Tqm Slides
- 1. Total Quality Management & Six Sigma … ..30 Contact Hrs. for Class of 2009
- 2. Total Quality Management ……concepts & understanding “TQM is a philosophy that represents a set of guiding principles that lays the foundation of a continuously improving and customer driven organization ” IT IS Encompassing and mobilizing entire organization to satisfy the customer Improving each individual and groups within the organization Integrating the philosophy and practices in day to day approach to work Influencing all product, services, systems, process & technology Long term and continuous and is sensitive to the social responsibilities of the enterprise Supporting ‘ High Performance Culture through teamwork, trust & leadership IT IS NOT A program, that has a beginning & an end. It is a continuous journey.
- 3. Prelude ……To introduction to TQM Philosophy of integrating market driven focus elements for continuous improvement in all work processes of the enterprise becomes necessary due to: Customer driven market revolution Fierce global competition Unpredictable market, changing expectations & moving targets Need to develop a customer focused culture Integrate market driven culture Focus on quality, cost, productivity Customer loyalty Change Management
- 4. Focus Elements of a Market Driven Enterprise Commitment to customer satisfaction Human Resource Development Total Quality Culture Error Prevention Philosophy Total Quality Solutions Design & Product Quality Quality Services Quality of Management & Services People Development Productivity, efficiency and effectiveness Process & Technologies for continuous improvement
- 5. History… Craftsmen… Early days, generations learning, own inspector. Early 20 th Century… Unskilled repetitive, start of interchangeability. Ford Story…. Standardization, concepts for quality, Mass Mfg. Post War….. American Society for Quality 1944, Safety, Public interest ‘producer beware’ Dr. Joseph Juran & Dr. Edward Demming story Pioneering work in Total Quality, but in Japan Demming returns to US (1980-1993) Product Quality to Performance Excellence ‘ Quality of Management’ as important as ‘Management of Quality’ American Society for Quality identifies future challenges Partnering, Learning system, Adaptability and speed of change Environmental Sustainability, Knowledge Focus, Globalization Customization & Differentiation, Shifting Demographics
- 6. Journey to TQM…. TQM All Employees involved Empowerment Teamwork Quality Strategy Quality Assurance Quality Systems ISO Quality Planning Quality Policy Quality Controls Problem Solving Quality Control Quality Standards Statistical Controls Process Performance Treat Quality Problems Inspection Error Detection Rectification Unhappy Customer
- 7. Criteria Leadership Strategic Planning Customer & Market Focus Information & Analysis Human Resources Development & Planning Process Management Business Results Weightage 12% 8% 8% 8% 10% 10% 44% Award Criteria … Ref: Malcolm Baldrige
- 8. Leadership …..TQM relevance Definition Traditional Leadership for Quality … Assortment of behaviors vision, hope, stimulation, mission, transformation dreams to reality, stewardship, Integration, courage, communication, consensual, conviction, empowering, deploying, motivating, motivating and tenacity. ‘ Executive Leadership’-not the only one Changed Business Scenario & New Economy demanding Unit, Team, Project and Transformational Leadership ‘ No more the one or few men show’ Strategic Plan Integration Quality is the key element to strategic planning for ‘ Quality management’ and ‘Performance Excellence’ under the current business environment Identification of such competitive advantages that is driven by customer and market.
