Work and simple_machines
- 2. What is work? In science, the word work has a different meaning than you may be familiar with. The scientific definition of work is: using a force to move an object a distance (when both the force and the motion of the object are in the same direction.) 2
- 3. Work or Not? According to the scientific definition, what is work and what is not? a teacher lecturing to her class a mouse pushing a piece of cheese with its nose across the floor 3
- 4. Work or Not? According to the scientific definition, what is work and what is not? a teacher lecturing to her class a mouse pushing a piece of cheese with its nose across the floor 4
- 5. 5
- 6. What’s work? A scientist delivers a speech to an audience of his peers. A body builder lifts 350 pounds above his head. A mother carries her baby from room to room. A father pushes a baby in a carriage. A woman carries a 20 kg grocery bag to her car? 6
- 7. What’s work? A scientist delivers a speech to an audience of his peers. No A body builder lifts 350 pounds above his head. Yes A mother carries her baby from room to room. No A father pushes a baby in a carriage. Yes A woman carries a 20 km grocery bag to her car? No 7
- 8. Formula for work Work = Force x Distance The unit of force is newtons The unit of distance is meters The unit of work is newton-meters One newton-meter is equal to one joule So, the unit of work is a joule 8
- 9. W=FD Work = Force x Distance Calculate: If a man pushes a concrete block 10 meters with a force of 20 N, how much work has he done? 9
- 10. W=FD Work = Force x Distance Calculate: If a man pushes a concrete block 10 meters with a force of 20 N, how much work has he done? 200 joules (W = 20N x 10m) 10
- 11. Power Power is the rate at which work is done. Power = Work*/Time (force x distance) * The unit of power is the watt. 11
- 12. Check for Understanding 1.Two physics students, Ben and Bonnie, are in the weightlifting room. Bonnie lifts the 50 kg barbell over her head (approximately .60 m) 10 times in one minute; Ben lifts the 50 kg barbell the same distance over his head 10 times in 10 seconds. Which student does the most work? Which student delivers the most power? Explain your answers. 12
- 13. Ben and Bonnie do the same amount of work; they apply the same force to lift the same barbell the same distance above their heads. Yet, Ben is the most powerful since he does the same work in less time. Power and time are inversely proportional. 13
- 14. 2. How much power will it take to move a 10 kg mass at an acceleration of 2 m/s/s a distance of 10 meters in 5 seconds? This problem requires you to use the formulas for force, work, and power all in the correct order. Force=Mass x Acceleration Work=Force x Distance Power = Work/Time 14
- 15. 2. How much power will it take to move a 10 kg mass at an acceleration of 2 m/s/s a distance of 10 meters in 5 seconds? This problem requires you to use the formulas for force, work, and power all in the correct order. Force=Mass x Acceleration Force=10 x 2 Force=20 N Work=Force x Distance Work = 20 x 10 Work = 200 Joules Power = Work/Time Power = 200/5 Power = 40 watts 15
- 16. History of Work Before engines and motors were invented, people had to do things like lifting or pushing heavy loads by hand. Using an animal could help, but what they really needed were some clever ways to either make work easier or faster. 16
- 17. Simple Machines Ancient people invented simple machines that would help them overcome resistive forces and allow them to do the desired work against those forces. 17
- 18. Simple Machines The six simple machines are: Lever Wheel and Axle Pulley Inclined Plane Wedge Screw 18
- 19. Simple Machines A machine is a device that helps make work easier to perform by accomplishing one or more of the following functions: transferring a force from one place to another, changing the direction of a force, increasing the magnitude of a force, or increasing the distance or speed of a force. 19
- 20. Mechanical Advantage It is useful to think about a machine in terms of the input force (the force you apply) and the output force (force which is applied to the task). When a machine takes a small input force and increases the magnitude of the output force, a mechanical advantage has been produced. 20
- 21. Mechanical Advantage Mechanical advantage is the ratio of output force divided by input force. If the output force is bigger than the input force, a machine has a mechanical advantage greater than one. If a machine increases an input force of 10 pounds to an output force of 100 pounds, the machine has a mechanical advantage (MA) of 10. In machines that increase distance instead of force, the MA is the ratio of the output distance and input distance. MA = output/input 21
- 22. No machine can increase both the magnitude and the distance of a force at the same time. 22
- 23. The Lever A lever is a rigid bar that rotates around a fixed point called the fulcrum. The bar may be either straight or curved. In use, a lever has both an effort (or applied) force and a load (resistant force). 23
- 24. The 3 Classes of Levers The class of a lever is determined by the location of the effort force and the load relative to the fulcrum. 24
- 25. 25
- 26. To find the MA of a lever, divide the output force by the input force, or divide the length of the resistance arm by the length of the effort arm. 26
- 27. First Class Lever In a first-class lever the fulcrum is located at some point between the effort and resistance forces. Common examples of first-class levers include crowbars, scissors, pliers, tin snips and seesaws. A first-class lever always changes the direction of force (I.e. a downward effort force on the lever results in an upward movement of the resistance force). 27
- 28. Fulcrum is between EF (effort) and RF (load) Effort moves farther than Resistance. Multiplies EF and changes its direction 28
- 29. Second Class Lever With a second-class lever, the load is located between the fulcrum and the effort force. Common examples of second-class levers include nut crackers, wheel barrows, doors, and bottle openers. A second-class lever does not change the direction of force. When the fulcrum is located closer to the load than to the effort force, an increase in force (mechanical advantage) results. 29
