Unit Two - Java Architecture and OOPS
- 1. flutterjunction.co Unit 2 Java Architecture and OOPS
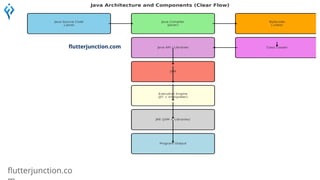
- 3. flutterjunction.co Java Architecture Java is based on the concept of Write Once, Run Anywhere (WORA). The architecture allows Java programs to run on any device that has a Java Virtual Machine (JVM). Java architecture defines how the Java platform works, from writing code to executing it. It includes: ● Java Language – The programming language you write code in. ● Java Compiler (javac) – Converts .java files into bytecode .class files. ● Java Virtual Machine (JVM) – Executes the bytecode. ● Java Runtime Environment (JRE) – Contains JVM + libraries to run Java applications. ● Java Development Kit (JDK) – Includes JRE + development tools (compiler, debugger, etc.).
- 4. flutterjunction.co ⚙️Main Components of Java Architecture a) Java Source Code (.java) ● Written by the developer. ● Contains classes, methods, and logic. a) Java Compiler (javac) ● Converts .java files into bytecode (.class files). ● Ensures code syntax is correct.
- 5. flutterjunction.co ⚙️Main Components of Java Architecture c) Bytecode ● Intermediate code. ● Platform-independent. ● Understood by the Java Virtual Machine (JVM). d) Java Virtual Machine (JVM) ● Executes the bytecode (.class files). ● Manages memory, security, garbage collection, and execution. ● JVM is Platform-Dependent but provides platform independence
- 6. flutterjunction.co ⚙️Main Components of Java Architecture e) Java Runtime Environment (JRE) ● Contains JVM + libraries. ● Required to run Java applications. ● JRE = JVM + Libraries ● Like a playground for Java programs f) Java Development Kit (JDK) ● Contains JRE + tools (e.g., compiler, debugger). ● Required to develop and run Java applications. ● JDK = JRE + Tools(compiler, debugger) ● JDK is Platform-Dependent
- 7. flutterjunction.co 📦 What Happens Internally? public class Hello { public static void main(String[] args) { Message msg = new Message(); msg.sayHello(); } } class Message { public void sayHello() { System.out.println("Hello from Java!"); } }
- 8. flutterjunction.co 📦 What Happens Internally? 1. Compilation ● javac Hello.java generates: ○ Hello.class ○ Message.class 2. Class Loading ● The Class Loader loads Hello.class into JVM memory. ● When it encounters new Message(), it loads Message.class.
- 9. flutterjunction.co 📦 What Happens Internally? 3. Linking Steps a) Verification ○ JVM checks if Message.class is valid bytecode. ○ Ensures no illegal bytecode instructions are present. b) Preparation ○ JVM allocates memory for static variables. c) Resolution ○ The call msg.sayHello() refers to Message.sayHello() method. ○ JVM resolves this symbolic reference to an actual method location in memory.
- 10. flutterjunction.co 📦 What Happens Internally? 4. Execution ● The method sayHello() is executed.
- 11. flutterjunction.co Class ● A class is a blueprint for creating objects. ● It defines the attributes (fields) and behaviors (methods). class Car { String color; void drive() { System.out.println("Driving..."); } }
- 12. flutterjunction.co Object ● An object is an instance of a class. ● It represents a real-world entity. ● Created using the new keyword. ● Can be tangible (car, animal etc) or intangible (banking system) Car myCar = new Car(); myCar.drive();
- 13. flutterjunction.co Class Methods ● Belongs to the class, not objects. ● Declared using the static keyword. ● Can be called without creating an object. ● Useful for utility functions. class MathUtils { static int square(int x) { return x * x; } } MathUtils.square(5); // 25
- 14. flutterjunction.co Instance Methods ● Belongs to an object. ● Can access instance variables and methods. ● Requires an object to call. class Person { String name; void sayHello() { System.out.println("Hello " + name); } } // Access Person As Person p = new Person(); p.name = "Alice"; p.sayHello();
- 15. flutterjunction.co Inheritance ● One class inherits properties of another. ● Promotes code reusability. ● Reduces redundancy. ● Use the extends keyword. ● Represents Java IS-A type of Relationship i.e parent child relationship class Animal { void sound() { System.out.println("Animal sound"); } } class Dog extends Animal { void bark() { System.out.println("Dog barks"); } }
- 16. flutterjunction.co Types of Inheritance 1. Single Inheritance 2. Multilevel Inheritance 3. Hierarchical Inheritance 4. Multiple Inheritance 5. Hybrid Inheritance
- 17. flutterjunction.co Single Inheritance ● One child class inherits from one parent class. ● Simplest form of inheritance. ● Promotes code reusability and clarity. ● Example: Dog inherits from Animal.