- 9. Leadership …..TQM relevance Effective Leadership Five Core Skills– vision, empowerment, intuition, self-understanding & value congruence Leadership Practices Customer Focus, Strategic vision, Quality value Creating sustainable leadership, environment, empowerment, innovate Setting high expectations, demonstrate substantial personal commitment and involvement, missionary zeal and constancy of purpose Integrating quality values in daily values, extensive communication Integrate public responsibility and community support in business practices TQ Leadership Contrasts….. Details Leadership & Public Responsibilities Public Health, safety & environment Compliance Corporate Citizenship, Community education, welfare, conservation Industry Obligation to Community
- 10. TQ Leadership Contrasts Traditional/Modernists Plan Projects Make plans Organize resource Preach M.B.O Push Products Lip service to quality Sell to customer Perform R&D Control People Control through systems Reward conformance punish deviation Maintain status QUO TQ Leaders Practice Envision the future Optimize the resource Participative management Produce Exemplary quality Service the customer Innovate Motivate people Development, talent & system Reward effort, skill development and empower Continuous improvement
- 11. Criteria Leadership Strategic Planning Customer & Market Focus Information & Analysis Human Resources Development & Planning Process Management Business Results Weightage 12% 8% 8% 8% 10% 10% 44% Award Criteria … Ref: Malcolm Baldrige
- 12. Understanding of Criteria Leadership Leadership System.. How the senior leaders guide the company in setting directions and in developing and sustaining an effective leadership system. Company Responsibility & Citizenship… How the company addresses the its responsibility to the public and how it practices good citizenship. Strategic Planning Strategy Development Process.. How the company sets strategic directions to better define and strengthen its competitive position and how the development process leads to action plan for deploying and aligning key plan and performance requirements. Company Strategy.. How the performance requirements and measures align with the human resource plan and how the plans project the co’s future as compared to the competitors and key benchmarks. Customer & Market Focus Customer & Market Knowledge.. How the company determines the long term requirements and preference of target and potential customers and market and anticipate needs to develop business opportunities . Customer Relationship & Satisfaction Enhancement.. How the company determines and enhances the satisfaction of customers to strengthen relationships to improve current offerings and to support customer and market related planning.
- 13. 4. Information & Analysis Selection & Use of Information & Data… How the co. selects, manages and uses the information and data needed to support key company process and improve the co’s performance. Selection & use of comparative information & data.. How the company selects, manages and uses comparative information data to improve co’s competitive position. Analysis & Review of Company’s Performance.. How the co. analyses and reviews overall performance to assess the progress relative to plans to identify key areas of improvement. 5. Human Resources Development & Management Work Systems.. What is the company’s work & job design and its compensation and recognition approaches to enable and encourage all employees to contribute effectively to achieve the co’s performance and learning objective. Employee Education Training & Development.. How the co’s training and education addresses its plan and needs including building knowledge & capabilities & contribute to improved employees’ performance and development. Employee Well-Being & Satisfaction.. How the company maintains its work environment and work climate to support the well-being, satisfaction and motivation of all its employees Understanding of Criteria
- 14. 6. Process Management Management of Product & Service Processes.. How the significantly modified and customized products and services are designed. How the product/services delivery systems are designed, implemented and improved. Management of Support Process.. How the co’s key support processes are designed, managed and continuously improved. Management of Supplier and Partnering.. How the co’s supplier and partnering processes, performance and relationships are managed and improved. 7. Business Results Customer Satisfaction Results.. How the co. performance on Customer Satisfaction Financial & Market Results…. Co’s key financial & marketplace performance Human Resource Results… Co’s Human Resource results including employee well-being, satisfaction, development and work system performance Supplier & Partner Results… Co’s supplier and partner results Company-Specific Results… How the company’s key operational performance and results significantly contribute to key company goals- customer satisfaction, operational effectiveness and financial/market place and performance. Understanding of Criteria
