The Impact of Network Variabilities on TCP Clocking Schemes
- 1. The Impact of Network Variabilities on TCP Clocking Schemes Kuan-Ta Chen, Polly Huang, Chun-Ying Huang, Chin-Laung Lei Department of Electrical Engineering National Taiwan University Global Internet 2005 Mar. 19, 2005
- 2. Outline Motivation Why pacing could be more bursty? The impact of network variabilities on the behavior of TCP clocking schemes Conclusion Global Internet 2005 2
- 3. TCP Clocking Schemes Self-clocking (a.k.a. ack-clocking) ACKs “self-clock” the data to the rate of the bottleneck link Pacing resembles to a rate control mechanism but preserves the concept of window control a common implementation: release a window of packets evenly within each round-trip time In intuition, pacing will result in more smooth traffic, and smooth traffic will lead to better performance, however, … Global Internet 2005 3
- 4. Motivation Aggarwal, Savage, Anderson found pacing often results in lower throughput and higher latency. We are motivated to evaluate ack-clocking and pacing schemes with more fundamental behavioral analysis, especially on the aspect of traffic burstiness. Global Internet 2005 4
- 5. Our main results Pacing traffic could be more bursty than ack-clocking traffic. The comparative traffic burstiness of TCP clocking schemes are largely affected by network path properties whether the round-trip times (RTT) are the same the number of flows Pacing is generally less bursty than ack-clocking with realistic settings, i.e., heterogeneous RTT flows. Global Internet 2005 5
- 6. Why pacing could be more bursty? Intuitively, pacing should be no more bursty than ack-clocking. We shall illustrate why the phenomenon could happen by behavioral models. Global Internet 2005 6
- 7. Behavioral models – equal window size Assumption: 3 flows, the same RTT, equal window size = 6 t: bottleneck service time are equally packet trains for a packet a packet train for each spaced in a RTT flow T/6 T/6 T/6 Global Internet 2005 7
- 8. Behavioral models – different window size Assumption: 3 flows, the same RTT, different windows size = 5, 3, 10, respectively. T/5 10 T/ T/3 Global Internet 2005 8
- 9. The effect of window un-synchronization Generate packet arrival sequences by the behavioral models T = 100 ms, t = 0.1 ms, 3 flows compare two cases synchronized windows: 30, 30, 30 un-synchronized windows: 20, 30, 40 Observe traffic burstiness based on the wavelet-based MultiResolution Analysis (MRA) for the synthesized traffic. Global Internet 2005 9
- 10. The energy plot Ack-clocking nearly remains its burstiness Pacing become more bursty The effect can be amplified by more flows (show later) Global Internet 2005 10
- 11. Validation and Simulations Observation: window un-synchronization can raise burstiness of pacing traffic. We conduct network simulations to: validate the observation examine the impact of flow multiplexing examine the impacts of other variabilities Global Internet 2005 11
- 12. Simulation Setup the network simulator is ns-2 1--50 flows, RTT are fixed to 100 ms network topology 1 1 4x Mbps x Mbps s R (bottleneck) 4x Mbps N N Global Internet 2005 12
- 13. The Effect of Multiplexing – Ack-clocking more bursty in small scales (still less bursty than Poisson) much less bursty in large scales Global Internet 2005 13
- 14. The Effect of Multiplexing – Pacing burstiness raises in all sub-RTT time scales due to the effect of window un- synchronization. Global Internet 2005 14
- 15. The Effect of Multiplexing – A Comparison 50 flows fl pacing is more bursty in most of sub-RTT time scales the comparative burstiness of two schemes are very different with and without flow multiplexing Global Internet 2005 15
- 16. Examine the effect of RTT heterogeneity The simulation setup is almost the same except: fixed to 50 flows RTTs are drawn from an uniform distribution over (100 ms, 300 ms) Global Internet 2005 16
- 17. The Effect of RTT Heterogeneity Ack-clocking is much more bursty mismatch of round trip times ack-solicited pkts are no longer spaced by t Pacing is unaffected RTT/window is already randomized by unsynchronized windows Global Internet 2005 17
- 18. More Network Variabilities Simulations with additional factors: multi-hop, two-way traffic, cross-traffic, and their combinations ID Topology RTT Two-Way Cross Heter. Traffic Traffic Fixed Dumbbell - - - VarRTT Dumbbell ✓ - - TwoWay Dumbbell ✓ ✓ - Cross Dumbbell ✓ - ✓ Real Parking-lot ✓ ✓ ✓ Global Internet 2005 18
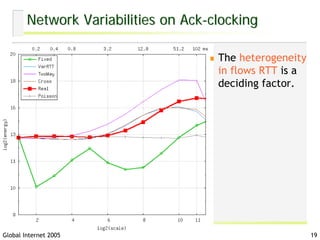
- 19. Network Variabilities on Ack-clocking The heterogeneity in flows RTT is a deciding factor. Global Internet 2005 19
- 20. Network Variabilities on Pacing None of variabilities significantly affect pacing’s behavior As long as RTTs are heterogeneous: Ack-cloking is no less bursty than Poisson Pacing is no more bursty than Poisson flPacing is less bursty Global Internet 2005 20
- 21. Conclusion Provided physical explanation for ‘why pacing could be more bursty than ack-clocking’ Comparative burstiness of the TCP clocking schemes are network condition dependent, especially RTT heterogeneity and flow multiplexing. It’s critical to include sufficient variabilities in performance evaluation of TCP based protocols. Global Internet 2005 21
- 22. Thank You!