Using a Library Database - Academic Search Complete
- 1. Academic Search Complete from EBSCO
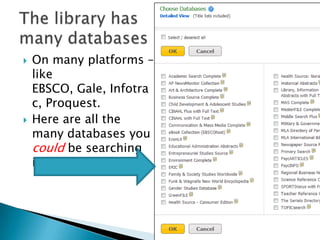
- 2. On many platforms – like EBSCO, Gale, Infotra c, Proquest. Here are all the many databases you could be searching in EBSCO
- 3. We have a few databases that are good for a multitude of topics. - we call them good multi-disciplinary databases. Today, we’re going to search one from EBSCO called Academic Search Complete:
- 4. From the Library Homepage http://library.highpoint.edu/
- 5. You should have brainstormed some keywords from the last module. Get those ready! Your search screen will look like the one below. So…what do you put in the highlighted boxes? Hint: there are many right answers and you might have to try many combinations of your keywords to get the articles you want.
- 6. In the last section you viewed, you learned about the words AND, OR, and NOT. You will use AND & OR the most. Imagine the articles you would like to find in the database. Arrange your keywords into facets of your topic. These facets are put into the database with the word AND. Think of alternatives to each of your main keywords. These synonyms are put into the database with the word OR.
- 7. In this example, I organize my keywords into a chart. This chart is attached to this module. Print it out and organize or at least think of your keywords in this format. My Sample Topic: What are the effects of cell phone use on college students? I pulled out my main keywords and put them in the top bubbles, like this. Write in the search word AND between the keywords.
- 8. Write in your alternative keywords below each main keyword. These can be exact synonyms, or they can be related words. Write the search word OR on the lines between synonyms.
- 9. Notice that I put words I wanted to keep together, like “college students” in QUOTES. This tells the database that you want to look for articles that have that exact phrase in there. Once you have your keywords organized on paper or mentally, you are ready to put these in the database!
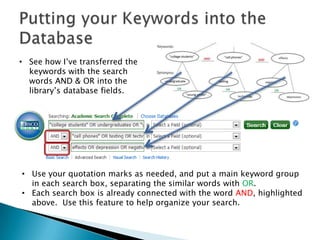
- 10. • See how I’ve transferred the keywords with the search words AND & OR into the library’s database fields. • Use your quotation marks as needed, and put a main keyword group in each search box, separating the similar words with OR. • Each search box is already connected with the word AND, highlighted above. Use this feature to help organize your search.
- 11. You won’t always need ALL of your keywords. The point of this is: ◦ You don’t know without trying different words which ones are going to work in the library databases. ◦ The “perfect” article or the ones you have in mind may not exist. This is good! You want to say something original in your papers – the articles you look for in the database should be related, but not exactly what you are trying to say.
- 12. How many search results did you get? Typically, when searching Google or related sites, you only look at the first one or two pages of results. Therefore, if you get a LOT of results, you should narrow down your search. Here are some ways to quickly do that:
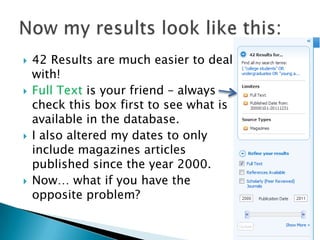
- 13. 42 Results are much easier to deal with! Full Text is your friend – always check this box first to see what is available in the database. I also altered my dates to only include magazines articles published since the year 2000. Now… what if you have the opposite problem?
- 14. If you’re getting no results or just a few, you should look at your keywords again. ◦ Remove some of your AND words. Remember: adding another facet narrows your search. ◦ Add some more OR words or synonyms. These will broaden your search. ◦ Look at any quotation marks you used in the database. Are you putting quotation marks around words that aren’t that common together? ◦ Think of some broader keywords. In my example, I included the word technology as an OR word for “cell phones.” This is a much bigger group of stuff and broadens my search considerably.
- 15. Once you have a manageable number of results, take a look at what you’ve found. Like in Google, each article has a clickable link in the title to get to more information. Clicking the top link in this screenshot will lead you to the next slide.
- 16. This article was written in Time magazine, and is short, only two pages long. Pay attention to the subject terms under the article’s information. These can help you think of additional keywords that may work better in the database than your own!
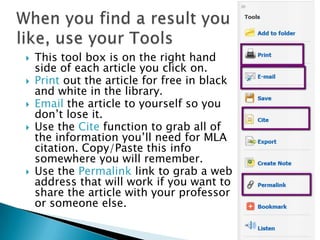
- 17. This tool box is on the right hand side of each article you click on. Print out the article for free in black and white in the library. Email the article to yourself so you don’t lose it. Use the Cite function to grab all of the information you’ll need for MLA citation. Copy/Paste this info somewhere you will remember. Use the Permalink link to grab a web address that will work if you want to share the article with your professor or someone else.
- 18. Research can be time consuming. Expect to spend time: ◦ Reading articles and finding ones that both work and those that don’t. ◦ Brainstorming alternative keywords and plugging them into the database. Try and try again. ◦ Asking for help if you get stuck. ◦ Reconsider your research question/topic. It may not be the same as when you start searching.
- 19. Organize your keywords from the last module. You may use the attached PDF or not. Find the database on the library website. Try keywords. Try other keywords. Read articles. Find one that you believe will add to your research. Print it out/Email it to yourself.