- 15. Strategic Planning “ The process of envisioning organization’s future and developing necessary procedures and operations to shape and achieve that future” Concept Plan that integrates an organization’s major goals Policies and actions sequences in alignment and supporting the goals Marshalling and allocating organization’s resources into an unique and viable posture Based on one’s relative strengths and competencies and anticipated changes in the environment Counter measures and actions anticipating contingent moves by intelligent opponents
- 16. Leading Practices Top management, employees & even customers actively participate in the planning process Systematic planning process for strategy development and deployment including measurement, feedback and review. Gathering and analysis of variety of data external & internal factors Alignment of short-term action plans with long term strategic objectives. Strategic Planning …Influence of TQ culture Vision Mission Guiding Principles Strategies Objectives Action Plans Environmental Scan Strategy Development
- 17. “ Converting the strategies into small doable goals and then ultimately deployed to the right teams & people in form of SMART objectives” Hoshin Kanri or Hoshin Planning Policy Deployment Management by Planning ‘ Team based deployment is most suited to TQ environment Strategic Deployment …TQ way
- 18. Strategic Planning Customer & market driven quality ‘integrated into bloodstream’ Integrated into the product, operations and service processes Operational Excellence to deliver on above Deployment Deployment to the right people with ‘smart’ objectives Organization’s ability to translate strategic objective into action plans Caliberations …What the auditor will look for Customer Driven Quality Operational Excellence TQM way to implement strategy TQ aspects include Empowerment Diffused Leadership Institutionalized Learning Innovation and Experimentation
- 19. Customer & Market Integration Customer Satisfaction Understanding Business driver Satisfaction & Loyalty Attitude & Behaviour Lifetime Value Business Possiblities New acquisition vis-à-vis retention Total Benefit Package No Longer only product or price Opportunities with what can be offered as a package
- 20. Expected Quality … of Product, Services & Delivery Actual Quality … of Execution, Information, Communication Perceived Quality… PQ= AQ – EQ Resultant Delight or Disgust Case of un-kept promise Some leading practices Define key customer groups, markets, competitors, potential customers & segment them Understand short term & long term needs & expectations, employ process for listening Build relationship with customer through commitments & promote trust & confidence, easy accessibility to people & information, effective service standards, train customer contact employees, effective follow up on all transactions Effective complaint management & resolution systems exceeding expectations Measure customer satisfaction compare with competition & use info to improve Creating a Satisfied Customer
- 21. Identification & Segmentation of Customers Juran’s Vital Few & Useful Many Concept Segmentation based on Geography, Demographic factors, Usage pattern, Volumes Expected levels of service Net Present Value Understanding Customer Needs Product Service Performance Reliability Feature Assurance Conformance Tangibles Durability Empathy Serviceability Responsiveness Aesthetics Understanding of the above under the three classes of; Dissatisfiers – Satisfiers – Exciters/ Delighters Gathering Customer Information Comment cards, Formal surveys, Focus groups, Direct Customer contact, Field Intelligence, Internet monitoring, multi-brand distribution, retail & service partners, Complaint analysis Information Analysis & Usage for Continuous Improvement Importance, Impact & performance gap analysis Identification of opportunities Decide measurements Deploy Creating a Satisfied Customer
- 22. “ Building of Customer Loyalty by developing Trust” Communication Interaction Relationships Moments of Truth Direct Contact …. Phone, letter, product & personnel Problems arising out of ‘un-kept promises’ Airlines e xamples (Scandinavian, South-West) * Opportunities during the entire process (ticketing to baggage delivery) ‘ Dignity of Customer’ Five aspects of CRM Accessibility & commitments Selecting & developing customer contact employees Relevant customer contact requirements Effective Complaint Management Strategic Partnerships and Alliances Customer Relationship Marketing Customer & Market Integration Creating a Satisfied Customer
