Vit D pdf
- 1. Vitamin ‘D’
- 2. Learning objectives • Introduction • Absorption/ transport and storage • Formation in body • Action/ function • Regulation • Deficiency • hypervitaminosis
- 3. • Fat soluble vit. • Resembles sterols in structure and fxn like hormoneà CHOLESTEROL. üDietary source • Ergocalciferol, aka vit D2(plant) • Cholecalciferol, aka vit D3( animal) üIn our body: • BUT, vit D is also synthesized in on exposure to sunlight à sunshine vitamin • So, NOT STRICTLY VITAMIN bcozà synthesized in the skin; against the criteria of vitamin. Introduction
- 4. üDietary sources • Fish, fish liver oils, egg yolk etc. • fortified foods (milk, butter, other dairy products etc.) üRecommended dietary allowance (RDA) ü 400 IU or 10 mg of cholecalciferol daily. BUT, ü In countries with good sunlight (like India) : 200 IU (or 5 mg of cholecalciferol) ü🌞🌝
- 5. • Dietary vit D absorbed ( bile salt)à fat soluble. • In intestinal mucosal cellà incorporated in chylomicronsà enters in circulation via lymph. • In circulationà bind with vit D binding protein ( DBP)à COMPLEX • Further, Vit D3 synthesized in skinà also binds with DBP. • Taken up by different tissueà liver & adipose tissue stores it. • > 90% is bound by DBP, < 1% IS FREE. Absorption, transport and storage
- 6. 👉 👉Formation of Vitamin D In our body 🌝🌞
- 7. 1. starts in Skin ( dermis & epidermis) • 7-Dehydrocholesterol (intermediate of cholesterol met, skin), • On exposure to UV light, à previtamin D à by breaking the bond betn 9 and 10 positionà B ring is opened. • In a period of Hours à cholecalciferol ( calciol)à by photochemical process. • Melanin competes 7-Dehydrocholesterol in absorbing UV rays ( black skin à less synthesis)
- 8. 2.Reaches to Liver üIn the liver, • cholecalciferol ( skin & food) , calciol 25-OH D3 ( calcidiol) ( ½ life 15 D) Rate is FAST üMAJOR STORAGE AND CIRCULATORY FORM OF VITAMIN D. üReleased in circulation bound with DBP Hydroxylated at 25th position By 25-hydroxylase
- 9. 3. Finally reaches to kidney üIn the kidney • Calcidiol (25-OH D) à 1-hydroxylation à to form 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D (calcitriol) by 1-⍺ hydroxylase (Slow,rate limiting.) • Biologically most active vitamin D. (1000 times more potent> calcidiol) • ½ life : 12-14 hrs. üBoth hydroxylase ( kidney & liver):for the hydroxylation process • cytochrome P450, • NADPH and • molecular oxygen.
- 10. 24, 25-hydroxy cholecalciferol üIn kidney, üAnother metabolite- 24, 25-hydroxy cholecalciferol is also formed. • when calcitriol is adequateà no more extra is requiredà a less imp compound 24,25-DHCC à by 24 hydroxylase. • The exact function of 24,25-DHCC is NOT KNOW
- 12. Functions üCalcitriol ( 1,25-DHCC) is the biologically most active. • Principal fxn is to maintain plasma calcium level. qCalcitriol acts on 3 different organs. 1. intestine 2. kidney 3. bone To Maintain plasma calcium. ( normal =9 -11 mg/dl).
- 13. • In intestine calcitriol binds with cytosolic receptor à form calcitriol receptor complex. • Complex reaches to nucleus à interacts with DNAà synthesis of calcium binding protein called calbindin. • ↑↑ calcium absorption • ↑↑ phosphate absorption 1)Action on the intestine. calbindin.
- 14. 2. Action on bone: Diverse üMobilizes bone mineral • In the osteoblast of bone à ↑↑es ca++ uptake à deposited as calcium phosphateà bone formation. üAt the same time, • Vitamin D is also believed to promote bone resorption & calcium mobilization to raise the levels of Ca and P in blood in association with PTH. • bone resorption by ↑↑ osteoclastic activity. • So, overall bone remodeling.
- 16. In one diagram: action of calcitriol.
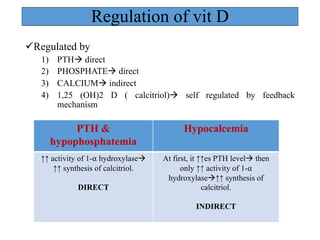
- 17. Regulation of vit D üRegulated by 1) PTHà direct 2) PHOSPHATEà direct 3) CALCIUMà indirect 4) 1,25 (OH)2 D ( calcitriol)à self regulated by feedback mechanism PTH & hypophosphatemia Hypocalcemia ↑↑ activity of 1-⍺ hydroxylaseà ↑↑ synthesis of calcitriol. DIRECT At first, it ↑↑es PTH levelà then only ↑↑ activity of 1-⍺ hydroxylaseà↑↑ synthesis of calcitriol. INDIRECT
- 18. Deficiency • Relatively less common, since can be synthesized in body. üBUT, • Insufficient exposure to sunlight+ low vit D dietà deficiency • Occurs in • Strict vegetarians • Chronic alcoholics • Liver or kidney disease • Fat malabsorption syndrome • Rickets in children • Osteomalacia in adults • Osteoporosis in old people
- 20. Hypervitaminosis D- toxicity • Among the vitamins, vit D is the most toxic in overdoses (10- 100 times RDA). üLeads to • Demineralization of bone ( resorption)+ increased calcium absorp from intestineà hypercalcemia • Prolonged hypercalcemiaà deposition in soft tissue like kidney & arteriesà calcinosis • Stones in kidney ( calculi) & rise in BP. üIn hypervitaminosis: toxicity • ↑↑ed calcitriolà↑↑es bone resorption BM stem cell à form more osteoclast cell & ↑↑ osteoclastic activity.
- 21. TASK FOR YOU….. 📝 JUSTIFY- VIT D is also hormone.