- 30. RF (load) is between fulcrum and EF Effort moves farther than Resistance. Multiplies EF, but does not change its direction 30
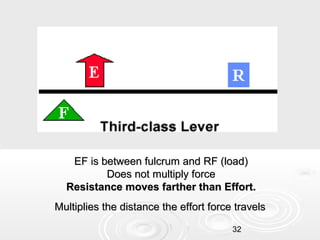
- 31. Third Class Lever With a third-class lever, the effort force is applied between the fulcrum and the resistance force. Examples of third-class levers include tweezers, hammers, and shovels. A third-class lever does not change the direction of force; third-class levers always produce a gain in speed and distance and a corresponding decrease in force. 31
- 32. EF is between fulcrum and RF (load) Does not multiply force Resistance moves farther than Effort. Multiplies the distance the effort force travels 32
- 33. Wheel and Axle The wheel and axle is a simple machine consisting of a large wheel rigidly secured to a smaller wheel or shaft, called an axle. When either the wheel or axle turns, the other part also turns. One full revolution of either part causes one full revolution of the other part. 33
- 34. Pulley A pulley consists of a grooved wheel that turns freely in a frame called a block. A pulley can be used to simply change the direction of a force or to gain a mechanical advantage, depending on how the pulley is arranged. A pulley is said to be a fixed pulley if it does not rise or fall with the load being moved. A fixed pulley changes the direction of a force; however, it does not create a mechanical advantage. A moveable pulley rises and falls with the load that is being moved. A single moveable pulley creates a mechanical advantage; however, it does not change the direction of a force. The mechanical advantage of a moveable pulley is equal to the number of ropes that support the moveable pulley. 34
- 35. Inclined Plane An inclined plane is an even sloping surface. The inclined plane makes it easier to move a weight from a lower to higher elevation. 35
- 36. Inclined Plane The mechanical advantage of an inclined plane is equal to the length of the slope divided by the height of the inclined plane. While the inclined plane produces a mechanical advantage, it does so by increasing the distance through which the force must move. 36
- 37. Although it takes less force for car A to get to the top of the ramp, all the cars do the same amount of work. A B C 37
- 38. Inclined Plane A wagon trail on a steep hill will often traverse back and forth to reduce the slope experienced by a team pulling a heavily loaded wagon. This same technique is used today in modern freeways which travel winding paths through steep mountain passes. 38
- 39. Wedge The wedge is a modification of the inclined plane. Wedges are used as either separating or holding devices. A wedge can either be composed of one or two inclined planes. A double wedge can be thought of as two inclined planes joined together with their sloping surfaces outward. 39
- 40. Screw The screw is also a modified version of the inclined plane. While this may be somewhat difficult to visualize, it may help to think of the threads of the screw as a type of circular ramp (or inclined plane). 40
- 41. MA of an screw can be calculated by dividing the number of turns per inch. 41
- 42. 42
- 43. Efficiency We said that the input force times the distance equals the output force times distance, or: Input Force x Distance = Output Force x Distance However, some output force is lost due to friction. The comparison of work input to work output is called efficiency. No machine has 100 percent efficiency due to friction. 43
- 44. Practice Questions 1. Explain who is doing more work and why: a bricklayer carrying bricks and placing them on the wall of a building being constructed, or a project supervisor observing and recording the progress of the workers from an observation booth. 2. How much work is done in pushing an object 7.0 m across a floor with a force of 50 N and then pushing it back to its original position? How much power is used if this work is done in 20 sec? 3. Using a single fixed pulley, how heavy a load could you lift? 44
- 45. Practice Questions 4. Give an example of a machine in which friction is both an advantage and a disadvantage. 5. Why is it not possible to have a machine with 100% efficiency? 6. What is effort force? What is work input? Explain the relationship between effort force, effort distance, and work input. 45
- 46. Practice Questions 1. Explain who is doing more work and why: a bricklayer carrying bricks and placing them on the wall of a building being constructed, or a project supervisor observing and recording the progress of the workers from an observation booth. Work is defined as a force applied to an object, moving that object a distance in the direction of the applied force. The bricklayer is doing more work. 2. How much work is done in pushing an object 7.0 m across a floor with a force of 50 N and then pushing it back to its original position? How much power is used if this work is done in 20 sec? Work = 7 m X 50 N X 2 = 700 N-m or J; Power = 700 N-m/20 sec = 35 W 3. Using a single fixed pulley, how heavy a load could you lift?Since a fixed lift? pulley has a mechanical advantage of one, it will only change the direction of the force applied to it. You would be able to lift a load equal to your own weight, minus the negative effects of friction. 46
- 47. Practice Questions 4. Give an example of a machine in which friction is both an advantage and a disadvantage. One answer might be the use of a car jack. Advantage of friction: It allows a car to be raised to a desired height without slipping. Disadvantage of friction: It reduces efficiency. 5. Why is it not possible to have a machine with 100% efficiency? Friction lowers the efficiency of a machine. Work output is always less than work input, so an actual machine cannot be 100% efficient. 6. What is effort force? What is work input? Explain the relationship between effort force, effort distance, and work input. The effort force is the force applied to a machine. Work input is the work done on a machine. The work input of a machine is equal to the effort force times the distance over which the effort force is exerted. 47