- 23. Designing Satisfaction Surveys Determination of purpose Who is the customer Who conducts the survey Choice of survey instrument…..written, phone, recording Type of questions asked….. LIKERT scale * Analysis & usage of Feedback Performance/importance/ Impact Matrix Customer Relationship Marketing Customer & Market Integration Creating a Satisfied Customer
- 24. Module Covers Duration Project Product Processes Support Processes Service Process Supplier & Partnership Processes Managing the Change 3 Contact Classes At the end of Module TQM… Process Management
- 25. New Economy Online shopping becoming common Frequent Customer Dissatisfaction reported “ it takes more than just a web site and brand communication” Q – Was necessary attention to customer requirements and relevance to process paid? Did the product designers have all the information & data about the customer & environment? Examples Delhi Road traffic design & management (not so good?) Delhi Metro ( can we say good so far?) Demming– “Most quality problems have been due to processes and seldom have they been due to men – as normally thought” TQM… Process Management
- 26. Some leading practices: Translation of customers requirements into product & service design early enough in the process taking into account all linkages between product design requirement, conversion processes, supplier capabilities & legal and environmental considerations. Ensuring that quality is built into the product and services and use proper technologies, qualitative tools and approaches during the developmental process. Product development process manages cross functional communication, reduce time, smooth and uninterrupted introduction of product and process. Define and Document important product, delivery & support processes and manage them as an important business process Define performance requirement for suppliers, partners and relationships Control quality and operational performance, identify significant variations, analyze root- causes, apply corrections and verify results. Continuously improve process Innovate for breakthrough performance improvements through benchmarking and re-engineering. TQM… Process Management
- 27. Benchmarked Process Idea generation Preliminary Concept Development Product/Process Development Full-Scale production Market introduction Market evaluation Design Approach Considerations Performance Cost Manufacturability/ Serviceability Facility, suppliers & partners capability & preparedness Safety & environment Streamlining Design process Concurrent engineering/simultaneous engineering Reduced Cycle-time Cross Functional involvement TQM… Process Management Product Design Process CONCEPTUALIZATION CONVERSION EXECUTION
- 28. TQM…Process Management ….Support Processes Basic Understanding of significant ones; Human Resources Processes Information Technology Processes Finance & Accounts Exercise: How the above processes get influenced by TQM culture Customer Orientation Strategic Fit Cross Functional Alignment Data Analysis Measurement and Controls Continuous Improvement
- 29. Decentralization & Strategic Outsourcing Adding new dimension to the significance Competency development, Talent retention & cost of ownership Flexibility & Speed to market Supplier Involvement Product Development From Design to Delivery Service & Spare parts Bench marking on Technology, Materials, Practices & Designs Guiding Principles Realization of the strategic importance of suppliers Developing win-win relationship with suppliers Establishing trust through transparency leading to mutual benefits Exercise : On customer orientation of suppliers TQM…Process Management ….Supplier & Partnership Processes
- 30. Juran’s Trend in Supplier Relationships Element Traditional/Adversarial TQM- Teamwork Focus No. of suppliers Multiple/Many Few/Often Single Duration of suppliers Annual Contracts 3yrs. or more Quality Criteria Conformance to Total Alignment Specifications Fit for use Emphasis on Surveys Procedures, Data & Process Capability systems Quality Planning Separate Joint, Certification Pattern of Partnership Arms Length Mutual Visits Secrecy Disclosures & Transparency Mutual Supervision Mutual Assistance TQM…Process Management ….Supplier Partnerships
- 31. Service Product Design: Exercise on application of TQM requirement checks On how it can influence the Delivery Process Typical Customer requirement to be converted in product & delivery How Service Processes are ‘unique’ Measurements are not always possible Dealing with softer side of life There is no standard customer Deliver of Front-end contacts getting influenced by: Too many things which are beyond his control or influence Physical Facility Professional Judgment Personal Behaviors TQM…Process Management ….Service Processes
