Servomechanisms
- 2. INTRODUCTION • Servomechanism, automatic device used to correct the performance of a mechanism by means of an error-sensing feedback. • The term servomechanism properly applies only to systems in which the feedback and error-correction signals control mechanical position or one of its derivatives such as velocity or acceleration. • All servomechanisms have at least these basic components: a controlled device, a command device, an error detector, an error- signal amplifier, and a device to perform any necessary error corrections (the servomotor).
- 3. • For example, an automotive power window control is not a servomechanism, as there is no automatic feedback that controls position,the operator does this by observation. By contrast the car's cruise control uses closed loop feedback,which classifies it as a servomechanism. • The Boeing 777 is the first heavy jet plane engineered to fly with all major flight-control functions managed by servomechanisms. The design of this revolutionary plane is based on the so-called “fly-by- wire” system. In normal flight a digital signal communicates the pilot’s instructions electrically to control servomechanisms that position the plane’s control surfaces as needed.
- 4. OPEN LOOP SYSTEM • In this system, an input is applied and an output obtained. Figure shows an example; assume an aircraft rudder controlled by an open loop system. • The demand, made by the pilot on the rudder bar, is picked up by the transducer which converts it to an electrical signal i.e. the demand signal. This signal is amplified and fed to the motor, which responds by moving the load i.e. the rudder. There is no positional feedback and the pilot does not know if the rudder has adopted the position requested. INPUT TRANSDUCER MOTOR LOAD DEMAND RESPONSE DEMAND SIGNAL AMP
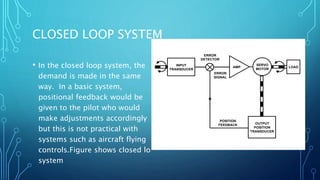
- 5. CLOSED LOOP SYSTEM • In the closed loop system, the demand is made in the same way. In a basic system, positional feedback would be given to the pilot who would make adjustments accordingly but this is not practical with systems such as aircraft flying controls.Figure shows closed lo system INPUT TRANSDUCER SERVO MOTOR LOAD OUTPUT POSITION TRANSDUCER ERROR DETECTOR POSITION FEEDBACK ERROR SIGNAL AMP
- 6. FOLLOW UP • If in our example the rudder were to be displaced from its demanded position, or from the optimum speed at which the demanded position may be achieved, an error signal occurs. • In the way described, there is a feedback signal and the system returns to its demanded position or speed. This process is called 'follow up'.
- 7. POSITIONAL FEEDBACK • Positional feedback is obtained from transducers positioned at the output. The feedback element, or transducer, converts the output shaft angle into a signal suitable for operating the error detector. In this case a voltage signal. The simplest form of element is a R- pot, or a helical potentiometer similar to that used as a control element. In practice, helical potentiometers are used since they give 360° coverage, which a R-pot cannot provide. Following figure shows positional feedback in a dc system.
- 9. TYPES OF SERVO There are two main classes of servomechanism - remote position control (RPC) servos and velocity control servos (velodynes): • RPC servos. These are used to control the angular, or linear position of a load. A typical example of the use of a RPC servo is the control of the direction in which a radar scanner is pointing. • Velodynes. These are used to control the speed of a load. In this case, the speed of the driving motor is made proportional to the input demand (usually a voltage). A typical example of the use of a velodyne is the control of a radar scanner, which is required to rotate with a constant angular velocity
- 10. APPLICATIONS OF SERVO • Automotive power steering uses hydraulic fluid under great pressure to power an actuator that redirects the wheels of a car as needed. The driver gently turns the steering wheel and the power- assist servomechanism provides much of the necessary energy needed to position the wheels. • High-performance airplanes need special servo-mechanisms called flight-control systems to compensate for performance instabilities that would otherwise compromise their safety.
- 11. THANK YOU