wk1.ppt
- 1. What is IS? IS – a set of interrelated components working together to collect, retrieve, process, store, and distribute information for the purpose of facilitating planning, control, coordination, analysis, and decision making in business organizations Input-process-output perspective People-organization-technology perspective
- 3. Choice Hotels Reservation System example:
- 5. Technology – the means by which data is transformed and organized for business use: Hardware Software Database Telecommunication People – the users of IS Organization -- a collection of functional units working together to achieve a common goal
- 6. Functional units of business organizations: production sales/marketing finance/accounting human resources maximize profit by producing goods and/or services
- 7. Functional Areas of Business The manufacturing and production function is responsible for producing the firm's goods and services. There are three stages of the manufacturing/ production process: inbound logistics production outbound logistics
- 8. Functional Areas of Business The sales and marketing function is responsible for finding customers for the firm's product or service and selling the firm's product or service to those customers. The sales and marketing process consists of identifying and creating markets developing markets maintaining markets
- 9. Functional Areas of Business The finance and accounting function is responsible for managing the firm's financial assets and maintaining the firm's financial records. The finance process involves managing the firm's financial assets, whereas the accounting process is involved primarily in financial record keeping.
- 10. Functional Areas of Business The human resource function is responsible for attracting and maintaining an appropriate work force for the firm. The human resources process entails attracting the work force developing the firm's work force to meet the firm's personnel needs maintaining the work force
- 11. Computer vs IS literacy
- 13. IS in Business Business functions Business processes A series of interrelated activities through which work is organized and focused to produce a product or service Business levels Strategic (long range planning) Tactical (co-ordinate & supervise) Operational (produce product & service)
- 14. The order generation and fulfillment process (Fig. 2.2)
- 16. Role of IS in Business Competitive advantage Low-cost (value chain) Market niche Product differentiation Customer loyalty Globalization People (language) Organization (culture) Technology (telecommunication)
- 17. The value chain views the firm as a series of basic activities that add value to a firm's products or services (Fig. 3-2) Primary activities •inbound logistics, •operations, •outbound logistics, •sales and marketing •service Support activities •administration and management •human resources •technology and procurement.
- 18. Quality Process simplification Benchmarking Customer focus Cycle time reduction Improve design & production Error reduction Reengineering Business processes redesign Ethical & social responsibility Information rights & privacy Intellectual property Accountability & liability Quality of life
- 19. IS Approach to Problem Solving Systems Analysis Systems Design
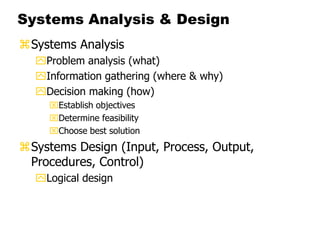
- 20. Systems Analysis & Design Systems Analysis Problem analysis (what) Information gathering (where & why) Decision making (how) Establish objectives Determine feasibility Choose best solution Systems Design (Input, Process, Output, Procedures, Control) Logical design
- 21. Systems Analysis & Design Systems Design Logical design (what will the system do?) Input: content, format, source, volume, frequency, timing Process: rule, model, formula, timing Output: content, format, organization, volume, freq., timing Storage: data, format, organization, relationship, volume Procedure: manual activities, rule, sequence, timing, location Control: security, accuracy, validity, supervision Physical design (how the system will work?) Input: keyboard, voice, scanner Process: PC, operating system, software Output: print-outs, files, audio Storage: tape, CD Procedure: batching, backup, auditing, data entry Control: batch control, password, audit logs Implementation (coding, testing, training)
- 22. Technology perspective to problem solving
- 23. Organizational perspective to problem solving