- 32. Cross Functionalism of TQM New culture demanding on ‘Organizational Change’ Type of Changes; Developmental Transitional Transformational Dissatisfaction with the STATUS QUO Frog Example ‘ the frog can’t realize the transition from comfort to danger’ Dissatisfaction with the NEW SITUATION Cross functional attention (apply the product development lense) Live to change in customer & market expectations Quality, cost, productivity & customer delivery focus TQM… ….Managing Change
- 33. New Model of Managing Vision communication Clear, concise & easily understandable Memorable Exciting & inspiring Challenging Excellence centered Stable but flexible Implementable & Tangible Specify Key Success Factors (KSF) Implementation Plan TQM… ….Managing Change
- 34. TEN COMMANDMENTS OF CHANGE Analyze the organization & its need for change Create a shared vision and common direction Separate from the past Create a sense of urgency Support a strong leader role Line up political sponsorship Graft an implementation plan Develop enabling structures Communicate, involve people & be honest Reinforce & institutionalize the change TQM… ….Managing Change
- 35. Alignment with the Strategy ‘ The competition can copy everything, but for the edge that your people can create. It is only them who can make 2+2 more than Four’ Satisfaction, loyalty and commitment of customer possible only through satisfied, loyal & committed employees Only Loyal employees can create Loyal customers Change of Paradigm Human Resource Management from Personnel Admin & Management From watch dog to strategic leadership through developing, coaching, training, teamwork, motivation & recognition Traditional versus Total Quality Human Resource Paradigm (table) TQM… ….Human Resource Development & Management
- 36. Traditional versus Total Quality Human Resource Paradigm (table) (PLEASE SEE THE WORD DOCUMENT ATTACHED)
- 37. How do the Leading Company’s do it; Integrate human resources plans with strategic objectives and action plans to fully address the needs and development of entire workforce Design work and jobs to promote organizational learning, innovation and flexibility for ever changing business needs. Develop effective performance management plans, compensation, reward and recognition approaches to support high performance and motivate employees. Promote cooperation and collaboration through teamwork Empower individuals and teams to make decisions that impact quality and customer satisfaction Make extensive investment in training, education and development Maintain work environment conducive to well-being & growth of all employees Monitor the extent and effectiveness of human resources practices & measure employee satisfaction as a means to continuous improvement. TQM… Human Resource Development & Management (Linking HR Plans to Business Strategy)
- 38. TQM… Human Resource Development & Management (Linking HR Plans to Business Strategy) Corporate operating principles to provide full opportunity to employees to reach their full potential by developing a high performance culture to support its vision, mission & goals Human Resource impacting Business Strategy Attract, develop, challenge & retain a diverse workforce to have skills in the organization to build business Involve & empower employees to improve processes & participation in decisions that impact business Recognize & reward performance that contribute to the business strategy and goals Continuously improve those elements of the work environment That enhance employees well-being, satisfaction and productivity Roadmap Staffing & Development Recognition & Reward Continuous Improvement Involved Employee
- 39. High Performance Work Systems … Work approaches used to systematically pursue ever-higher levels of overall organizational and human performance… Characterized By Flexibility, innovation, knowledge & skill sharing, alignment with organization directions, customer focus and rapid response to ever changing business needs and market requirements. Requires Extensive employee involvement Empowerment Training & Education Teamwork Communication Compensation & Recognition Attention to Employee well-being TQM… Human Resource Management
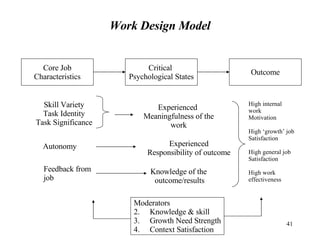
- 40. Job & Work Design Work design refer to how employee are organized in formal & informal units such as departments & teams Job design refers to responsibilities and tasks assigned to individuals … Both are vital to organizational effectiveness & employee satisfaction Need Must Be Understood (Refer Table) Critical Psychological states Core job characteristics Moderating Variables Outcomes Concept of Job Enrichment Enlargement/ Enrichment TQM… Human Resource Management
