 0.65 10 3 6.5 10 Note: This is not in scientific notation.
- 7. When an equation in one variable is solved the answer is a point on a line. Divide and write the result in scientific notation: 2 4 10 88 1 10 964 9 . . 15 5 10 6 6 10 32 1 . . 20 10 2 . 21 10 0 2 . 6 10 3 5 .
- 9. Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Divide. 3 6 2 4 3 18 24 x y z x y 3 6 2 4 3 18 24 1 x y z x y 3 4 6 3 2 18 24 x y z 1 3 2 3 4 x y z 3 2 3 1 4 1 1 y z x 3 2 3 4 y z x
- 10. 1 24 18 2 3 6 4 3 z y y x x Divide. 3 6 2 4 3 18 24 x y z x y 3 1 24 18 2 3 6 4 3 z y y x x 4 1 x y3 1 x z y 4 3 2 3
- 11. Dividing Monomials 1. Divide the coefficients or simplify them to fractions in lowest terms. 2. Use the quotient rule for the exponents with like bases. 3. Write the final expression so that all exponents are positive.
- 12. When an equation in one variable is solved the answer is a point on a line. Divide: 7 2 4 5 42 28 q p r q p 3 2 4 5 4 4 y xy xy xy 64 43 3 3 3 2 q r p
- 13. Objective 4 Divide a polynomial by a monomial.
- 15. Divide. 6 2 3 2 36 9 6 3 x y x y x x y 6 2 3 2 2 2 36 9 6 3 3 3 x y x y x x y x y x y 4 2 12 3 x y x xy Divide each term in the polynomial by the monomial.
- 16. If a, b, and c are real numbers, variables, or expressions with c 0, then Dividing a Polynomial by a Monomial Divide each term in the polynomial by the monomial. . a b a b c c c
- 17. When an equation in one variable is solved the answer is a point on a line. Divide: 2 2 5 3 5 15 30 xyz xyz yz x 2 2 2 4 4 4 28 16 hk k h hk hk h k k 7 4 2 3 6 3 2 z x
- 18. Objective 6 Simplify expressions using rules of exponents.
- 19. Exponents Summary Zero as an exponent: a0 = 1, where a 0. Negative exponents: Product rule for exponents: Quotient rule for exponents: Raising a power to a power: Raising a product to a power: Raising a quotient to a power: 1 1 , , n n n n a a a a m n m n a a a m m n n a a a n m mn a a n n n ab a b n n a b b a n n n a a b b
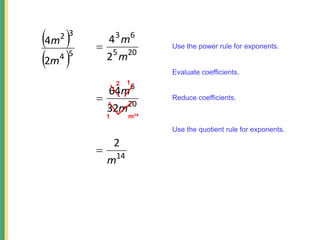
- 20. Use the quotient rule for exponents. Use the power rule for exponents. 20 5 6 3 2 4 m m 5 4 3 2 2 4 m m 14 2 m 20 6 32 64 m m 2 1 1 m14 Evaluate coefficients. Reduce coefficients.
- 23. When an equation in one variable is solved the answer is a point on a line. Simplify: p n m p n m 3 1 2 1 6 3 3 7 2 4 6 3 y y 3 2 7 3 p n m 13 24 1 y
- 24. Slide 5- 24 Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Simplify. a) b) c) d) 2 5 3 a a 16 1 a 4 1 a 16 a 4 a 5.6
- 25. Slide 5- 25 Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Simplify. a) b) c) d) 2 5 3 a a 16 1 a 4 1 a 16 a 4 a 5.6
- 26. Slide 5- 26 Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Divide. a) b) c) d) 5.6 6 8 4 6 3 18 15 18 x x x x 2 5 6 6 x x 2 2 6 5 6 x x 2 6 5 6 x x x x 6 5 6
- 27. Slide 5- 27 Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Divide. a) b) c) d) 5.6 6 8 4 6 3 18 15 18 x x x x 2 5 6 6 x x 2 2 6 5 6 x x 2 6 5 6 x x x x 6 5 6