- 18. flutterjunction.co Multilevel Inheritance ● A class inherits from a child class which in turn inherits from another parent class. ● Forms a chain of inheritance. ● Animal → Mammal → Dog
- 19. flutterjunction.co Hierarchical Inheritance ● Multiple child classes inherit from a single parent class. ● Common features of the parent are shared with all child classes. ● Example: Dog, Cat, and Cow all inherit from Animal.
- 20. flutterjunction.co Multiple Inheritance ● A single class inherits from two or more parent classes. ● Can lead to ambiguity if parents have methods with the same name (handled differently in each language). ● Example: FlyingCar inherits from both Car and Aeroplane.
- 21. flutterjunction.co Hybrid Inheritance ● A combination of two or more types of inheritance. ● Can involve multiple and hierarchical inheritance together. ● Needs careful design to avoid complexity and ambiguity. ● In Java, we can achieve hybrid inheritance only through Interfaces
- 22. flutterjunction.co Polymorphism ● Ability to take many forms. ● Improves flexibility and reusability. ● Enables dynamic method binding. Types 1. Method Overloading (Compile-Time Polymorphism) 2. Method Overriding (Run-Time Polymorphism)
- 23. flutterjunction.co Method Overloading ● Same method name, different parameters. ● Resolved at compile-time. ● Java determines which method to call based on the arguments passed to it. class Calc { public void add(int a, int b) { System.out.println("Sum Int" + (a+b)); } public void add(double a, double b) { System.out.println("Sum doubles: " + (a+b)); } } public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { Calc calc = new Calc(); calc.add(5, 10); calc.add(5.5, 10.5); } }
- 24. flutterjunction.co Method Overriding ● Occurs when a subclass has a method with the same name and signature as a method in its superclass. ● Subclass can override the method to provide its own implementation. ● Method that gets called is determined at runtime based on the object that the method is called on.
- 25. flutterjunction.co Method Overriding Example class Animal { public void makeSound() { System.out.println("Animal Sound"); } } class Dog extends Animal { @Override public void makeSound() { System.out.println("Bark"); } } class Cat extends Animal { @Override public void makeSound() { System.out.println("Meow"); } }
- 26. flutterjunction.co Method Overriding Example public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { Animal animal=new Animal(); Animal animal1 = new Dog(); Animal animal2 = new Cat(); animal.makeSound(); animal1.makeSound(); animal2.makeSound(); } }
- 27. flutterjunction.co Interface ● Interface is a contract: it defines what a class must do, but not how. ● All methods are abstract by default (Java 8+ allows default/static methods). ● Supports multiple inheritance and abstraction. ● Helps in achieving loose coupling. interface Animal { void makeSound(); } class Dog implements Animal { public void makeSound() { System.out.println("Bark"); } }
- 28. flutterjunction.co Abstract Class ● A class that cannot be instantiated. ● Can contain both abstract and concrete methods. ● Used to provide common base functionality. ● Use abstract keyword. abstract class Shape { abstract void draw(); void display() { System.out.println("Shape"); } } class Circle extends Shape { void draw() { System.out.println("Drawing Circle"); } }
Editor's Notes
- #5: JVM itself is platform-dependent because each operating system requires its own version of the JVM (e.g., JVM for Windows, JVM for Linux, etc.). This means the JVM is specifically built for each platform. However, the reason Java is platform-independent is that Java source code is compiled into bytecode. This bytecode is not tied to any platform. The JVM then runs this bytecode on any platform, making Java programs work on any system, as long as the right JVM is installed.