- 41. Work Design Model Critical Psychological States Outcome Core Job Characteristics Moderators Knowledge & skill Growth Need Strength Context Satisfaction Skill Variety Task Identity Task Significance Experienced Meaningfulness of the work Autonomy Feedback from job Experienced Responsibility of outcome Knowledge of the outcome/results High internal work Motivation High ‘growth’ job Satisfaction High general job Satisfaction High work effectiveness
- 42. Employee Involvement Levels of involvement (refer table) Suggestion Scheme Resistance to EI Empowerment Sincere belief and trust in people Leaders and managers relinquish some authority New responsibilities of managers Building of confidence Training & Education TQ demands heavy investment in Training & Education Generally includes quality awareness, leadership, project management, communication, teamwork, problem solving, interpretation & analysis of data, meeting customers requirements, process analysis and simplification, waste reduction, cycle time reduction, error- proofing Measure Effectiveness of Training TQM… Human Resource Management
- 43. List of Employee Involvement LEVEL ACTION PRIMARY OUTCOME Information Sharing Managers decide and inform employees Conformance Dialogue Managers get input and then decide Acceptance Special Problem Solving Managers assign one time problems to selected employees Contribution Intra Group Problem Solving Intact groups meet weekly to solve local problems Commitment Inter Group Problem Solving Cross functional teams meet to solve mutual problems Cooperation Focused Problem Solving Intact groups deepen daily involvement in a specific issue Concentration Limited Self Direction Teams at selected sites function full time with minimum supervision Accountability Total Self Direction Executives facilitates self management in an all team company Ownership
- 44. Compensation …. salary & wages Production incentive Department incentive Non-production incentive Indirect incentive Recognition & Reward Individual & team awards Involving everyone Measurable objectives- Quality, Cost, Productivity, Delivery Publicize Extensively Make it a fun TQM… Human Resource Management
- 45. Teamwork Quality circles Problem solving teams Management teams Work teams …..self managed teams Project teams Virtual teams …. ‘Boundary Less’ Success Factors Team goal clarity Improvement plan Clarity of role/definition Clarity of communication Decision procedures Clear ground rules Information access TQM… Human Resource Management
- 46. Behavioral Influence Horizontal job enlargement Vertical job enlargement/enrichment Job Rotation Contemporary Trends Job flexibility Responsibility & empowerment Training & development Teamwork Compensation Hourly rates/ daily rates/ monthly rates Piece rates- generally detrimental to quality Incentives Profit sharing Work Measurements.. Time and motion study TQM… HR Management Development …The Changing Nature with TQM
- 47. Measurements and Continuous Improvement Performance Measurement Traditionally many companies have almost entirely depended upon the financial sand operational efficiencies and productivity. Unfortunately many of these are inaccurate and lack focus on quality and hence drive wrong behaviors Balance score Card Concept “ Translates strategy into measures that uniquely communicate the version to the organization and ensure behaviors suited and aligned to desired improvement” Ø Financial Measures Shareholders returns, Profitability, revenue growth, ROI, EVA Ø Internal Measures Quality levels, Productivity, Cycle time, Costs, etc. Ø Customers perspective Service levels, Customers Satisfaction, repeat Business etc Ø Innovation & Learning Perspective Employee Sat, market innovation, intellectual Capital, skills development
- 48. Measurements & Continuous Improvement ( contd.) Two Segments of measure Leading Measures Projections of what is likely to happen and the measures driving the behaviors and improvements Lagging measures Results of what has already happened and would provide opportunities for analysis and correction Performance excellence Model Encourages grouping of performance measure into following five sets 1. Customer 2. Financial and Market 3. Human resources 4. Supplier & partnership performance 5. Organizational Effectiveness
- 49. Measurements of quality (Products & Processes) Cost of Quality model Traditional Model Conformance costs Prevention cost Appraisal Non Conformance Internal External failures Challenges Quality costs do not appear in the accounting ledger There is a considerable time delay between costs and results Accounting rules do not put quality on the credit side Numerous estimates to be made There are considerable hidden costs Behavior of cost elements during implementation of TQM
