Understanding Ecosystems: Structure, Components, and Functions..pptx
- 1. Ecosystem S. Nahidha Begum II. M.Sc Microbiology Sacred Heart College
- 2. What is an Ecosystem? An ecosystem is a complex network of interactions among living organisms (biotic components) and their physical environment (abiotic components). These interactions involve the flow of energy and cycling of nutrients, which help sustain the ecosystem's structure and function. The term "ecosystem" was introduced by A.G. Tansley in 1935, highlighting the interconnectedness of organisms and their surroundings.
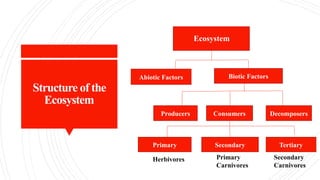
- 3. Structure of the Ecosystem Abiotic Factors Biotic Factors Producers Consumers Decomposers Primary Secondary Tertiary Ecosystem Herbivores Primary Carnivores Secondary Carnivores
- 4. Structure of the Ecosystem The structure of an ecosystem is defined by the organization and relationships of its biotic and abiotic components: Biotic Components: These are the living parts of an ecosystem, including all organisms that interact with each other and their environment. Abiotic Components: These are the non-living physical and chemical aspects of an ecosystem that affect the living organisms. Both biotic and abiotic components are interdependent, creating an open system where energy and matter flow continuously through the ecosystem.
- 5. Biotic Components Biotic components are categorized based on their roles in the ecosystem, particularly their nutritional relationships:- Producers (Autotrophs): These are organisms that can produce their own food using sunlight or chemical energy. The most common producers are green plants, which perform photosynthesis, converting sunlight into chemical energy stored in glucose. Other examples include algae and certain bacteria that can perform photosynthesis or chemosynthesis. Producers are the foundation of the food chain, providing energy for all other organisms in the ecosystem.
- 6. Biotic Components Consumers (Heterotrophs): These organisms cannot produce their own food and must rely on consuming other organisms for energy. Consumers are further classified into different levels based on their dietary habits: Primary Consumers: Herbivores that eat producers. Examples include deer, rabbits, and caterpillars. Secondary Consumers: Carnivores or omnivores that eat primary consumers. Examples include wolves, snakes, and some bird species. Tertiary Consumers: Top predators that eat secondary consumers. Examples include lions, eagles, and sharks. and phosphorus are available for plant growth.
- 7. Biotic Components Decomposers (Saprotrophs): These organisms break down dead and decaying organic matter, recycling nutrients back into the ecosystem. Decomposers include fungi, bacteria, and certain insects. They play a crucial role in nutrient cycling, ensuring that essential elements like nitrogen and phosphorus are available for plant growth.
- 8. Abiotic Components Abiotic components are the non-living elements of an ecosystem that influence the living organisms. These include:- Physical Factors: Elements like sunlight, temperature, wind, altitude, and turbidity of water.- Chemical Factors: Nutrients, minerals, pH levels, salinity, and the composition of air and water. These abiotic factors determine the types of organisms that can live in a particular environment and how they interact with each other.
- 9. Functions of Ecosystem Ecosystems perform several critical functions that are essential for maintaining life on Earth: Regulating Ecological Processes: Ecosystems control essential processes such as photosynthesis, respiration, and decomposition, which help sustain life and maintain ecological balance. Cycling of Nutrients: Ecosystems facilitate the continuous cycling of nutrients between biotic and abiotic components. For example, plants absorb nutrients from the soil, which are then transferred through the food chain and eventually returned to the soil by decomposers. Maintaining Trophic Levels: Ecosystems maintain a balance among different trophic levels (producers, consumers, and decomposers), ensuring the stability of food chains and webs.
- 10. Functions of Ecosystem Cycling of Minerals: Ecosystems cycle minerals like carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus through biogeochemical cycles. These cycles are essential for the growth and development of organisms and help regulate the Earth's climate. Energy Flow: The abiotic components, such as sunlight, are crucial for the synthesis of organic molecules through photosynthesis. The energy captured by producers flows through the ecosystem as organisms consume each other, creating a dynamic exchange of energy that supports various life forms.
- 11. Thank you