- #6: Key Components JRE Provides JVM Runs Java bytecode by converting it to machine code Java Class Libraries (API) Pre-built classes (e.g., String, Scanner, ArrayList) used in programs Supporting Files Configuration files, error messages, and tools for execution Together, JRE provides: Memory management Allocates memory for objects, stack, heap, etc. Security features Manages permissions and secure code execution Error handling Handles runtime exceptions Multithreading support Allows concurrent execution (e.g., for games, apps) Garbage collection Frees unused memory automatically JDK The JDK is a software kit used to develop Java applications. It includes everything you need to write, compile, and run Java code. | Term | Analogy | | ---- | ----------------------------------------------------------------------- | | JVM | TV screen (shows the video) | | JRE | TV + remote + speakers (everything needed to **watch**) | | JDK | TV + remote + camera + editing tools (everything to **create + watch**) |
- #9: Valid bytecode is bytecode that follows Java's rules and structure, so it can be safely executed by the JVM. Valid bytecode | Rule | Explanation | | -------------------------------------------- | ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------- | | ✅ Follow the **Java bytecode specification** | The `.class` file must have the correct format (magic number, constant pool, etc.) | | ✅ Have correct **instructions and operands** | The code must use valid operations for the data it works on | | ✅ Not **violate access rules** | For example, it can’t access private methods of another class | | ✅ Not perform **illegal memory access** | It can’t refer to memory locations it shouldn't | | ✅ Pass **type checking** | e.g., You can't assign a string to an integer variable | | ✅ Follow **stack discipline** | Java uses a stack-based machine — the bytecode must correctly push and pop data | Why is Valid Bytecode Important? It ensures security — so no harmful or hacked code gets executed. It ensures stability — your Java program runs safely without crashing. It allows platform independence — bytecode can run the same way on all JVMs.
- #14: Use class methods for shared logic and instance methods for object-specific behavior.
- #21: Advantages of Inheritance: Code Reusability: Inheritance allows for code reuse and reduces the amount of code that needs to be written. The subclass can reuse the properties and methods of the superclass, reducing duplication of code. Abstraction: Inheritance allows for the creation of abstract classes that define a common interface for a group of related classes. This promotes abstraction and encapsulation, making the code easier to maintain and extend. Class Hierarchy: Inheritance allows for the creation of a class hierarchy, which can be used to model real-world objects and their relationships. Polymorphism: Inheritance allows for polymorphism, which is the ability of an object to take on multiple forms. Subclasses can override the methods of the superclass, which allows them to change their behavior in different ways.
- #27: A class can implement multiple interfaces. Interfaces are ideal for defining common behaviors across unrelated classes. Why Interface in Java? 1. Achieve Abstraction Interfaces help hide implementation details. Only the method signatures are declared; implementation is done in classes. 🔹 2. Support Multiple Inheritance Java does not support multiple inheritance with classes. But a class can implement multiple interfaces, allowing multiple behaviors. 🔹 3. Define a Contract An interface defines what a class must do, not how. Ensures that classes follow a certain structure. 🔹 4. Loose Coupling Code becomes more flexible and maintainable. You can change implementations without changing the interface. 🔹 5. Enable Polymorphism You can use interface types to refer to objects of any class that implements it. Helps in writing generic and scalable code.
- #28: ✅ Why Use Abstract Classes in Java? 🔹 1. Partial Abstraction Abstract classes let you define both: Abstract methods (without body) Use abstract methods when you want all subclasses to provide their own version of a specific behavior. Concrete methods (with body) Use when some methods need to be common across subclasses. 🔹 2. Code Reusability You can write common functionality in the abstract class. Subclasses can reuse or override this functionality. 🔹 3. Define a Base Class Acts as a template or blueprint for related classes. Prevents creation of generic/incomplete objects directly. 🔹 4. Controlled Inheritance Helps enforce rules through abstract methods. But also gives freedom with shared logic in concrete methods. 🔹 5. Constructor Support Unlike interfaces, abstract classes can have constructors. Useful for initializing common fields.






![flutterjunction.co
📦 What Happens Internally?
public class Hello {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Message msg = new Message();
msg.sayHello(); }
}
class Message {
public void sayHello() {
System.out.println("Hello from Java!");
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit2-javaarchitectureandoops-250515074732-74132521/85/Unit-Two-Java-Architecture-and-OOPS-7-320.jpg)















![flutterjunction.co
Method Overloading
● Same method name, different parameters.
● Resolved at compile-time.
● Java determines which method to call based on the arguments passed to it.
class Calc {
public void add(int a, int b) {
System.out.println("Sum Int" + (a+b));
}
public void add(double a, double b) {
System.out.println("Sum doubles: " + (a+b));
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Calc calc = new Calc();
calc.add(5, 10);
calc.add(5.5, 10.5);
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit2-javaarchitectureandoops-250515074732-74132521/85/Unit-Two-Java-Architecture-and-OOPS-23-320.jpg)


![flutterjunction.co
Method Overriding Example
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Animal animal=new Animal();
Animal animal1 = new Dog();
Animal animal2 = new Cat();
animal.makeSound();
animal1.makeSound();
animal2.makeSound();
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit2-javaarchitectureandoops-250515074732-74132521/85/Unit-Two-Java-Architecture-and-OOPS-26-320.jpg)