- 50. Limitations of Cost of Quality Model Does not resolve quality problem Communication of COQ does not simulate cost reduction Report does not specify action Do not capture all costs COQ is of little use for evaluating quality programme Some important costs are eliminated and not reflected Delays between cost and effect Subjected at times to judgments and estimates Tendency to be short term Concept of ‘Return to quality’ (ROQ) model Examples of training & Development Introduction of prevention for Market Returns
- 51. Measurements & Continuous Improvement Market Driven Quality Model Three Major Components Setting of Initiatives A system of quality measurement Process Reviews Target;Central objective is around defect elimination (SIX- SIGMA) Key Quality Measures in a Benchmarked Co Customer Related – Percent Shipping, Warehouse Errors, Return Cycle Time Product Quality Measures – PPM defects (internal/external), Life test results Process Quality Measures – Cycle Time, Rework at various stages, Final Yield Supplier Performance Measures – PPM defective, Purity Level, Test Results Organizational Effectiveness Measures – Cost of Conformance, Cost of non-conformance & COQ
- 53. Business Performance Measures & Indicators Business Performance Supplier & Partner Organizational Effectives Defects & errors Productivity Cycle time Regulatory & legal compliance New product introductions Community Service Safety Environment Perceived Value Overall satisfaction Complaints Gains & Losses of Customer Customer awards & satisfaction Return of equity Return of Investment Operating profit Earnings per share Market share % new product sales Absenteeism Turn over Training effectiveness Grievances Suggestion Rates Employee Satisfaction Customer Human Resource Financial & Market Financial Market Quality & Delivery Price & cost saving
- 54. Closing of Gaps … . Between final output & the expectations and needs of the customers. Addressed through either continuous improvement, breakthroughs, or a combination of both Application of the two, not only relevant to quality improvements but also to general management Concept of “ foolproofing” or POKAYOKE. Types of data Numeric or quantitative Categorical or qualitative.
- 55. TQM… Continuous Improvement ….Basic Tools Flow Charts Cause & Effect Diagrams Fish bone diagrams or Ishikawa Diagrams Numeric Data Summarization Measures of location Mean & Median Measures of Spread Standard Deviation, Variance, Range& Percentiles Graphic relationship between two variables Scatter Diagrams
- 56. 54 not available
- 57. Tabular & Graphic Summarization of data Tabular: Frequency distribution Proportions Absolute Frequencies Relative frequencies Cumulative Distributions (The above are used for both qualitative as well as quantitative)
- 58. Graphic: Qualitative Tally sheets Location plots Bar charts Paired bar charts Pie charts Pareto diagrams 2. Quantitative 1. Tally sheets 2. Histograms 3. Stem & leaf 4. Run charts
- 59. Continuous Improvement ……Basic Tools Seven Steps to Continuous Improvement (PDCA or Shewhart Cycle) Select a problem and describe it clearly Study the present system PLAN Identify the possible causes Plan and implement a solution DO Evaluate Effects CHECK Standardize the effective solution ACT Reflect on process and develop future plans.
- 60. STATISTICAL PROCESS CONTROL (SPC) Methodology Prepare - Choose the variable or attribute to be measured - Determine the basis, size and frequency of sampling - Set up the control chart 2. Data Collection 3. Determination of trial control limits 4. Analysis and Interpretation 5. use as a problem solving 6. Use the chart for process capability analysis
- 61. X – R Charts __ X = Xi -------- ; i=1 to k k __ __ __ X = Xi -------- ; i=1 to k k __ R=Range; R= Ri -------- ; i=1 to k k Normal Distribution Curve NDC with different Mean and identical NDC with identical Mean and different standard deviation standard deviation
- 62. Difference between Run- Charts and Control Charts Variable Control Charts STATE OF CONTROL OUT OF PROCESS CONTROL - Seven continuous above or below mean - Six consecutive increasing or decreasing - Two consecutive points in outer quartile UCL u LCL
- 63. CONTROL CHARTS FOR ATTRIBUTES P – Chart – Proportion defective in a sample C – Chart – Nos. defective in a sample RANGE CHART (R) __ __ LCL = D3R UCL = D4R __ R = u R/ K K= No. of samples; R = Range of Each Sample; D3 & D4 = Table Constants
- 64. MEAN CHART (X) __ __ __ __ X = x1+x2+x3 ---------------- __ __ K UCL = x + A2 R __ __ LCL = X – A2R A2 = Tabular Constant USING X bar – R CHART TOGETHER
- 65. 61 not available