SPoC: search-based pseudocode to code
- 1. SPoC: Search-based Pseudocode to Code • Sumith Kulal • Panupong Pasupat • Kartik Chandra • Mina Lee • Oded Padon • Alex Aiken • Percy Liang
- 3. Abstract mapping pseudocode to long programs that are functionally correct treat the translation of each pseudocode line as a discrete portion of the program If program fails to compile, an error localization method tries to identify the portion of the program responsible for the failure 3
- 4. Introduction map natural language descriptions Perform non-trivial computations input-output pairs usually give little information about the intermediate states of the program 4
- 5. Data collection Programs and test cases: NAPS dataset Decomposition: decompose each program into code lines Pseudocode: recruited 59 workers on Amazon Mechanical Turk to write pseudocode Statistics: dataset contains 18,356 programs Training and test sets: they created two test sets 5
- 6. Problem Statement • The system is given (a) a sequence x of L pseudocode lines 𝑥1; 𝑥2; : : : ; 𝑥𝐿, where 𝑥𝑖 is a string with indentation level `I K public test cases in the form of input-output string pairs (𝑇𝑖𝑛1 ; 𝑇𝑜𝑢𝑡1); : : : ; (𝑇𝑖𝑛𝑘 ; 𝑇𝑜𝑢𝑡𝑘). ▸ The task is to synthesize a program y consisting of L code lines 𝑦1; 𝑦1; : : : ; 𝑦𝐿 ▸ The program is accepted if it successfully compiles and passes all public test cases 6
- 7. Base approach (Translation) • They used a standard seq2seq translation model with an LSTM encoder and decoder • An attention-based copying mechanism • A coverage vector 7
- 8. Base approach (Best-first search) 1. Create a priority Queue pqueue. 2. insert ‘start’ in pqueue : pqueue.insert(start) 3. delete all elements of pqueue one by one. 1) if, the element is goal . Exit. 2) else, traverse neighbor’s and mark the node examined. 4. End. 8
- 9. Base approach (Best-first search) Advantages: ▸ Best first search can switch between BFS and DFS by gaining the advantages of both the algorithms. ▸ This algorithm is more efficient than BFS and DFS algorithms. Disadvantages: ▸ It can behave as an unguided depth-first search in the worst case scenario. ▸ It can get stuck in a loop as DFS. ▸ This algorithm is not optimal. 9
- 10. Experiments (Translation accuracy) Used BELU score in best first search only 18.2% of programs in TESTP and 32.0% of programs in TESTW is correct in every line. the top candidate of each line have an even lower success rates of 17.8% on TESTP and 30.7% on TESTW 10
- 11. Experiments (Translation accuracy) 11 Figure: (a) While the translation accuracy is high at the line level, we need to consider the result at the program level. For each program, we count the number of lines i where (b) the top candidate ci1 is incorrect (c) none of the candidates 𝑐𝑖𝑗 ꞓ 𝑐𝑖 is correct.
- 12. Experiments (Oracle success rate) ▸ count the number of lines i where the candidate list 𝑐𝑖 does not have any correct candidate ▸ 44.8% of programs in TESTP and 28.6% of programs in TESTW have least one difficult line where the translation model does not produce a correct prediction ▸ It achieve a maximum success rate of 55.2% on TESTP and 71.4% on TESTW 12
- 13. Experiments (Synthesis results) Error line, 𝑖∗ = 𝑖𝑒𝑟𝑟 - ∆i Where, 𝑖∗ = predicted line 𝑖𝑒𝑟𝑟 = error in line ∆i = corresponding line 13
- 14. Experiments (Synthesis results) 14 Figure: Success rates at budgets B of best-first search with different error localization methods
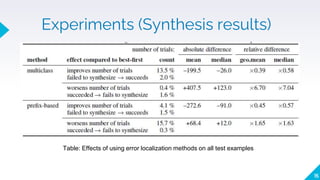
- 15. Experiments (Synthesis results) 15 Table: Effects of using error localization methods on all test examples
- 16. Experiments (Error analysis) ▸ s is half = “s == "half“ ▸ interpreted as “s / 2 == 0” or “s % 2 == 0” ▸ This causes the search to ultimately fail whereas best-first search finds a correct program in 80 search iterations 16
- 17. Related work (Program synthesis) ▸ formulate synthesis as a constraint satisfaction problem ▸ requires that the synthesis problem can be translated to a theory with effective constraint solvers ▸ brute force enumeration of programs works surprisingly well ▸ when the search space is too large for enumeration, randomized search guided by a cost function can be effective 17
- 18. Related work (Semantic parsing) It is a task of converting a NLP text into a logical form (a machine- understandable format) One of its traditional tasks is to parse a given into an executable database query Instead of a single query, some work aims to parse a sequence of queries that can be sequentially executed (max 5 sentences) 18
- 19. Related work (Error localization) uses neural models to localize errors focused on localizing and correcting syntax errors semantic errors such as variable misuse and variable replace Their work identifies error locations by interpreting compiler error messages 19