Small-Scale Fading and Multipath
- 1. SUBJECTIVE ASSIGNMENT 2 Presented By N.KAMALEESWARI Application no: 5b2c04def30211e98c07b32d30b69784 SASTRA Deemed to be University.
- 2. ACKNOWLEDGEMENT I would like to acknowledge ALL MY STAFF FOR THEIR constant support and help with such a good presentation videos. I pay my gratitude to Academic Writing course which taught me how to write a research article and how to publish an article without plagiarism and also about the digital writing. I thank my parents and almighty for their blessings and grace.
- 3. Small-Scale Fading and Multipath
- 4. Small-Scale Multipath Propagation • The three most important effects • Rapid changes in signal strength over a small travel distance or time interval • Random frequency modulation due to varying Doppler shifts on different multipath signals • Time dispersion caused by multipath propagation delays • Factors influencing small-scale fading • Multipath propagation: reflection objects and scatters • Speed of the mobile: Doppler shifts • Speed of surrounding objects • Transmission bandwidth of the signal • The received signal will be distorted if the transmission bandwidth is greater than the bandwidth of the multipath channel. • Coherent bandwidth: bandwidth of the multipath channel.
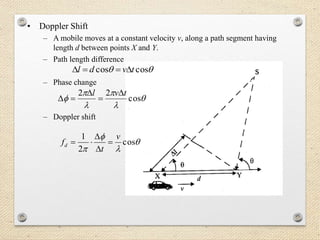
- 5. • Doppler Shift – A mobile moves at a constant velocity v, along a path segment having length d between points X and Y. – Path length difference – Phase change – Doppler shift coscos tvdl cos 22 tvl cos 2 1 v t fd
- 6. Types of Small-Scale Fading • Multipath delay spread leads to time dispersion and frequency selective fading. • Doppler spread leads to frequency dispersion and time selective fading. • Multipath delay spread and Doppler spread are independent of one another.
- 8. Flat Fading • If the channel has a constant gain and linear phase response over a bandwidth which is greater than the bandwidth of the transmitted signal, the received signal will undergo flat fading. • The received signal strength changes with time due to fluctuations in the gain of the channel caused by multipath. • The received signal varies in gain but the spectrum of the transmission is preserved.
- 9. • Flat fading channel is also called amplitude varying channel. • Also called narrow band channel: bandwidth of the applied signal is narrow as compared to the channel bandwidth. • Time varying statistics: Rayleigh flat fading. • A signal undergoes flat fading if and CS BB ST period)(symbolbandwidthreciprocal:ST signaledtransmitttheofbandwidth:SB bandwidthcoherent:CB spreaddelayrms:
- 10. Frequency Selective Fading • If the channel possesses a constant-gain and linear phase response over a bandwidth that is smaller than the bandwidth of transmitted signal, then the channel creates frequency selective fading. signal spectrum channel response received signal spectrum f f f )( fS CB
- 11. • Frequency selective fading is due to time dispersion of the transmitted symbols within the channel. – Induces intersymbol interference • Frequency selective fading channels are much more difficult to model than flat fading channels. • Statistic impulse response model – 2-ray Rayleigh fading model – computer generated – measured impulse response • For frequency selective fading and CS BB ST
- 12. • Frequency selective fading channel characteristic
- 13. Fading Effects Due to Doppler Spread • Fast Fading: The channel impulse response changes rapidly within the symbol duration. – The coherent time of the channel is smaller then the symbol period of the transmitted signal. – Cause frequency dispersion due to Doppler spreading. • A signal undergoes fast fading if and CS TT DS BB
- 14. • Slow Fading: The channel impulse response changes at a rate much slower than the transmitted baseband signal s(t). – The Doppler spread of the channel is much less then the bandwidth of the baseband signal. • A signal undergoes slow fading if and CS TT DS BB