understanding-the-flag-register-a-key-component-of-processor-architecture-20240927213451OMEJ.pptx
- 1. Flag Register Understanding the Purpose and Structure of the Flag Register in a CPU ⥫
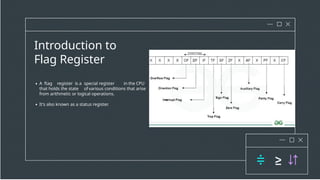
- 2. Introduction to Flag Register A ftag register is a special register in the CPU that holds the state ofvarious conditions that arise from arithmetic or logical operations. It's also known as a status register.
- 3. Structure of a Flag Register Size of the Flag Register 16-bit, or even 32-bit Typically, the flag register is 8-bit, depending on the architecture. Each bit corresponds to a specific flag. Common Flags • Zero (Z): Set if the result of an operation is zero. • Sign (S): Indicates the sign of the result (1 for negative, 0 for positive). • Carry (C): Set if an arithmetic operation results in a carry out of the most significant bit. • Overflow (O): Set if an arithmetic operation results in an overflow. • Parity (P): Set if the number of set bits in the result is even • Auxiliary Carry (AC): Used for Binary Coded Decimal (BCD) operations set if there is a carry from bit 3 to bit 4.
- 4. Types of Flags Status Flags Show the outcome of an operation. Examples: Zero (Z), Carry (C), Overflow (O). Control Flags Control the operation of the CPU. • Examples: Interrupt Flag (IF) to control interrupt handling, Direction Flag (DF) to determine the direction of string operations.
- 5. Zero Flag (Z) Purpose: Set when the result of an arithmetic or logic Operation is zero. Usage Example: • After subtracting two numbers, if the result is zero, the Zero flag is set, which might trigger a conditional jump in assembly language (e.g., JZ for "Jump if Zero").
- 6. Carry Flag (C) Purpose: Set when an arithmetic Operation results in a carry out or borrow into the most significant bit . Usage Example: Used in multi-precision arithmetic where larger numbers are split across multiple registers.
- 7. Sign Flag (S) Purpose: Set when the result of an operation is negative. Usage Example: A 1 in the sign ftag means the result is negative; a 0 meansthe result is positive.
- 8. Overflow Flag (O) Purpose: Set when the result of an operation exceeds the maximum positive number a register can hold, resulting in an overftow. Usage Example: Commonly used insigned arithmetic operations to detect when a result is too large or too small.
- 9. Practical Applications Branching: Flags are often used in branching statements (e.g., JZ, JC, JS, etc.), enabling programs to make decisions based on previous arithmetic operations. Error Detection: Flags like Overftow and Carry are used to detect errors in arithmetic calculations. Interrupts and Control: Control ftags manage the operation mode of the CPU, such as enabling or disabling interrupts.
- 10. Conclusion Summary: The Flag Register is crucial for controlling the CPU’s behavior and making decisions during program execution. Key Takeaways: Flags indicate the result of an operation. They are integral in both arithmetic and logic operations.