Semantic scaffolds for pseudocode to-code generation (2020)
- 1. Semantic Scaffolds for Pseudocode-to-Code Generation Ruiqi Zhong, Mitchell Stern, Dan Klein
- 2. Abstract ⦿ A method for program generation based on semantic scaffolds ⦿ Searching over plausible scaffolds then using these as constraints for a beam search over programs ⦿ Applied hierarchical search method to the SPoC dataset 2
- 3. Contribution ⦿ proposed the use of semantic scaffolds to add semantic constraints to models for long form language-to-code generation tasks ⦿ introduced a hierarchical beam search algorithm ⦿ achieved a new state-of-the-art accuracy of 55.1% on the SPoC dataset 3
- 4. 2.1 Data ⦿ focused on the SPoC dataset ⦿ It consists of C++ solutions to problems from Code forces ⦿ It contains 18,356 programs in total with 14.7 lines per program on average 4
- 5. 2.2 Task ⦿ Suppose the target program has L lines ⦿ Natural language pseudocode annotation 𝑥𝑙 and an indentation level 𝑖𝑙 ⦿ Goal is to find a candidate program y based on (𝑥1; 𝑖1); : : : ; (𝑥𝐿; 𝑖𝑙) 5
- 6. 3. Combination Constraints ⦿ this approach ignores any dependence between different lines ⦿ if we naively combine certain subsets of candidates together, the resulting program will be invalid due to the use of undeclared variables or mismatching braces ⦿ we propose to enforce certain syntactic and semantic constraints when combining candidate code pieces 6
- 7. 3.1 Syntactic Constraints ⦿ restrict our attention to the set of “primary expressions” consisting of high-level control structures such as if, else ⦿ parse the candidate code pieces for each line into a list of primary expression symbols ⦿ exist a grammatical derivation that combines their respective symbols 7
- 8. 3.2 Symbol Table Constraints ⦿ this approach ignores any dependence between different lines ⦿ extract the variable names ⌾ undeclared variables are not used ⌾ variables are not re-declared within the same scope 8
- 9. 4.1 Beam Search ⦿ The search begins with k randomly generated states ⦿ At each step, all the successors of all k states are generated ⦿ If any one of the successors is a goal, the algorithm halts ⦿ Otherwise, it selects the k best successors from the complete list and repeats 9
- 10. 4.1 Beam Search ⦿ Advantages: ⌾ potentially reducing the time, of a search ⌾ the memory consumption of the search is less than others ⦿ Disadvantages: ⌾ the search may not result in an optimal goal and may not even reach a goal at all ⌾ terminates for two cases: a required goal node is reached, or a goal node is not reached and there are no nodes left to be explored 10
- 11. 5. Implementation (Empty Pseudocode) ⦿ 26% of the lines in the data set do not have pseudocode annotations ⦿ Such as “int main() {”, “{”, “}”, etc. ⦿ They did not use the any code pieces for these lines 11
- 12. 5. Implementation ⦿ Empty Pseudocode ⌾ “int main() -> {”, “{”, “}”, ⦿ Search Algorithm ⌾ OpenNMT ⦿ Parsing Code Pieces ⦿ Search Algorithm 12
- 13. 5. Implementation (Search Algorithm Hyper parameters) ⦿ They consider the top C = 100 code pieces for each line ⦿ default beam width W is 50 for scaffold search ⦿ the top K = 20 scaffolds for the subsequent generation 13
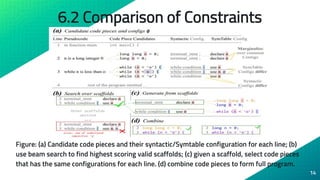
- 14. 6.2 Comparison of Constraints Figure: (a) Candidate code pieces and their syntactic/Symtable configuration for each line; (b) use beam search to find highest scoring valid scaffolds; (c) given a scaffold, select code pieces that has the same configurations for each line. (d) combine code pieces to form full program. 14
- 15. 6.2 Comparison of Constraints ⦿ No Constraints: the best-first search method that scores lines independently. ⦿ Syntactic Constraints: the constraints on the primary expression and indentation level ⦿ Symbol Table Constraints: both the syntactic constraints and the symbol table constraints described ⦿ Back off: sometimes hierarchical beam search with the SymTable constraints fails to return any valid scaffold. We back off to just the Syntactic constraints if this happens. 15
- 16. 7.2 Rejection by Constraints ⦿ Syntactic Constraints: ⌾ “}”, “int main(){”, “{”, ”return 0”, “};” ⌾ if(...){” and “if(...)” ⦿ Symbol Table (SymTable) Constraints ⌾ Set N to 222222 -> int N = 222222 or int N = 222222 16
- 17. 7.3 Code Piece Error Analysis ⦿ The model generation is wrong despite clear pseudocode ⦿ variable type clarification ⦿ Syntactic context ⦿ consists of variable name types 17